0% found this document useful (0 votes)
45 views4 pagesQuantum Theory and Atomic Structure
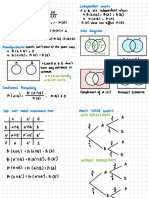
The document discusses Quantum Theory and Niel Bohr's model of atomic structure, which describes electrons orbiting the nucleus in fixed paths with quantized energy levels. It highlights the limitations of Bohr's model for atoms with more than one electron and explains the properties of electromagnetic radiation emitted during electron transitions between energy levels. Additionally, it covers the emission spectrum of hydrogen and the calculation of photon energies related to electron movements.
Uploaded by
qdwmpmv7k9Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
45 views4 pagesQuantum Theory and Atomic Structure
The document discusses Quantum Theory and Niel Bohr's model of atomic structure, which describes electrons orbiting the nucleus in fixed paths with quantized energy levels. It highlights the limitations of Bohr's model for atoms with more than one electron and explains the properties of electromagnetic radiation emitted during electron transitions between energy levels. Additionally, it covers the emission spectrum of hydrogen and the calculation of photon energies related to electron movements.
Uploaded by
qdwmpmv7k9Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd