0% found this document useful (0 votes)
412 views7 pagesFront End Wafer Processing
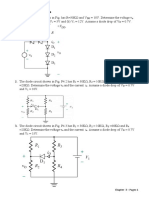
Front End Wafer Processing involves creating integrated circuits on silicon wafers through steps like photolithography, etching, and doping, while Back End Assembly and Test focuses on separating, packaging, and testing individual chips. Key processes include wafer testing, dicing, die bonding, and wire bonding to ensure functionality and reliability. The document also outlines potential interview questions and answers related to semiconductor manufacturing processes.
Uploaded by
kanmaniharitha.officialCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
412 views7 pagesFront End Wafer Processing
Front End Wafer Processing involves creating integrated circuits on silicon wafers through steps like photolithography, etching, and doping, while Back End Assembly and Test focuses on separating, packaging, and testing individual chips. Key processes include wafer testing, dicing, die bonding, and wire bonding to ensure functionality and reliability. The document also outlines potential interview questions and answers related to semiconductor manufacturing processes.
Uploaded by
kanmaniharitha.officialCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd