0% found this document useful (0 votes)
65 views18 pages4 4 Lagrange-Presentation
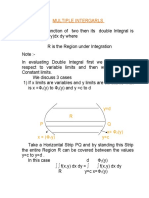
The document discusses Lagrange interpolation, a numerical method for estimating values of a polynomial based on known data points. It details the formula derivation, including the calculation of coefficients A0, A1, ..., An, and provides an example of estimating y(4) using given x and y values. The document serves as a comprehensive guide to understanding and applying Lagrange interpolation in numerical methods.
Uploaded by
anonymous0100101010Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
65 views18 pages4 4 Lagrange-Presentation
The document discusses Lagrange interpolation, a numerical method for estimating values of a polynomial based on known data points. It details the formula derivation, including the calculation of coefficients A0, A1, ..., An, and provides an example of estimating y(4) using given x and y values. The document serves as a comprehensive guide to understanding and applying Lagrange interpolation in numerical methods.
Uploaded by
anonymous0100101010Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd