0% found this document useful (0 votes)
356 views3 pagesPhy310 Exp2
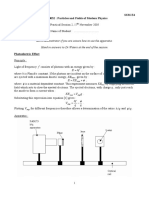
The experiment aims to determine the maximum kinetic energy of photoelectrons emitted from a photocell when light of a certain frequency is applied. It utilizes the photoelectric effect and involves measuring the current produced by photoelectrons while adjusting the stopping potential until the current reaches zero. The methodology includes setting up the apparatus, recording data, and analyzing the results to calculate the stopping potential and maximum kinetic energy.
Uploaded by
syairaa284Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
356 views3 pagesPhy310 Exp2
The experiment aims to determine the maximum kinetic energy of photoelectrons emitted from a photocell when light of a certain frequency is applied. It utilizes the photoelectric effect and involves measuring the current produced by photoelectrons while adjusting the stopping potential until the current reaches zero. The methodology includes setting up the apparatus, recording data, and analyzing the results to calculate the stopping potential and maximum kinetic energy.
Uploaded by
syairaa284Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd