0% found this document useful (0 votes)
60 views8 pagesGRASP
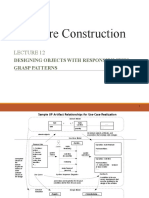
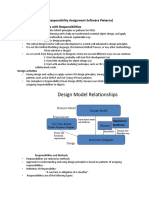
The document discusses GRASP (General Responsibility Assignment Software Patterns), which provides guidelines for assigning responsibilities in object-oriented design, including principles like Creator, Information Expert, Low Coupling, High Cohesion, and Controller. Each principle addresses specific design challenges, such as determining object creation responsibilities, delegating responsibilities based on information ownership, and maintaining low coupling and high cohesion for better maintainability and reusability. The document also includes examples and benefits associated with each principle to illustrate their application in software design.
Uploaded by
vedarajCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
60 views8 pagesGRASP
The document discusses GRASP (General Responsibility Assignment Software Patterns), which provides guidelines for assigning responsibilities in object-oriented design, including principles like Creator, Information Expert, Low Coupling, High Cohesion, and Controller. Each principle addresses specific design challenges, such as determining object creation responsibilities, delegating responsibilities based on information ownership, and maintaining low coupling and high cohesion for better maintainability and reusability. The document also includes examples and benefits associated with each principle to illustrate their application in software design.
Uploaded by
vedarajCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd