0% found this document useful (0 votes)
28 views5 pagesChapter 1 Sci X
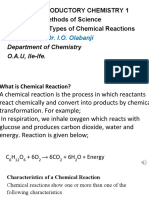
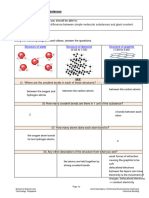
The document discusses chemical reactions, highlighting their characteristics, types, and the importance of balancing chemical equations. It covers various types of reactions including combination, decomposition, displacement, and double displacement reactions, along with concepts of oxidation and reduction. Additionally, it addresses the effects of oxidation in everyday life, such as corrosion and rancidity.
Uploaded by
amrittripathichintuCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
28 views5 pagesChapter 1 Sci X
The document discusses chemical reactions, highlighting their characteristics, types, and the importance of balancing chemical equations. It covers various types of reactions including combination, decomposition, displacement, and double displacement reactions, along with concepts of oxidation and reduction. Additionally, it addresses the effects of oxidation in everyday life, such as corrosion and rancidity.
Uploaded by
amrittripathichintuCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd