Class 11 Mathematics - Detailed Chapter-wise Formulas
1. Locus
A locus is the set of points satisfying a specific condition.
- Circle: (x - a)^2 + (y - b)^2 = r^2
- Perpendicular bisector: Points equidistant from two points.
- Parabola: y^2 = 4ax or x^2 = 4ay.
2. Transformation of Axes
- x = x'costheta - y'sintheta
- y = x'sintheta + y'costheta
- Lengths and angles are preserved in rotation.
- Origin shifted: x = x' + h, y = y' + k.
3. Pair of Straight Lines
- General form: ax^2 + 2hxy + by^2 + 2gx + 2fy + c = 0
- Condition for pair of lines: abc + 2fgh - af^2 - bg^2 - ch^2 = 0.
4. Straight Lines
- Slope-intercept: y = mx + c
- Two-point: (y - y1)/(x - x1) = (y2 - y1)/(x2 - x1)
- Intercept form: x/a + y/b = 1
- Normal form: xcosalpha + ysinalpha = p.
5. DC's and DR's
- Direction cosines: l = cosalpha, m = cosbeta, n = cosgamma
- l^2 + m^2 + n^2 = 1
- Direction ratios proportional to direction cosines.
6. 3D Geometry
- Distance between points: sqrt[(x2 - x1)^2 + (y2 - y1)^2 + (z2 - z1)^2]
- Section formula, midpoint, and centroid formulas in 3D.
7. The Plane
- General form: ax + by + cz + d = 0
- Distance from point: D = |ax0 + by0 + cz0 + d| / sqrt(a^2 + b^2 + c^2)
- Angle between two planes: costheta = (a1a2 + b1b2 + c1c2)/(|N1||N2|).
8. Differentiation
- Power Rule: d/dx(x^n) = nx^{n-1}
- Chain Rule: d/dx[f(g(x))] = f'(g(x)) * g'(x)
- Derivatives of sin, cos, tan, etc.
9. Tangents and Normals
- Tangent slope: dy/dx at x = a
- Tangent equation: y - y1 = m(x - x1)
- Normal: slope = -1/m
10. Limits
- lim(x->a) (f(x)) = L
- lim(x->0) sinx/x = 1
- lim(x->0) (1 - cosx)/x^2 = 1/2
- Algebra of limits.
11. Continuity
- f is continuous at x=a if: lim x->a- f(x) = lim x->a+ f(x) = f(a)
- Polynomial functions are continuous everywhere.
12. Errors and Approximations
- Absolute Error = |Measured - Actual|
- Relative Error = Absolute / Actual
- Percentage Error = (Relative Error * 100)%
13. Rate Measure
- dy/dx represents the rate of change of y with respect to x
- Related rates: Use chain rule.
�14. Rolle’s and Lagrange’s Theorems
- Rolle's: f(a) = f(b), f is continuous and differentiable => exists c in (a,b) s.t. f'(c) = 0
- Lagrange's: f'(c) = [f(b) - f(a)] / (b - a)
15. Maxima and Minima
- If f'(x) = 0 and f''(x) < 0 -> maxima
- If f''(x) > 0 -> minima
- First and second derivative tests.
16. Functions
- f(x) is a rule assigning unique output to each input
- Domain, codomain, and range
- f(g(x)) is composition.
17. Mathematical Induction
- Base step: prove true for n = 1
- Inductive step: assume true for n = k, prove for k + 1
=> statement is true for all n.
18. Matrices
- Matrix addition: A + B = [a■■ + b■■]
- Multiplication: AB = [Σ a■■ * b■■]
- Identity, transpose, inverse.
19. Addition of Vectors
- If A = a1i + a2j, B = b1i + b2j, then A + B = (a1 + b1)i + (a2 + b2)j
- Parallelogram law.
20. Multiplication of Vectors
- Dot product: A*B = |A||B|costheta
- Cross product: A*B = |A||B|sintheta * n■
- Scalar and vector products.
21. Trigonometric Ratios
- sin^2x + cos^2x = 1
- 1 + tan^2x = sec^2x
- cot^2x + 1 = csc^2x
22. Transformations
- sin(A ± B) = sinA cosB ± cosA sinB
- cos(A ± B) = cosA cosB ■ sinA sinB
- 2sinAcosB = sin(A + B) + sin(A - B)
23. Trigonometric Equations
- sinx = a => x = npi + (-1)^n sin-¹a
- cosx = a => x = 2npi ± cos-¹a
24. Inverse Trigonometric Functions
- sin-¹x + cos-¹x = pi/2
- tan-¹x + cot-¹x = pi/2
- Domains and principal values are important.
25. Hyperbolic Functions
- sinhx = (e^x - e^-x)/2
- coshx = (e^x + e^-x)/2
- cosh^2x - sinh^2x = 1
26. Properties of Triangles
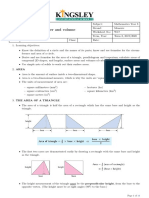
- Area = (1/2)ab sinC
- Law of sines: a/sinA = b/sinB = c/sinC = 2R
- a^2 = b^2 + c^2 - 2bc cosA