Professional Documents
Culture Documents
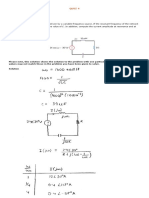
Answers of Tutorial 1-Ch1
Answers of Tutorial 1-Ch1
Uploaded by
Maryam YousfOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Answers of Tutorial 1-Ch1
Answers of Tutorial 1-Ch1
Uploaded by
Maryam YousfCopyright:
Available Formats
MECH2118 Manufacturing processes
Answers for: Tutorial 1 (Lecture 1) Compiled by Dr Ghassan Al-Kindi Typical Answers to the questions
1.1 Answer. A primary industry is one that cultivates and exploits natural resources, such as agriculture or mining. A secondary industry takes the outputs of primary industries and converts them to consumer and capital goods. Examples of secondary industries are textiles and electronics. A tertiary industry is in the service sector of the economy. Examples of tertiary industries are banking and education. 1.2 Answer. Capital goods are those purchased by other companies to produce goods or supply services. Examples of capital goods are aircraft and construction equipment. 1.3 Answer. Generally production quantity is inversely related to product variety. A factory that produces a large variety of products will produce a smaller quantity of each. A company that produces a single product will produce a large quantity. 1.4 Answer. Manufacturing capability refers to the technical and physical limitations of a manufacturing firm and each of its plants. Three categories of capability include technological processing capability, physical size and weight, and production capacity. 1.5 Answer. The three basic categories of engineering materials are (1) metals, (2) ceramics, and (3) polymers. A fourth category, composites, is a non-homogeneous mixture of the other types and therefore is not a basic category. 1.6 Answer. A shaping process changes the geometry of the work material (machining or forging). A surface processing operation does not alter the geometry, but instead alters the properties and/or appearance of the surface of the work (painting or plating) 1.7 Answer. The two subclasses of assembly processes are (1) permanent joining and (2) mechanical fastening. Examples of permanent joining include welding or adhesive bonding. Examples of mechanical fastening include threaded fasteners, such as nuts and bolts, and rivets. 1.8 Answer. Batch production is where groups, lots, or batches are processed together through the manufacturing operations. All units in the batch are processed at a given station before the group proceeds to the next station. In a medium or low quantity production situation, the same machines are used to produce many types of products. Whenever a machine switches from one product to another, a changeover occurs. The changeover requires the machine setup to be torn down and set up for the new product. Batch production allows the changeover time to be distributed across a larger number of parts and hence reduce the average operation time per part. 1.9 Answer. A process layout is one where the machinery in a plant is arranged based on the type of process it performs. To produce a product it must visit the departments in the order of the operations that must be performed. This often includes large travel distances within the
plant. A process layout is often used when the product variety is large the operation sequences of products are dissimilar. A product layout is one where the machinery is arranged based on the general flow of the products that will be produced. Travel distance is reduced because products will generally flow to the next machine in the sequence. A product layout works well when all products tend to follow the same sequence of production. 1.10 Answer. A common approach for organizational structures includes the following three manufacturing support departments: (1) manufacturing engineering, (2) production planning and control, and (3) quality control.
Multiple Choice Quiz answers
1.1 Answer. (a), (e), and (f). 1.2 Answer. (c). 1.3 Answer. (d). 1.4 Answer. (c) and (e). 1.5 Answer. (a). 1.6 Answer. (a) and (d). 1.7 Answer. (f) and (g). 1.8 Answer. (c) and (d). 1.9 Answer. (d). 1.10 Answer. (d). 1.11 Answer. (c) and (e).
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (844)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5810)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- People of The Philippines vs. Hon Judge Perfecto A.S. Laguio, Jr.Document24 pagesPeople of The Philippines vs. Hon Judge Perfecto A.S. Laguio, Jr.Vlad LipsamNo ratings yet
- Auditing Theory CabreraDocument23 pagesAuditing Theory CabreraGem Alcos Nicdao100% (2)
- Content Knowledge and Its Application Within and Across Curriculum AreasDocument3 pagesContent Knowledge and Its Application Within and Across Curriculum AreasMeg BeltranNo ratings yet
- Nosotros NoDocument2 pagesNosotros NoAlcindorLeadonNo ratings yet
- Sportster 1800Document111 pagesSportster 1800Tatiana SemenutinaNo ratings yet
- Crude Oil ProcessingDocument26 pagesCrude Oil ProcessingMohamed GhareebNo ratings yet
- Digitalcre8or Award Syllabus and Assessment Criteria: Unit A. Understand, Capture and Manipulate Digital Audio - DetailDocument33 pagesDigitalcre8or Award Syllabus and Assessment Criteria: Unit A. Understand, Capture and Manipulate Digital Audio - DetailjohnvandongenNo ratings yet
- Lower Limbs PracticalDocument45 pagesLower Limbs PracticalOleashedNo ratings yet
- 7 Ijaebm Vol No 2 Issue No 1 Fast Food Outlets Consumer Expectations and Perception From Kelantan Malaysia 073 076Document4 pages7 Ijaebm Vol No 2 Issue No 1 Fast Food Outlets Consumer Expectations and Perception From Kelantan Malaysia 073 076api-3785704320% (1)
- NOTES For NEUROIMAGING (Brain and Skull Anatomy) 1Document3 pagesNOTES For NEUROIMAGING (Brain and Skull Anatomy) 1Hanako Sasaki AranillaNo ratings yet
- Product InformationDocument938 pagesProduct InformationkevalNo ratings yet
- 4024 w15 QP 22 MergedDocument20 pages4024 w15 QP 22 MergedSheikh Mohammad ForhadNo ratings yet
- FANVIL I21tDocument2 pagesFANVIL I21tossidiazNo ratings yet
- Bahasa InggerisDocument16 pagesBahasa InggerisSiti Rahmah100% (1)
- Expression of Offering Help: Dinda Lana Estetika 2201417023Document8 pagesExpression of Offering Help: Dinda Lana Estetika 2201417023Dinda LanaNo ratings yet
- Manual Resident Evil Revelations 2 PS3Document16 pagesManual Resident Evil Revelations 2 PS3BRUNO SANTOSNo ratings yet
- Paste Deposition Modeling (PDM)Document3 pagesPaste Deposition Modeling (PDM)Eleisa SilvaNo ratings yet
- 2 Homework Set No. 2: Problem 1Document3 pages2 Homework Set No. 2: Problem 1kelbmutsNo ratings yet
- Todd Jackson by Amy GadeDocument4 pagesTodd Jackson by Amy Gadeapi-300163172No ratings yet
- The Comparative Effect of Goat's Manure and UreaDocument19 pagesThe Comparative Effect of Goat's Manure and UreaKayecel Marie Denzon GumapacNo ratings yet
- The Modernist Moment at The University of LeedsDocument26 pagesThe Modernist Moment at The University of LeedstobyNo ratings yet
- EE103 - Compiled Quizes PDFDocument25 pagesEE103 - Compiled Quizes PDFJacob PopcornsNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Continuum Mechanics, Second Edition: More InformationDocument27 pagesAn Introduction To Continuum Mechanics, Second Edition: More InformationHariharanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Socialization - FE 401Document25 pagesChapter 4 Socialization - FE 401UN SophaktraNo ratings yet
- Diversey in IndiaDocument4 pagesDiversey in IndiaahbninNo ratings yet
- ARIS Client Installation GuideDocument23 pagesARIS Client Installation GuideSubscriber SNo ratings yet
- Python Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) : TutorialDocument11 pagesPython Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) : TutorialPavankumar KaredlaNo ratings yet
- Abhignya - Vineland Social Maturity ScaleDocument7 pagesAbhignya - Vineland Social Maturity Scaleabhignya kothaNo ratings yet
- Developing Personal Responsibility and Leadership Traits in All Your Employees: Part 1 Shaping and Harmonizing The High-Performance DriversDocument11 pagesDeveloping Personal Responsibility and Leadership Traits in All Your Employees: Part 1 Shaping and Harmonizing The High-Performance DriversStackwell IndiaNo ratings yet
- Coursebook - Petroleum Geology of The Middle EastDocument8 pagesCoursebook - Petroleum Geology of The Middle EastSalman AhmadNo ratings yet