0% found this document useful (0 votes)
79 views11 pagesTest Case Rule 1
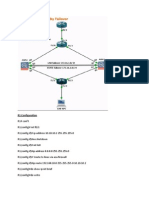
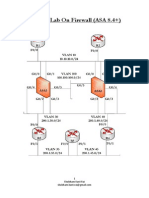
The document outlines findings from a firewall failover scenario, detailing event IDs 103005 and 104003 related to primary and secondary firewall failures. It explains the theoretical concepts of Cisco ASA, its active/passive failover configuration, and the hardware/software requirements for failover setups. Additionally, it discusses syslog messages, correlation rule creation for monitoring failover events, and recommendations for further actions in case of incidents.
Uploaded by
Abhi 077Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
79 views11 pagesTest Case Rule 1
The document outlines findings from a firewall failover scenario, detailing event IDs 103005 and 104003 related to primary and secondary firewall failures. It explains the theoretical concepts of Cisco ASA, its active/passive failover configuration, and the hardware/software requirements for failover setups. Additionally, it discusses syslog messages, correlation rule creation for monitoring failover events, and recommendations for further actions in case of incidents.
Uploaded by
Abhi 077Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd