0% found this document useful (0 votes)
30 views5 pagesDigestive Glands
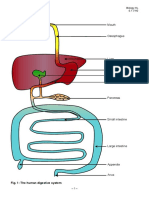
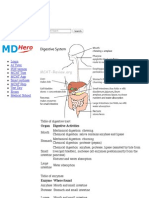
The document provides a detailed explanation of digestive glands, including their locations, secretions, substrates, and end products of digestion. It covers major glands such as salivary glands, gastric glands, liver, pancreas, and intestinal glands, outlining their specific roles in breaking down food. The final absorbable nutrients are also summarized, indicating how carbohydrates, proteins, and fats are processed for absorption.
Uploaded by
mohammedismail202012Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
30 views5 pagesDigestive Glands
The document provides a detailed explanation of digestive glands, including their locations, secretions, substrates, and end products of digestion. It covers major glands such as salivary glands, gastric glands, liver, pancreas, and intestinal glands, outlining their specific roles in breaking down food. The final absorbable nutrients are also summarized, indicating how carbohydrates, proteins, and fats are processed for absorption.
Uploaded by
mohammedismail202012Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd