LAB 07 Newton Raphson & Secant Method
Lab Report 07
Objective:
Solving Newton Raphson Method & Secant Method in coding form using MATLAB.
Theory:
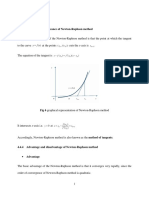
In numerical analysis, Newton's method, also known as the Newton–Raphson method,
named after Isaac Newton and Joseph Raphson, is a root-finding algorithm which
produces successively better approximations to the roots (or zeroes) of a real-valued
function.
Newton Raphson Method:
The Newton-Raphson method (also known as Newton's method) is a way to quickly
find a good approximation for the root of a real-valued function f(x)=0f(x) = 0f(x)=0.
It uses the idea that a continuous and differentiable function can be approximated by a
straight line tangent to it.The most basic version starts with a single-variable function
f defined for a real variable x, the function's derivative f ′, and an initial guess x0 for a
root of f. If the function satisfies sufficient assumptions and the initial guess is close,
then
is a better approximation of the root than x0. Geometrically, (x1, 0) is the intersection
of the x-axis and the tangent of the graph of f at (x0, f (x0)): that is, the improved guess
is the unique root of the linear approximation at the initial point. The process is
repeated as
until a sufficiently precise value is reached. This algorithm is first in the class of
Householder's methods, succeeded by Halley's method. The method can also be
extended to complex functions and to systems of equations.
1
�LAB 07 Newton Raphson & Secant Method
MATLAB Code:
>>clc
>>close all
>>clear all
>>n=input('Enter the number of iteration:')
>>for i=0:1:n
>> if i==0
>>syms('x')
>>y=exp(-x(i+1))-x(i+1)
>>k=diff(y(i+1))
>>x(1)=0;
>>d=vpa(subs(k,x(i+1)));
>>fv=subs(y(i+1),x(i+1));
>>x(i+2)=x(i+1)-(fv/d)
>>else
>>d=vpa(subs(k,x(:,i+1)));
>>fv=subs(y,x(:,i+1));
>>x(i+2)=x(:,i+1)-(fv/d)
>>end
>> if i>0
>> e(i)=(x(:,i+1)-x(:,i))/x(:,i+1)*100
>> if norm(e(:,1))<.01
>> break
>>end
>>end
>>end
2
�LAB 07 Newton Raphson & Secant Method
MATLAB Work:
Input:
Output:
3
�LAB 07 Newton Raphson & Secant Method
4
�LAB 07 Newton Raphson & Secant Method
5
�LAB 07 Newton Raphson & Secant Method
Secant Method
Theory:
Secant method is an iterative tool of mathematics and numerical methods to find the
approximate root of polynomial equations. During the course of iteration, this method
assumes the function to be approximately linear in the region of interest. Although
secant method was developed independently, it is often considered to be a finite
difference approximation of Newton’s method. But, being free from derivative, it is
generally used as an alternative to the latter method.Newton’s method was based on
using the line tangent to the curve of y = f (x), with the point of tangency (x0, f (x0)).
When x0 ≈ r, the graph of the tangent line is approximately the same as the
graph of y = f (x) around x = r. We then used the root of the tangent line to
approximate r.
The Secant Method:
There are some steps which are involved in secant method.
1. Initialization:
Two initial guesses x0 and x1 of r are chosen.
2. Iteration:
For n = 1; 2; 3; · · ·,
until certain stopping criterion is satisfied (required solution accuracy or maximal
number of iterations is reached).
Advantages of secant method:
1. It converges at faster than a linear rate, so that it is more rapidly convergent than
the bisection method.
2. It does not require use of the derivative of the function, something that is not
available in a number of applications.
3. It requires only one function evaluation per iteration, as compared with Newton’s
method which requires two.
Disadvantages of secant method:
6
�LAB 07 Newton Raphson & Secant Method
1. It may not converge.
2. There is no guaranteed error bound for the computed iterates.
3. It is likely to have difficulty if f ’(r) = 0. This means the x-axis is tangent to the
graph of y= f (x) at x = r.
4. Newton’s method generalizes more easily to new methods for solving simultaneous
systems of nonlinear equations.
Input:
Output: