0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views2 pages1.4G Networks
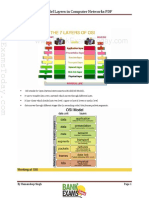
4G networks, launched in 2012, utilize an all-IP architecture based on LTE standards, significantly enhancing radio and core network functionality. Key components include the Evolved NodeB for radio access management and various functional nodes like the MME and PGW for session management and data routing. While 4G supports high-speed applications and IoT, it falls short for ultra-low latency needs, prompting the evolution towards 5G technology.
Uploaded by
herevicky19Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views2 pages1.4G Networks
4G networks, launched in 2012, utilize an all-IP architecture based on LTE standards, significantly enhancing radio and core network functionality. Key components include the Evolved NodeB for radio access management and various functional nodes like the MME and PGW for session management and data routing. While 4G supports high-speed applications and IoT, it falls short for ultra-low latency needs, prompting the evolution towards 5G technology.
Uploaded by
herevicky19Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd