0% found this document useful (0 votes)
292 views2 pagesPump Up Test Method
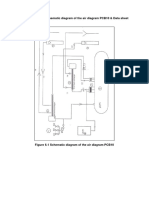
The document outlines the procedure for conducting a pump up test to determine the compressor capacity in a compressed air system using the receiver filling method. It includes steps for preparing the air receiver, measuring pressures, and calculating capacity using specific formulas. The document also provides examples of calculations for isothermal and actual compression scenarios.
Uploaded by
elgiashish15Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as XLSX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
292 views2 pagesPump Up Test Method
The document outlines the procedure for conducting a pump up test to determine the compressor capacity in a compressed air system using the receiver filling method. It includes steps for preparing the air receiver, measuring pressures, and calculating capacity using specific formulas. The document also provides examples of calculations for isothermal and actual compression scenarios.
Uploaded by
elgiashish15Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as XLSX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd