0% found this document useful (0 votes)
37 views18 pagesLab Component 1
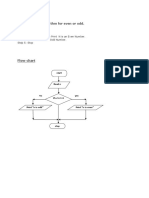
The document outlines various algorithms, flowcharts, and pseudo codes for solving common programming problems, including finding the roots of quadratic equations, summing numbers, reversing strings, checking for palindromes, determining leap years, swapping numbers, counting vowels, finding anagrams, converting decimal to binary, and implementing bubble sort. Each problem is presented with a clear algorithmic approach and corresponding pseudo code. This serves as a comprehensive guide for basic algorithm implementation in programming.
Uploaded by
dalaldhruv725Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
37 views18 pagesLab Component 1
The document outlines various algorithms, flowcharts, and pseudo codes for solving common programming problems, including finding the roots of quadratic equations, summing numbers, reversing strings, checking for palindromes, determining leap years, swapping numbers, counting vowels, finding anagrams, converting decimal to binary, and implementing bubble sort. Each problem is presented with a clear algorithmic approach and corresponding pseudo code. This serves as a comprehensive guide for basic algorithm implementation in programming.
Uploaded by
dalaldhruv725Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd