SQL Complete Cheat Sheet for Analytics Interviews
1. Basic SQL
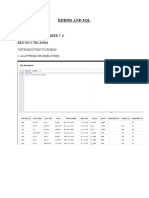
SELECT name, salary FROM employees WHERE department = 'HR';
SELECT DISTINCT department FROM employees;
SELECT name, salary FROM employees ORDER BY salary DESC LIMIT 5;
2. Aggregate Functions
SELECT COUNT(*) AS total, AVG(salary) AS avg_salary FROM employees;
SELECT department, AVG(salary) FROM employees GROUP BY department;
SELECT department, COUNT(*) FROM employees GROUP BY department HAVING COUNT(*) > 5;
3. Joins
SELECT [Link], [Link] FROM employees e INNER JOIN orders o ON [Link]=o.customer_id;
SELECT [Link], [Link] FROM customers c LEFT JOIN orders o ON c.customer_id=o.customer_id;
4. Subqueries
SELECT name FROM employees WHERE salary > (SELECT AVG(salary) FROM employees);
SELECT MAX(salary) FROM employees WHERE salary < (SELECT MAX(salary) FROM employees);
5. Set Operations
SELECT name FROM employees UNION SELECT name FROM customers;
SELECT name FROM employees INTERSECT SELECT name FROM customers;
6. Window Functions
SELECT name, ROW_NUMBER() OVER(ORDER BY salary DESC) AS rn FROM employees;
SELECT name, RANK() OVER(ORDER BY salary DESC) AS rnk FROM employees;
7. CASE
SELECT name, CASE WHEN salary>100000 THEN 'High' ELSE 'Low' END AS band FROM employees;
8. String Functions
SELECT CONCAT(first_name, ' ', last_name), LENGTH(name) FROM employees;
9. Date & Time
SELECT CURRENT_DATE, NOW();
SELECT * FROM orders WHERE order_date >= CURRENT_DATE - INTERVAL 7 DAY;
10. Constraints
�CREATE TABLE emp(id INT PRIMARY KEY, name VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL);
11. Indexes
CREATE INDEX idx_salary ON employees(salary);
12. Normalization
1NF: No repeating groups, 2NF: Remove partial dependency, 3NF: Remove transitive dependency
13. Transactions
BEGIN; UPDATE employees SET salary=salary*1.1 WHERE dept='HR'; COMMIT;
14. Views
CREATE VIEW high_salary AS SELECT name FROM employees WHERE salary>100000;
15. Stored Procedures
CREATE PROCEDURE getHighSal() BEGIN SELECT name FROM employees WHERE salary>100000;
END;
16. CTE
WITH dept_avg AS (SELECT department, AVG(salary) avg_sal FROM employees GROUP BY department)
SELECT * FROM dept_avg;
17. NULL Handling
SELECT COALESCE(commission,0) FROM employees;
18. Data Analysis
DAU: SELECT COUNT(DISTINCT user_id) FROM user_activity WHERE activity_date=CURRENT_DATE;
GMV: SELECT SUM(amount) FROM orders WHERE order_date=CURRENT_DATE;
19. Advanced Queries
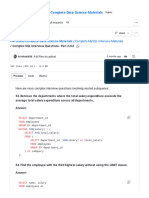
SELECT name, department, salary FROM (SELECT name, department, salary, RANK() OVER(PARTITION
BY department ORDER BY salary DESC) rnk FROM employees) t WHERE rnk<=3;
20. Business Questions
A/B Testing: SELECT group_name, AVG(conversion) FROM ab_test GROUP BY group_name;
Churn: SELECT user_id FROM users WHERE last_login < CURRENT_DATE - INTERVAL 30 DAY;
Meesho-Specific Analytics
GMV: SELECT SUM(amount) FROM orders WHERE order_date BETWEEN '2025-07-01' AND '2025-07-31';
�Retention: SELECT cohort, COUNT(DISTINCT user_id) FROM user_activity GROUP BY cohort;
Funnel: SELECT step, COUNT(DISTINCT user_id) FROM funnel_events GROUP BY step ORDER BY step;