0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views8 pagesQuestionnaire
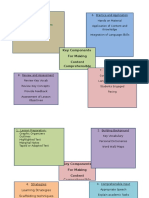
The document outlines detailed lesson plans for Functional English, Reading Comprehension, Grammar, and Writing, each with specific learning goals, instructional techniques, and assessment methods. It emphasizes the importance of engaging students through practical activities, positive classroom environments, and tailored materials to enhance language skills. Each lesson plan includes strategies for questioning, feedback, and skill development to ensure effective learning outcomes.
Uploaded by
OMAR BELAZRICopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views8 pagesQuestionnaire
The document outlines detailed lesson plans for Functional English, Reading Comprehension, Grammar, and Writing, each with specific learning goals, instructional techniques, and assessment methods. It emphasizes the importance of engaging students through practical activities, positive classroom environments, and tailored materials to enhance language skills. Each lesson plan includes strategies for questioning, feedback, and skill development to ensure effective learning outcomes.
Uploaded by
OMAR BELAZRICopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd