0% found this document useful (0 votes)
47 views23 pagesForming and Shaping Processes 1
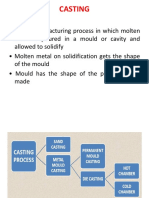
The document discusses forming and shaping processes in manufacturing technology, focusing on methods like forging, rolling, extrusion, drawing, and sheet metal forming, which alter raw materials, primarily metals, through plastic deformation. It details various techniques, including hot and cold forging, direct and indirect extrusion, and different drawing and sheet metal forming processes, highlighting their applications and products. Additionally, it covers primary shaping processes such as casting, powder metallurgy, and molding.
Uploaded by
lacentjayCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
47 views23 pagesForming and Shaping Processes 1
The document discusses forming and shaping processes in manufacturing technology, focusing on methods like forging, rolling, extrusion, drawing, and sheet metal forming, which alter raw materials, primarily metals, through plastic deformation. It details various techniques, including hot and cold forging, direct and indirect extrusion, and different drawing and sheet metal forming processes, highlighting their applications and products. Additionally, it covers primary shaping processes such as casting, powder metallurgy, and molding.
Uploaded by
lacentjayCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd