0% found this document useful (0 votes)
69 views3 pagesA Solar Ray Tracker
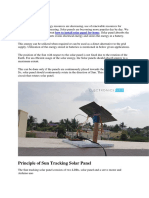
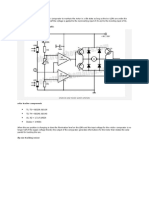
The document outlines the materials and steps needed to build a solar ray tracker that optimizes solar panel positioning for maximum sunlight exposure. It describes how two Light Dependent Resistors (LDRs) detect light direction to control motors that adjust the panel's orientation. The tracker aims to increase solar panel efficiency and energy generation by keeping the panel facing the sun.
Uploaded by
kwattegamaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
69 views3 pagesA Solar Ray Tracker
The document outlines the materials and steps needed to build a solar ray tracker that optimizes solar panel positioning for maximum sunlight exposure. It describes how two Light Dependent Resistors (LDRs) detect light direction to control motors that adjust the panel's orientation. The tracker aims to increase solar panel efficiency and energy generation by keeping the panel facing the sun.
Uploaded by
kwattegamaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd