0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views5 pagesWorksheet Sletv Moodle
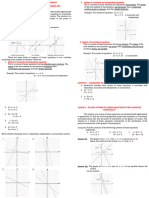
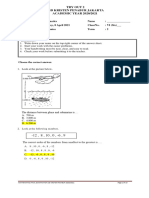
This document is a worksheet for Grade 8 students at SMPK PENABUR Gading Serpong, focusing on systems of linear equations with two variables. It explains the definition of linear equations, various methods for solving them (substitution, elimination, mix method, and graph method), and includes examples and word problems. Additionally, it touches on non-linear equations and provides enrichment exercises involving linear equations with three variables.
Uploaded by
catherinenstsCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views5 pagesWorksheet Sletv Moodle
This document is a worksheet for Grade 8 students at SMPK PENABUR Gading Serpong, focusing on systems of linear equations with two variables. It explains the definition of linear equations, various methods for solving them (substitution, elimination, mix method, and graph method), and includes examples and word problems. Additionally, it touches on non-linear equations and provides enrichment exercises involving linear equations with three variables.
Uploaded by
catherinenstsCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd