0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesSAT Geometry Trig Formula Sheet
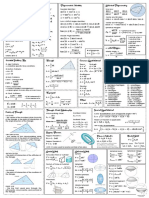
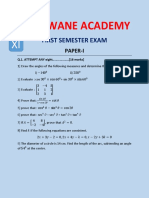
This document is a comprehensive formula sheet for SAT Math, focusing on Geometry and Trigonometry. It includes essential rules and formulas for angles, triangles, quadrilaterals, circles, coordinate geometry, 3D geometry, and trigonometric functions. Additionally, it provides tips for common mistakes and a bonus section with common trigonometric values.
Uploaded by
Tim ChanCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesSAT Geometry Trig Formula Sheet
This document is a comprehensive formula sheet for SAT Math, focusing on Geometry and Trigonometry. It includes essential rules and formulas for angles, triangles, quadrilaterals, circles, coordinate geometry, 3D geometry, and trigonometric functions. Additionally, it provides tips for common mistakes and a bonus section with common trigonometric values.
Uploaded by
Tim ChanCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd