0% found this document useful (0 votes)
60 views3 pagesHW 3
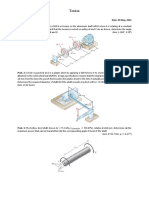
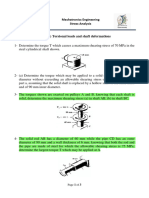
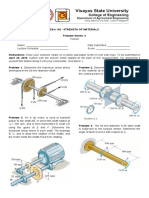
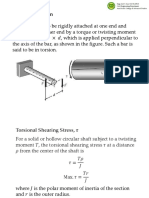
This document outlines Homework #3 for the Solid Mechanics course (ENGR-UH 2211) due on February 10, 2026. It includes a series of problems focusing on calculating maximum shearing stress, required diameters for shafts, angle of twist, and torque limits for various materials and configurations. The problems reference specific chapters from the Beer et al. textbook, emphasizing practical applications of solid mechanics principles.
Uploaded by
hi2151Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
60 views3 pagesHW 3
This document outlines Homework #3 for the Solid Mechanics course (ENGR-UH 2211) due on February 10, 2026. It includes a series of problems focusing on calculating maximum shearing stress, required diameters for shafts, angle of twist, and torque limits for various materials and configurations. The problems reference specific chapters from the Beer et al. textbook, emphasizing practical applications of solid mechanics principles.
Uploaded by
hi2151Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd