Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tungsten
Uploaded by
ahmedCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Tungsten
Uploaded by
ahmedCopyright:
Available Formats
Tungsten
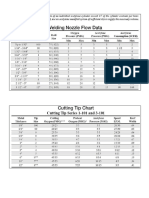
Selecting the correct tungsten electrode is important to getting high-quality welds and making your
welding easier. Some important factors to be considered in making the right choice are type of
power source (Inverter or transformer), material to be welded (steel, aluminum, or stainless steel),
and the thickness of the material.
Pure Tungsten (TP) - Green Tip
Readily forms a ball on the end, and generally used with transformer-based power sources for AC
welding of aluminum.
2% Thoriated Tungsten (TT2) - Red Tip
The most common tungsten currently being used, generally utilized for DC welding of steel and
stainless steel and offers good overall performance. A drawback is that this tungsten has a low level
radiation hazard.
2% Ceriated Tungsten (TC2) - Grey Tip
An excellent substitute for 2% Thoriated tungsten if you are using a transformer-based power
source for DC welding. Popular for thinner materials because it requires less amperage to start.
Offers a stable arc and can be used for both AC and DC welding with inverter power sources.
1 ½% Lanthanated Tungsten (TL15) - Gold Tip
Also a great substitute for 2% Thoriated tungsten. Offers good arc starting characteristics and
longer life than 2% Thoriated. It can be used for both AC and DC welding with both inverter and
transformer power sources.
2% Lanthanated Tungsten (TL2) - Blue Tip
The most commonly used, non-radioactive tungsten and also a great substitute for 2% Thoriated
tungsten. It offers some of the best arc starting characteristics and longer life than 2% Thoriated, a
good tungsten for pulsing or welding that requires frequent re-ignitions with a short weld cycle.
Can be used for both AC and DC welding with both inverter and transformer power sources.
You might also like
- Assignment No. 4 BlankDocument15 pagesAssignment No. 4 BlankahmedNo ratings yet
- Grade Structure Revamping TemplateDocument1 pageGrade Structure Revamping TemplateahmedNo ratings yet
- Fuel TrimsDocument6 pagesFuel TrimsahmedNo ratings yet
- 5S PrincipleDocument53 pages5S PrincipleAmir M. VillasNo ratings yet
- YIC Materials Testing Lab Equipment and ExperimentsDocument2 pagesYIC Materials Testing Lab Equipment and ExperimentsahmedNo ratings yet
- Illness Caused by Welding Fume and GasesDocument2 pagesIllness Caused by Welding Fume and GasesahmedNo ratings yet
- Department OF Mechanical Engineering Technology: Heat Engines LaboratoryDocument2 pagesDepartment OF Mechanical Engineering Technology: Heat Engines LaboratoryahmedNo ratings yet
- Sectional ViewDocument2 pagesSectional ViewahmedNo ratings yet
- Science Answer KeyDocument1 pageScience Answer KeyahmedNo ratings yet
- Abdullah - Book Appointment With Consulate General of Pakistan, Jeddah PDFDocument1 pageAbdullah - Book Appointment With Consulate General of Pakistan, Jeddah PDFahmedNo ratings yet
- Measuring Metal Strength (Tensile & Impact Strength)Document5 pagesMeasuring Metal Strength (Tensile & Impact Strength)ahmedNo ratings yet
- 6 Mistakes That Can Lead To Cracked WeldsDocument4 pages6 Mistakes That Can Lead To Cracked WeldsahmedNo ratings yet
- Drill Bit Size ChartDocument22 pagesDrill Bit Size ChartahmedNo ratings yet
- 7 Ways You Are Violating Welding Procedures and Don't Know ItDocument2 pages7 Ways You Are Violating Welding Procedures and Don't Know ItahmedNo ratings yet
- Plasma 2Document13 pagesPlasma 2ahmedNo ratings yet
- Btus, CFMS, and Gges DemystifiedDocument2 pagesBtus, CFMS, and Gges DemystifiedahmedNo ratings yet
- Tip Data For OFWDocument1 pageTip Data For OFWahmedNo ratings yet
- Deposition Rates For Stick ElectrodesDocument3 pagesDeposition Rates For Stick ElectrodesahmedNo ratings yet
- PlasmaDocument8 pagesPlasmaahmedNo ratings yet
- PlasmaDocument7 pagesPlasmaahmedNo ratings yet
- Why Is "Cold Cutting" Superior To Plasma Cutting?Document9 pagesWhy Is "Cold Cutting" Superior To Plasma Cutting?ahmedNo ratings yet
- Plasma 2Document14 pagesPlasma 2ahmedNo ratings yet
- CGA Selection Chart for Pure & Mixed Industrial GasesDocument1 pageCGA Selection Chart for Pure & Mixed Industrial GasesSadot GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Grinding Wheel SpecificationsDocument2 pagesGrinding Wheel SpecificationsahmedNo ratings yet
- ASGEpg187 PDFDocument3 pagesASGEpg187 PDFbkprodhNo ratings yet
- Help Welding Calculation - WeldingDocument14 pagesHelp Welding Calculation - Weldingahmed100% (1)
- Method of Calculating The Cooling Rate in HAZ During WeldingDocument6 pagesMethod of Calculating The Cooling Rate in HAZ During WeldingahmedNo ratings yet
- To Be Free From Oil and Dirt ADAPTOR, CGA-022 To 1/4 NPT GDG PSMDocument1 pageTo Be Free From Oil and Dirt ADAPTOR, CGA-022 To 1/4 NPT GDG PSMahmedNo ratings yet
- UNCUNF Threads - SizeDocument1 pageUNCUNF Threads - SizeahmedNo ratings yet
- A Complete Guide To Pipe SizesDocument25 pagesA Complete Guide To Pipe SizesahmedNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Aluminum Extrusions in Solar Power ApplicationsDocument4 pagesAluminum Extrusions in Solar Power ApplicationsСтанислав ПодольскийNo ratings yet
- Nissan Skyline R34 Workshop Manual EnglishDocument401 pagesNissan Skyline R34 Workshop Manual Englishrecklessone0% (2)
- Green ConcreteDocument22 pagesGreen ConcreteQseem Khan100% (1)
- PC400 400LC-8R PDFDocument8 pagesPC400 400LC-8R PDFAsmar FixNo ratings yet
- Section 8 - Synchronism-Check Protection (25) : SEL-751A Feeder Protection Relay - APP 751ADocument19 pagesSection 8 - Synchronism-Check Protection (25) : SEL-751A Feeder Protection Relay - APP 751ABouazzaNo ratings yet
- Fermentor TypesDocument33 pagesFermentor TypesFahad MukhtarNo ratings yet
- Pneumatic Maneuvering SystemDocument65 pagesPneumatic Maneuvering Systemminhankyaw100% (3)
- Response of Water Resources Systems To Climate ChangeDocument355 pagesResponse of Water Resources Systems To Climate ChangePat Prodanovic100% (5)
- ADV P Application Information Fuse DescriptionsDocument1 pageADV P Application Information Fuse DescriptionsdipenkhandhediyaNo ratings yet
- Solar Water HeaterDocument27 pagesSolar Water HeaterSantosh ThapaNo ratings yet
- Electronics MCQsDocument17 pagesElectronics MCQslovelyosmile253No ratings yet
- LPG Parts Diagram BreakdownDocument43 pagesLPG Parts Diagram BreakdownناصرقوجيلNo ratings yet
- Kinetics: Effects of Concentration & Temperature on Reaction RatesDocument4 pagesKinetics: Effects of Concentration & Temperature on Reaction Ratescrybaby0% (1)
- Anomaly Events GuideDocument33 pagesAnomaly Events GuideRichard LittlesNo ratings yet
- Unit 4: Fault Analysis EssentialsDocument9 pagesUnit 4: Fault Analysis EssentialsBALAKRISHNAN100% (2)
- Encore 22 lb. Capacity Front Load DryerDocument2 pagesEncore 22 lb. Capacity Front Load Dryermairimsp2003No ratings yet
- EBARA Company ProfileDocument11 pagesEBARA Company ProfileMohamed IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Guide energy efficiency best practicesDocument8 pagesGuide energy efficiency best practicesshiyakNo ratings yet
- Lessons Learned-Nuclear Gauge002Document66 pagesLessons Learned-Nuclear Gauge002Michael Murillo BaraquioNo ratings yet
- HYpact Compact HybridDocument24 pagesHYpact Compact HybridMateo Alvez100% (1)
- SKF TIH 030M - 230V SpecificationDocument3 pagesSKF TIH 030M - 230V SpecificationÇAĞATAY ÇALIŞKANNo ratings yet
- Vibration Isolation Selection GuideDocument5 pagesVibration Isolation Selection GuidearifzakirNo ratings yet
- Type FL Low Profile NTC Temperature Sensor: AmphenolDocument3 pagesType FL Low Profile NTC Temperature Sensor: Amphenolmauricio alfonsoNo ratings yet
- Elec Engg Exit Exam 2018 (Part 9)Document10 pagesElec Engg Exit Exam 2018 (Part 9)Master JaguarNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines DC Motor NewDocument27 pagesElectrical Machines DC Motor NewPranav MahadikNo ratings yet
- EPL 0006898 ArticleDocument28 pagesEPL 0006898 ArticleGuillermo IdarragaNo ratings yet
- 21st Refinery Technology Meet - The CompendiumDocument474 pages21st Refinery Technology Meet - The CompendiumAnurag Ingle100% (5)
- Airframe Fuel SystemDocument30 pagesAirframe Fuel SystemLuis GarciaNo ratings yet
- Residential Cooling Load CalculationDocument24 pagesResidential Cooling Load CalculationAngeloTomalonNo ratings yet
- Documents - MX - Absorption Exercises Treybal PDFDocument6 pagesDocuments - MX - Absorption Exercises Treybal PDFJvson Vens Sance100% (1)