Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Free Trade Areas: Year 13
Uploaded by
api-110990005Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Free Trade Areas: Year 13
Uploaded by
api-110990005Copyright:
Available Formats
Free Trade Areas
Year 13
Imports & Exports
An import is the UK purchase of a good or service made overseas. An export is the sale of a UK-made good or service overseas. A nation trades because it lacks the raw materials, climate, specialist labour, capital or technology needed to manufacture a particular good. Trade allows a greater variety of goods and services.
Government can help businesses
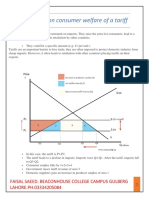
Tariffs Tariffs (import duties) are surcharges on the price of imports. raises the price of the import; reduces the demand for imports; encourages demand for home-produced substitutes; raises revenue for the government. Quotas Quotas restrict the actual quantity of an import allowed into a country. Note that a quota: raises the price of imports; reduces the volume of imports; encourages demand for domestically made substitutes.
The European Union (EU)
The EU has a common market, but most believe its now a single market:
free movement of capital and labour within member countries; (No Tariffs, Quotas). free trade between member countries; common tariffs against non-members; standardised trade and customs procedures, e.g. metric measurements; 12 of the 25 EU member states are part of the single currency - the euro, which was introduced in these countries in January 2002. The UK has elected to stay outside the euro.
What is a Common Market?
These are groups of countries have completely free trade internally and a single unified trade policy covering all member countries trade with the rest of the world. But besides free movement of goods and services, there is also free movement of people and capital. The E.U is a common market
What is a Free Trade Area?
These are groups of countries that trade completely freely with each other, no trade barriers, but each country retains own independent trade policies in relation to the rest of the world. E.g. NAFTA North American Free Trade Area Canada; USA; Mexico
Winners of Free Trade
Consumers due to increased competition:
Increased competition for suppliers Greater pressure on businesses to keep their costs and prices down Increased competition can lead to a dilution of monopoly power which reduces the potential for exploiting consumers This leads to the elimination of less efficient smaller rivals and raise standards of living around the world
Winners of Free Trade
Businesses due to:
Increased imports or exports If become efficient Increased economies of scale Increased efficiency of production and reduce costs May be able to use up surplus raw materials Comparative Advantage
Losers of Free Trade
Government possibly? They are keen to protect jobs in their own country, by using barriers to restrict international competition. Infant Industries Less efficient businesses/suppliers
You might also like
- What Is International TradeDocument6 pagesWhat Is International Tradejem dela cruzNo ratings yet
- Features of Free Trade: Free Trade Is A Policy by Which A Government Does Not Discriminate Against Imports or InterfereDocument6 pagesFeatures of Free Trade: Free Trade Is A Policy by Which A Government Does Not Discriminate Against Imports or Interfereatul_rockstarNo ratings yet
- Business Theme 4Document7 pagesBusiness Theme 4CNo ratings yet
- Definition: Free Trade Is A Largely Theoretical Policy Under Which Governments Impose Absolutely No Tariffs, Taxes, or DutiesDocument25 pagesDefinition: Free Trade Is A Largely Theoretical Policy Under Which Governments Impose Absolutely No Tariffs, Taxes, or DutiesLê Đặng Minh ThảoNo ratings yet
- Chap 8,9Document17 pagesChap 8,9Trâm PhạmNo ratings yet
- Internationl TradeDocument12 pagesInternationl TradeIneshkaNo ratings yet
- 1 PageDocument2 pages1 Pagevaidyajayesh006No ratings yet
- Macroeconomics AssignmentDocument13 pagesMacroeconomics AssignmentAlly SallimNo ratings yet
- The Political Economy of International Trade: By: Ms. Adina Malik (ALK)Document23 pagesThe Political Economy of International Trade: By: Ms. Adina Malik (ALK)Mr. HaroonNo ratings yet
- Least Restrictive and Loosest Form of Economic Integration Among CountriesDocument4 pagesLeast Restrictive and Loosest Form of Economic Integration Among CountriesAnti CovidNo ratings yet
- Barriers To International TradebaDocument6 pagesBarriers To International TradebafhinojosacNo ratings yet
- Regional Integrations IBMDocument64 pagesRegional Integrations IBMdileepsuNo ratings yet
- F) Principles of Absolute and Comparative AdvantageDocument3 pagesF) Principles of Absolute and Comparative AdvantageSameera ShahzadNo ratings yet
- Trading BlocDocument5 pagesTrading BlocMehak joshiNo ratings yet
- Free Trade and Fair TradeDocument5 pagesFree Trade and Fair Tradekanishka singhNo ratings yet
- Photo (HỌC KỸ) CÂU HỎI RA THIDocument19 pagesPhoto (HỌC KỸ) CÂU HỎI RA THIvuvtp21No ratings yet
- Chap 2,5Document16 pagesChap 2,5Trâm PhạmNo ratings yet
- International EconomicsDocument33 pagesInternational EconomicsCher DorinaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Introduction of International TradeDocument22 pagesChapter 1 - Introduction of International TradeAisyah AnuarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Introduction of International TradeDocument22 pagesChapter 1 - Introduction of International TradeAisyah AnuarNo ratings yet
- Team 3 ProjectDocument14 pagesTeam 3 ProjectGabriela LorenaNo ratings yet
- Tariff and Non TariffDocument18 pagesTariff and Non TariffAjaykumar ChilukuriNo ratings yet
- Global Q2Document7 pagesGlobal Q2seahbryantyNo ratings yet
- Tariff and Non-Tariff BarriersDocument41 pagesTariff and Non-Tariff Barriersjagdish91100% (1)
- Barriers To International TradeDocument3 pagesBarriers To International TradeKanika KapoorNo ratings yet
- E A L B S: NIT Nternational UsinessDocument42 pagesE A L B S: NIT Nternational UsinessArnieNo ratings yet
- RW Free Trade and Trade PolicyDocument13 pagesRW Free Trade and Trade PolicyG JustNo ratings yet
- Regional Economic Groups No TaskDocument2 pagesRegional Economic Groups No Taskapi-529669983No ratings yet
- International Trade BarriersDocument19 pagesInternational Trade BarriersYanix SeraficoNo ratings yet
- The Economic Costs of Tariffs & The Economics of ProtectionismDocument24 pagesThe Economic Costs of Tariffs & The Economics of ProtectionismBalkan CharyyevNo ratings yet
- TradeDocument4 pagesTradeYan Myo ZawNo ratings yet
- 27 - International TradeDocument5 pages27 - International Tradehoangduylong.iccNo ratings yet
- Free Trade Policy: Free Trade Occurs When There Are No Artificial Barriers Put in Place by Governments To RestrictDocument3 pagesFree Trade Policy: Free Trade Occurs When There Are No Artificial Barriers Put in Place by Governments To Restrictpaban2009No ratings yet
- Final On Economic IntDocument10 pagesFinal On Economic IntVandanaNo ratings yet
- What Are Tariffs and Non TariffsDocument4 pagesWhat Are Tariffs and Non TariffsRonalie SustuedoNo ratings yet
- IB Political Economy FINALDocument31 pagesIB Political Economy FINALUmme A. TasnimNo ratings yet
- 5.2 AFM Investment Appraisal International 231223Document13 pages5.2 AFM Investment Appraisal International 231223Kushagra BhandariNo ratings yet
- Submitted By: Zain Saleem Roll No.: F18BA138 Section: Afternoon A' Subject: Macro Economics Submitted To: Sir LatifDocument5 pagesSubmitted By: Zain Saleem Roll No.: F18BA138 Section: Afternoon A' Subject: Macro Economics Submitted To: Sir LatifZain SaleemNo ratings yet
- Political EcoDocument4 pagesPolitical Ecoenamulbari56No ratings yet
- The Effect On Consumer Welfare of A TariffDocument7 pagesThe Effect On Consumer Welfare of A TariffAmna KashifNo ratings yet
- International Trade and Agreement Summary Reviewer Chapter 1 To 3Document4 pagesInternational Trade and Agreement Summary Reviewer Chapter 1 To 3Ralph AbutinNo ratings yet
- Ch18 GlobaleconomyDocument47 pagesCh18 GlobaleconomyAlbertoNo ratings yet
- Trade Barriers, Dumping Anti DumpingDocument30 pagesTrade Barriers, Dumping Anti Dumpingqwertyuiop_6421100% (3)
- Internatiuonal Business Unit 2Document17 pagesInternatiuonal Business Unit 2Janardhan VNo ratings yet
- What Is Meant by Protectionism?: Chapter Three: Protectionism and Free TradeDocument4 pagesWhat Is Meant by Protectionism?: Chapter Three: Protectionism and Free TradeBenazir HitoishiNo ratings yet
- 2nd ReadingDocument4 pages2nd ReadingRena MabinseNo ratings yet
- European Union Mercosur: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument3 pagesEuropean Union Mercosur: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaTricia DazaNo ratings yet
- The Political Economy of Trade PolicyDocument23 pagesThe Political Economy of Trade PolicyNeha SargamNo ratings yet
- Definitions:: Local, National, and International BusinessesDocument4 pagesDefinitions:: Local, National, and International BusinessesLanaNo ratings yet
- Interntionl Businessunit 3Document6 pagesInterntionl Businessunit 3Tharun VelammalNo ratings yet
- Economics NotesDocument27 pagesEconomics Notes570 BAF Drashti ShahNo ratings yet
- Marketing Notes 5-International Marketing HandoutDocument10 pagesMarketing Notes 5-International Marketing HandoutInformation should be FREENo ratings yet
- MIdterms Reviewer in IBTDocument15 pagesMIdterms Reviewer in IBTkara mNo ratings yet
- TariffDocument5 pagesTariffIrina MiQuiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 25 Business in The International CommunityDocument4 pagesChapter 25 Business in The International CommunityVincent ChurchillNo ratings yet
- A Level Economics ProtectionismDocument8 pagesA Level Economics Protectionismchinsw1996No ratings yet
- Ôn tập kinh tế quốc tế cuối kỳ 6Document36 pagesÔn tập kinh tế quốc tế cuối kỳ 6thuyntp22No ratings yet
- International Business: Strategy, Management, and The New RealitiesDocument25 pagesInternational Business: Strategy, Management, and The New Realitiesmobeenscribd1No ratings yet
- The Political Economy of International TradeDocument26 pagesThe Political Economy of International Tradesonia_hun885443No ratings yet
- Imports & Exports: Year 13Document12 pagesImports & Exports: Year 13api-110990005No ratings yet
- Revision For G041: Mrs N ChahalDocument3 pagesRevision For G041: Mrs N Chahalapi-110990005No ratings yet
- GCE Economics & Business Year 13 Unit 4bDocument2 pagesGCE Economics & Business Year 13 Unit 4bapi-110990005No ratings yet
- Efficiency Production & Operations: Production Efficiency: ProductivityDocument1 pageEfficiency Production & Operations: Production Efficiency: Productivityapi-110990005No ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument1 pageIntroductionapi-110990005No ratings yet
- Check List For B (Iii) : Skills Shown Throughout Documents Achieved Page Number To Show EvidenceDocument1 pageCheck List For B (Iii) : Skills Shown Throughout Documents Achieved Page Number To Show Evidenceapi-110990005No ratings yet
- Spreadsheet TaskDocument2 pagesSpreadsheet Taskapi-110990005No ratings yet
- As Ict Unit 1 - ChecklistDocument1 pageAs Ict Unit 1 - Checklistapi-110990005No ratings yet
- Economies of ScaleDocument11 pagesEconomies of Scaleapi-110990005No ratings yet
- Transmission of PII ProcedureDocument2 pagesTransmission of PII ProcedureBayNo ratings yet
- Henry Dunant 2016 ProsecutionDocument36 pagesHenry Dunant 2016 Prosecutionkarti_am100% (13)
- I Fought For My Life-1Document2 pagesI Fought For My Life-1Akarsh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Important Procedure Regarding The Name PDFDocument12 pagesImportant Procedure Regarding The Name PDFTravis Morgan81% (16)
- Wicksell and Pareto: Their Relationship in The Theory of Public FinanceDocument28 pagesWicksell and Pareto: Their Relationship in The Theory of Public FinanceOyuna Bat-OchirNo ratings yet
- Did RA 9285 Repeal or Amend Our System of Barangay Justice?Document6 pagesDid RA 9285 Repeal or Amend Our System of Barangay Justice?deuce scriNo ratings yet
- Feminism - Where We Stand - Belle HooksDocument2 pagesFeminism - Where We Stand - Belle HooksAsja FejzicNo ratings yet
- Contact List TE 34Document2 pagesContact List TE 34Keanu JeeNo ratings yet
- Renewal Form Reqm8vihluguDocument1 pageRenewal Form Reqm8vihluguMelojane AciertoNo ratings yet
- ComRep Comm Brgy Affairs (B) 2021-11-15 CamaliganDocument4 pagesComRep Comm Brgy Affairs (B) 2021-11-15 Camaliganfinance2018 approNo ratings yet
- Flashcards - Health, Human Rights and Intervention - Edexcel Geography A-LevelDocument41 pagesFlashcards - Health, Human Rights and Intervention - Edexcel Geography A-LevelSashiNo ratings yet
- Bibliography Sexual Health Issues WTDDocument4 pagesBibliography Sexual Health Issues WTDndoybbx65No ratings yet
- Study Guide - SocHum PDFDocument23 pagesStudy Guide - SocHum PDFrbsmun9469No ratings yet
- Hatta 1958Document12 pagesHatta 1958Madelief WhiteNo ratings yet
- Stphen Krashen WebinarDocument2 pagesStphen Krashen WebinarMuttaqina ImamaNo ratings yet
- 11-04-2022 Stoneman, T. 18 Responsive DocumentsDocument2,154 pages11-04-2022 Stoneman, T. 18 Responsive DocumentsTyler WatkinsNo ratings yet
- Pol - Science - CH 2 The End of Bipolarity Part 3 - Class XIIDocument11 pagesPol - Science - CH 2 The End of Bipolarity Part 3 - Class XIISnehaNo ratings yet
- Satyagraha-An Idea Shaping IndiaDocument11 pagesSatyagraha-An Idea Shaping IndiaLpranathi SekkharNo ratings yet
- Bahrain: AMB Country Risk ReportDocument4 pagesBahrain: AMB Country Risk ReportaakashblueNo ratings yet
- Barangay Data Capture Form Monitoring of Incidence On Violence Against Children (Vac) During The Covid-19 PandemicDocument1 pageBarangay Data Capture Form Monitoring of Incidence On Violence Against Children (Vac) During The Covid-19 PandemicChristopher Gatdula100% (2)
- GR No. 125469Document5 pagesGR No. 125469Karen Gina DupraNo ratings yet
- Newsletter - SEE Forum On Climate Change AdaptationDocument9 pagesNewsletter - SEE Forum On Climate Change AdaptationlibertteNo ratings yet
- Ofw - Ap10Document6 pagesOfw - Ap10Maria Rebecca CorazonNo ratings yet
- Republic, Lost: How Money Corrupts Congress - and A Plan To Stop ItDocument6 pagesRepublic, Lost: How Money Corrupts Congress - and A Plan To Stop Itwamu885No ratings yet
- Seerah of Prophet Muhammad 97 - Maria The Copt & Death of Ibrahim - Dr. Yasir Qadhi - 19th Nov 2014Document7 pagesSeerah of Prophet Muhammad 97 - Maria The Copt & Death of Ibrahim - Dr. Yasir Qadhi - 19th Nov 2014Yasir Qadhi's Complete Seerah SeriesNo ratings yet
- Remman Enterprises v. PRB-Yap, K. C2020Document2 pagesRemman Enterprises v. PRB-Yap, K. C2020Krystoffer Yap100% (5)
- SinaloaDocument1 pageSinaloaLaísa SalanderNo ratings yet
- Consti CasesDocument5 pagesConsti CasesVIA ROMINA SOFIA VILLA VELASCONo ratings yet
- Lok Adalat - A Critical AppraisalDocument5 pagesLok Adalat - A Critical Appraisalaiswaryapavi_4893981No ratings yet
- Landscape Irrigation Systems CommissioningDocument1 pageLandscape Irrigation Systems CommissioningHumaid ShaikhNo ratings yet