Stocks
return = capital gain/loss + dividends
Price Earnings ratio
Book value Ratio
Earnings per share
2
FUTURES
3
SOYBEAN
4
WTI
S
T
K
+
- LONG Asset
S
T
K
+
-
SHORT Asset
S
T
Strike
+
- LONG CALL
S
T
Strike
+
-
SHORT CALL
S
T
Strike
+
-
LONG PUT
S
T
Strike
+
-
SHORT PUT
SPOT MARKET = CASH DERIVATIVES MARKET
S
T
K
+
-
LONG ASSET
S
T
Strike
+
-
LONG PUT
S
T
K
+
-
PROTECTED LONG
S
T
K
+
-
SHORT Asset
S
T
Strike
+
-
LONG CALL
S
T
K
+
-
PROTECTED SHORT
Risk
Return
5%
10%
15%
25%
20%
0,70% 0,80% 0,60% 0,90% 1,00%
nat
sg
ubs
lcl
jpm
dex
ca
bnp
bar
agf
axa
Investors are rational
5%
10%
15%
25%
20%
0,70% 0,80% 0,60% 0,90% 1,00%
nat
sg
ubs
lcl
jpm
dex
ca
bnp
bar
agf
axa
Risk
Return
Investors are rational
Expected return of a stock
= =
s
s s i
r r p r E * ) (
Return
+6% +14% -2%
25%
50%
Probability
Stock A
+6% +15% -3%
30%
40%
Return
Probability
Stock B
E(rA) = (-2%x25%)+(6%x50%)+(14%x25%)= 6%
E(rB) = (-3%x30%)+(6%x40%)+(15%x30%)= 6%
Expected return of a stock
To determine the probability p:
- Estimate based on various hypothesis
- Estimate based on historical performance
The RISK is determined by its variance and standard deviation
= =
s
s s i
r r p r E * ) (
2
i i
o o =
2 2
*) ( ] [
i
s
s s i
r r p r Var o = =
Expected return of a portfolio
=
=
n
j
j j p
r p r E
1
) (
q is the proportion of the stock in the portfolio, r is the return
| |
2 2 1 1
. . ] [ r q r q Var r Var
p
+ =
The risk of the portfolio depends on the degree of correlation
between stocks within the portfolio
Variance of the portfolios
Expected return of the
portfolio
A
B
C
D
E
Stock 1
Stock 2
Composition of the
portfolios:
A : 100% stock 1
B : 75% stock 1
C : 50% stock 1
D : 25% stock 1
E : 0% stock 1
Couple (r,o) if = 1
The same causes lead to the same moves: there is a linear relationship between the
stocks y= ax+b with a > 0
A
B
C
D
E
stock 1
stock 2
Composition of the
portfolios:
A : 100% stock 1
B : 75% stock 1
C : 50% stock 1
D : 25% stock 1
E : 0% stock 1
Expected return of the
portfolio
Variance of the portfolios
Couple (r,o) if = -1
The same causes lead to the opposite moves: there is a linear relationship between
the stocks y= ax+b with a < 0
A
B
C
D
E
stock 1
stock 2
Expected return of the
portfolio
Composition of the
portfolios:
A : 100% stock 1
B : 75% stock 1
C : 50% stock 1
D : 25% stock 1
E : 0% stock 1
Variance of the portfolios
Couple (r,o) if = 0
The same causes lead to different moves
Volatility
20 30 10 40 50
Risk which cannot be diversified = systematic risk
Risk which can be diversified = specific
1
Asymptotic : market risk
Number of shares in a portfolio
- A portfolio which is fully diversified has NO specific risk
- A diversified portfolio has systematic risk ONLY
- A diversified portfolio is THE MARKET and has a MARKET RISK
- The Beta of a stock measures its systematic risk
- It is measured against MARKET RISK
- It is expressed as the ratio between the volatility of the stock and
the volatility of the market
- It is expressed in number of market risks
M
M i
i
Var
Cov
,
= |
r
i
r
M
i
- The Beta measures the sensitivity of a stock to the market
- It is the coefficient of the linear relationship
- Beta > 0 : reacts the same way as the market to systematic risks
- Beta < 0 : reacts opposite way to the market
- Beta > 1: reacts more than the market
- Beta < 1: react less than the market
CAPM: Capital Asset Pricing Model
- A way to price the risk
- Based on the relationship:
- Expected return = price of time + price of risk
- Hypotheses:
- It is possible to create diversified portfolios
- It is possible to invest in risk-free assets
Expected standard deviation
Expected Return
5%
10%
15%
25%
20%
20% 30% 10% 40% 50%
Efficient frontier:
All possible efficient portfolios which rational investors can choose
A
B
r
free
10%
15%
25%
20%
20% 30% 10% 40% 50%
Risky asset
Expected return
Expected standard deviation
r
f
10%
15%
25%
20%
20% 30% 10% 40% 50%
P
M
Expected return
Expected standard deviation
r
f
10%
15%
25%
20%
20% 30% 10% 40% 50%
P
M
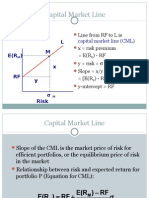
Market Line
Borrowing
Deposit
Expected standard deviation
Expected return
Expected Return
r
f
P
M
|=1
E(r
M
)
Equation of the market line:
E(r
i
) = r
f
+
i
[E(r
M
) r
f
]
where
[E(r
M
) r
f
] is the Market Risk Premium
|
i
E(r
i
)
r
f
r
f
E(r
M
)-r
f
i
[E(r
M
)-r
f
]
Market Risk
( )
( )
f M f
r k r
premium risk Market * rate Risk-f ree
rate
Risk-f ree
portf olio market
of return Expected
* rate Risk-f ree
asset f inancial a on return Expected
+ =
+ =
|
.
|
\
|
+ =
* |
|
|
Historical volatility = return
Return
r
f
P
M
|=1
E(r
M
)
A
B
if the forecast return is
higher than the expected
return (CAPM theoretical) ,
then the price of the stock is
UNDERVALUED
if the forecast return is
LOWER than the expected
return (CAPM theoretical) ,
then the price of the stock is
OVERVALUED
UNDERVALUED
OVERVALUED