0% found this document useful (0 votes)
707 views19 pagesUnderstanding Proprioceptive Neuromuscular Facilitation
Proprioceptive Neuromuscular Facilitation (PNF) is an exercise technique based on principles of functional anatomy and neurophysiology. It uses techniques of facilitation and inhibition through muscle stretching and contraction to increase strength, flexibility, range of motion, and coordination. PNF involves specific patterns of movement with manual pressure and verbal cues to elicit stretch reflexes, reciprocal inhibition, and autogenic inhibition for rehabilitation purposes.
Uploaded by
Dany VirgilCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
707 views19 pagesUnderstanding Proprioceptive Neuromuscular Facilitation
Proprioceptive Neuromuscular Facilitation (PNF) is an exercise technique based on principles of functional anatomy and neurophysiology. It uses techniques of facilitation and inhibition through muscle stretching and contraction to increase strength, flexibility, range of motion, and coordination. PNF involves specific patterns of movement with manual pressure and verbal cues to elicit stretch reflexes, reciprocal inhibition, and autogenic inhibition for rehabilitation purposes.
Uploaded by
Dany VirgilCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Proprioceptive Neuromuscular Facilitation
- Early Research
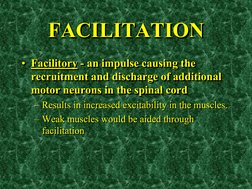
- Facilitation
- Inhibition
- Neurophysiological Basis
- Rational for Use
- Principles of PNF
- Patterns
- Techniques