0% found this document useful (0 votes)
206 views17 pagesIP Address Range Calculation Guide
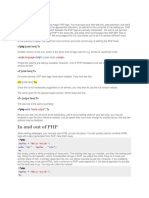
Dividing a network into smaller subnets allows organizations to better organize their IP addresses and network traffic. The number of subnets created by subnetting can be calculated by subtracting the bits in the classful subnet mask from the bits in the custom subnet mask. For example, subnetting the 192.168.1.0/24 network with a 28-bit subnet mask would create 16 subnets. Within each subnet, the number of available host IP addresses is calculated by subtracting the subnet bits from 32, then subtracting 2 from the result.
Uploaded by
bingCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
206 views17 pagesIP Address Range Calculation Guide
Dividing a network into smaller subnets allows organizations to better organize their IP addresses and network traffic. The number of subnets created by subnetting can be calculated by subtracting the bits in the classful subnet mask from the bits in the custom subnet mask. For example, subnetting the 192.168.1.0/24 network with a 28-bit subnet mask would create 16 subnets. Within each subnet, the number of available host IP addresses is calculated by subtracting the subnet bits from 32, then subtracting 2 from the result.
Uploaded by
bingCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd