85% found this document useful (20 votes)
3K views24 pagesForms and Purposes of Oral Communication
Oral communication involves expressing ideas and information through spoken words. It includes face-to-face communication and communication using mechanical devices. Face-to-face communication allows for stronger emotional engagement through body language and gestures. Oral communication has various forms like meetings, presentations, and interviews. It is used to convey information, persuade, and ensure understanding. Effective oral communication considers elements like content, organization, delivery, voice modulation, and clarity of speech.
Uploaded by
Muhammad SaimCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
85% found this document useful (20 votes)
3K views24 pagesForms and Purposes of Oral Communication
Oral communication involves expressing ideas and information through spoken words. It includes face-to-face communication and communication using mechanical devices. Face-to-face communication allows for stronger emotional engagement through body language and gestures. Oral communication has various forms like meetings, presentations, and interviews. It is used to convey information, persuade, and ensure understanding. Effective oral communication considers elements like content, organization, delivery, voice modulation, and clarity of speech.
Uploaded by
Muhammad SaimCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Introduction to Oral Communication: Introduces the types and purposes of oral communication, emphasizing the key components such as speaker and message.
- Key Concepts of Oral Communication: Discusses the fundamental concepts involved in oral communication including speaker, message, and context.
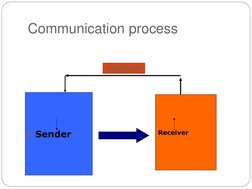
- Communication Process: Illustrates the communication process using a simple sender-receiver model.
- Modes of Speech Communication: Explores different modes of communication focusing on verbal and non-verbal elements.
- Elements of Oral Communication: Defines the three core elements of oral communication: content, organization, and delivery.
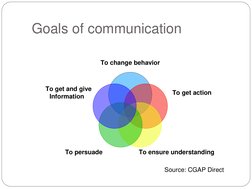
- Goals of Communication: Lists the primary goals of communication such as persuasion, understanding, and action.
- Forms of Oral Communication: Describes forms of oral communication including face-to-face and mechanical means.
- Attributes of Good Oral Communication: Details key attributes like clarity, stress, and intonation that define effective communication.
- Principles of Oral Communication: Highlights principles like brevity, clarity, and sequence in crafting oral messages.
- Types and Styles of Oral Communication: Explores different speech types such as prepared and impromptu, along with communication styles.
- Effective Communication in Business: Discusses the role of effective communication in improving business relations and productivity.
- Emotional Significance of Messages: Examines how emotional cues influence the interpretation of messages.
- Supervisor's Oral Skills: Emphasizes the importance of oral skills for supervisors in managing teams effectively.
- Effective Communicator: Defines the characteristics of an effective communicator, focusing on honesty and clarity.
- Oral vs. Written Communication: Compares and contrasts oral and written communication, noting pros and cons of each method.