71% found this document useful (7 votes)
3K views12 pagesControl Plans
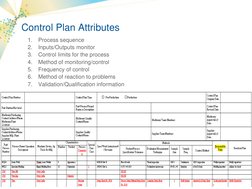
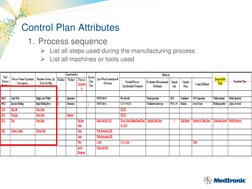
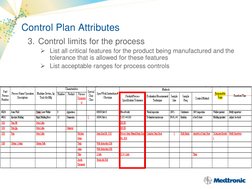
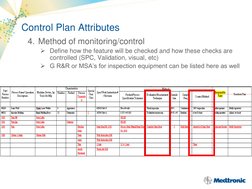
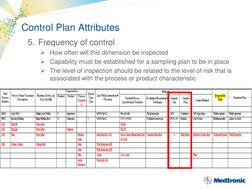
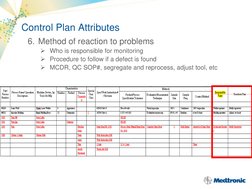
A control plan is a process management tool used to identify and monitor critical inputs and outputs of a process to ensure goals are continually met. Key elements of a control plan include risk management, supplier evaluation, contracts, control plan methodology, product acceptance, supplier performance monitoring, development, certification, change control, and corrective action. Attributes of a control plan outline the process sequence, inputs/outputs monitoring, control limits, monitoring methods, monitoring frequency, problem reaction methods, and validation/qualification information.
Uploaded by
aman_ranhotraCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
71% found this document useful (7 votes)
3K views12 pagesControl Plans
A control plan is a process management tool used to identify and monitor critical inputs and outputs of a process to ensure goals are continually met. Key elements of a control plan include risk management, supplier evaluation, contracts, control plan methodology, product acceptance, supplier performance monitoring, development, certification, change control, and corrective action. Attributes of a control plan outline the process sequence, inputs/outputs monitoring, control limits, monitoring methods, monitoring frequency, problem reaction methods, and validation/qualification information.
Uploaded by
aman_ranhotraCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd