Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Course 3 - Trauamt Urechii
Uploaded by
Liviu LivaxOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Course 3 - Trauamt Urechii
Uploaded by
Liviu LivaxCopyright:
Available Formats
MIDDLE EAR TRAUMATISMS
CLASSIFICATION
1.DIRECTLY TRAUMATISMS
THE TYMPANIC MEMBRANE TRAUMATISMS BY
FOREIGNS BODY
TYMPANIC MEMBRENE BURNS
PRESIONAL TRAUMATISMS- BLAST, BARO TRAUMAS,
BANG SUPERSONIC
ACOUSTIC ACUTE TRAUMA
ELECTRICALY TRAUMATISMS
2. INDIRECTLY TRAUMATISMS
ASSOCIATED TRAUMA
LABIRINTHI FRACTURE
EXTRALABIRINTH FRACTURE
3. OSSICULAR BONES INJURIES
LABYRINTHINE CONCUSSION
TYMPANIC TRAUMATISMS PRODUCED BY FOREIGNE
BODY
Symptomatology: pain, subepithelial hemorrage
TM perforation with osicular chain dislocation,
vestibular(vertiginous) phenomena
ENT Examination: perforation in the centre of the MT
Treatment: suction, dry endaural dressing in the
external auditory canal
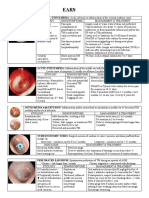
TYMPANIC MEMBRANE BURNS
Symptomatology:
Intensive pain
EAC with (pete marmorate) marble trourought spots
TM hypermia, and hiperemic,turgid
large TM perforation situated in anthero-inferior part
of the MT
Treatment:
Endaural dressing
Antibiotic treatment
MYRINGOPLASTY after 6 month after one
suppuration
BARO TRAUMATISMS
It is produced by a pressure increasing of surrounding
environment ,after one applying one box on the ear.
Valsalva maneuver is difficult to performed
Symptomatology:
The tympanical congestionin the eptimpanic region
Difuze congestionwith a retraction of the MT
Hemothympan
Linear breack of the MT
Affects the Ossicular chain functionality
BARO TRAUMAS
Hearing loss by unilateral compression
Hearing loss by bilateral decompression- is progressively
installed ,horinzontal curve
BARO TRAUMATISMS FROM AVIATION
Classification:
Acute: ear pain, tinnitus, vertigo
Subacute: transient and vague ear pain
Chronic : low frequency transmission hearing loss- after it
is turns into mixed hearing loss, and large perforation
ENT Examination: thickened and retracted Tympanic
membrane, hammer leveling, unilateral pain, vertigo,
tinnitus, and large perforation
Treatment: cleaning the EAC, after that Myringoplasty
BLAST
Movement of air mass by explosion and deflagration
It produced degenerative lesions to the labyrinth by internal ear
hemorrage and concussion
SUPERSONIC BANG
It is produced by 130-145 dB sonic energy, that has a short time
action
In this situation are produced hydrodynamical changes due to a
fragile cochlea
Symptomatology: plugged ear , hearing loss with associate
vertigo, degenerative labyrinth Lesions(injuries) , neural sensory
hearing loss to high frequency
Treatment:
Vasodilatators drugs
ACOUSTIC ACUTE TRAUMA
- Appears trough exposer to loud noise over a 2 hours-7
days period of time
- Perception hearing loss by high frequency with a noch
by 400 Hz.
- Nervous exhaustion Phenomenon
- Treatment: vasodylatatory and vitamins drugs
ELECTRICAL TRAUMATISMS
It is produced by electrocution
Is produced:
- Directly primary lesions of TM
- Late secondary lesions
Perception or mixed hearing loss
Tympanic membrane perforations
Associated phenomena: bone necrosis, psichiatric
disorders, cerebral atrophy, affecting language, facial
paralysis, ocular complications
INDIRECTLY MIDDLE EAR TRAUMATISMS
ASSOCIATED TRAUMAS
- Mastoidean traumas
- Temporo-parietaly
- occipital
- occipito-parietal
Longitudinal fractures- tympanic membrane and tympanic
cavity with intact maintaining of facial nerve
Transverse fracture-way, vestibule, cochlea ,inferior wall of
Tympanic cavity, N. facial without affecting the
tympanic membrane
Oblique fractures
LABYRINTH AND EXTRALABYRINTH FRACTURES
Fracture Labyrinth: Bony labyrinth fracture. The bony
labyrinth, fracture of temporaly bone , and labyrinthine
concussion
Fracture Extralabyrinth : fracture of tymoanic cavity , tip
rock, mastoidean cells and EAC
Symptoms:
- Perforation of tympanic Membrane
- othoragy
- licvoree
- hearing loss to Deafness
- Balance disorder
Paralysis N. V, VI, VII
Treatment: conservative or surgical- mixed surgical teams
POST TRAUMATICALY LESIONS OF THE
TYMPANO-OSSICULAR SYSTEM
Symptomatology:
Transmission hearing loss, that will transforme in mixed and
neural or perception
Tinnitus
Balance disorders
Localisation: Incudo-stapedian joint , long incus apophyses,
stedo- vestibular joint
Clinical Diagnosis:
Tympanometrie with stapedian reflex
Tonal Audiometry
Opening the tympanic cavity to make the diagnostic
Treatament:
Surgical-ossicular bones
LABYRINTH CONCUSSION
It is a clinical manifestatio in the absence of a fracture
Definition: irreversible damage to neurosensorial elements-
oval window and the first round of turns of the cochlea
Symptomatology:
Hearing loss
Tinnitus
Nevralgic ear pain
Perception Hearing loss degenerative type by high
frequency and after that by low frequency
Treatment: it is necessary to make stimulator implants
transistors
You might also like
- MCAT Beh Sci WorksheetsDocument171 pagesMCAT Beh Sci WorksheetsGrace100% (4)
- Approach To Ear Problem Ratna FinalDocument52 pagesApproach To Ear Problem Ratna FinalRatnaSuryatiNo ratings yet
- Osce EarexamDocument2 pagesOsce EarexamminhaapNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy and Physiology For NursesDocument48 pagesHuman Anatomy and Physiology For NursesKelly J Wilson86% (21)
- Lecture 2 Ent.Document70 pagesLecture 2 Ent.kiprotich weldonNo ratings yet
- Chronic Otitis Media (Mesotympanitis. Epitympanitis) - Otogenous Intracranial ComplicationsDocument53 pagesChronic Otitis Media (Mesotympanitis. Epitympanitis) - Otogenous Intracranial Complicationssimi yNo ratings yet
- Acute Suppurative Otitis MediaDocument19 pagesAcute Suppurative Otitis MediaRajesh Sharma100% (1)
- Ryan Martin Ko, M.DDocument54 pagesRyan Martin Ko, M.DDhaval Makwana100% (2)
- ENT - UnitDocument63 pagesENT - Unitsuganthi rajesh kannaNo ratings yet
- External Ear DiseaseDocument60 pagesExternal Ear Diseasenitas23100% (1)
- Otitis MediaDocument32 pagesOtitis MediaRiya GautamNo ratings yet
- Course 4 - Otitele MediiDocument45 pagesCourse 4 - Otitele MediiLiviu LivaxNo ratings yet
- ENT Voice & Speech DisordersDocument116 pagesENT Voice & Speech DisordersAnuja DalalNo ratings yet
- Hearing LossDocument4 pagesHearing LossmuhammadridhwanNo ratings yet
- Hearing Loss: Mubarak MD Dhawal Mbbs (Iua), Morl (Mak) ENT Lecturer April 2019Document46 pagesHearing Loss: Mubarak MD Dhawal Mbbs (Iua), Morl (Mak) ENT Lecturer April 2019gibreilNo ratings yet
- Ear DischargeDocument69 pagesEar DischargeNabylah YutakaNo ratings yet
- Made By: DR Aditya RanjanDocument32 pagesMade By: DR Aditya RanjanArjun SainiNo ratings yet
- Otalgia, Temporal Bone Fracture, C.S.F. Otorrhea, OtotoxicityDocument54 pagesOtalgia, Temporal Bone Fracture, C.S.F. Otorrhea, OtotoxicityAyman YakoutNo ratings yet
- Revesion of External and Middle Ear PathologiesDocument52 pagesRevesion of External and Middle Ear PathologiesAhlam DreamsNo ratings yet
- Symptom A To Logy of EarDocument36 pagesSymptom A To Logy of Ear98480sam23006100% (1)
- Pemicu 4 "Mengapa Telingaku Tak Dapat Mendengar?": Adrian - 405100018 - Blok PenginderaanDocument71 pagesPemicu 4 "Mengapa Telingaku Tak Dapat Mendengar?": Adrian - 405100018 - Blok PenginderaanRilianda SimbolonNo ratings yet
- Management of Diseases of Ear, Nose and ThroatDocument16 pagesManagement of Diseases of Ear, Nose and ThroatSaurabh LamkhadeNo ratings yet
- Acute Suppurative Otitis MediaDocument24 pagesAcute Suppurative Otitis MediaDr Tipu SultanNo ratings yet
- ENT Course 1-2-3 General, Rhino. OtoDocument30 pagesENT Course 1-2-3 General, Rhino. Ototaliya. shvetzNo ratings yet
- ENT CourseDocument29 pagesENT Coursetaliya. shvetzNo ratings yet
- Pseudomonas Aeruginosa : Most CommonDocument2 pagesPseudomonas Aeruginosa : Most CommonSoojung Nam100% (1)
- Lecture 1 Otitis MediaDocument82 pagesLecture 1 Otitis MediaTarun SharmaNo ratings yet
- Davao Medical School Foundation: Chris Robinson D. Laganao, MD, DPBO-HNSDocument48 pagesDavao Medical School Foundation: Chris Robinson D. Laganao, MD, DPBO-HNSVasiliás PrawinNo ratings yet
- A. Nasal Symptoms 1. Nasal Obstruction Is The Commonest Symptom. - This Leads To MouthDocument6 pagesA. Nasal Symptoms 1. Nasal Obstruction Is The Commonest Symptom. - This Leads To MouthRubi MeeajanNo ratings yet
- Prof - Dr. Mohamed Talaat EL - GhonemyDocument33 pagesProf - Dr. Mohamed Talaat EL - Ghonemyadel madanyNo ratings yet
- Penyakit Gangguan KeseimbanganDocument31 pagesPenyakit Gangguan KeseimbanganFitrach AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Diseases of The External Ear 2Document57 pagesDiseases of The External Ear 2Mimo HemadNo ratings yet
- Ear Discharge HandoutDocument9 pagesEar Discharge HandoutPorori BookshopNo ratings yet
- 15 Menieres DiseaseDocument72 pages15 Menieres DiseaseDrravikumar BhandariNo ratings yet
- Chronic Suppurative Otitis Media (Chronic Otitis Media)Document40 pagesChronic Suppurative Otitis Media (Chronic Otitis Media)pewpewpiesNo ratings yet
- مراجعة الأوسكىDocument238 pagesمراجعة الأوسكىHala BahaaNo ratings yet
- Tinnitus: Dr. Naveen. G Iind Year Post Graduate Dept. of Ent VMKVMCH, SalemDocument35 pagesTinnitus: Dr. Naveen. G Iind Year Post Graduate Dept. of Ent VMKVMCH, SalemDr. Naveen. GNo ratings yet
- CholesteotomaDocument33 pagesCholesteotomaWael ShamyNo ratings yet
- External Ear Pathology - PresentationDocument25 pagesExternal Ear Pathology - PresentationNipun MalhotraNo ratings yet
- AMBOSS Ear QuestionsDocument10 pagesAMBOSS Ear QuestionsSahil DnkNo ratings yet
- Middle Ear Diseases by Prof Mahmoud AttiaDocument84 pagesMiddle Ear Diseases by Prof Mahmoud AttiaWesam TayaNo ratings yet
- ENT Notes For Med StudentsDocument4 pagesENT Notes For Med Studentsnikki100% (1)
- Acute and Chronic Middle OtitisDocument52 pagesAcute and Chronic Middle Otitisfiras thawabiaNo ratings yet
- Chapter IIDocument9 pagesChapter IIMuhamad AriefNo ratings yet
- Ear Nose and Throat 2Document34 pagesEar Nose and Throat 2api-195799092No ratings yet
- The Ear and It's DisordersDocument104 pagesThe Ear and It's DisordersAyaBasilioNo ratings yet
- Some Ear DisordersDocument71 pagesSome Ear DisordersCosbyNo ratings yet
- Otitis MediaDocument98 pagesOtitis MediaLody Lean CruzNo ratings yet
- ENT Lectures 1Document123 pagesENT Lectures 1lxnalexander100% (1)
- Dizziness 3Document37 pagesDizziness 3Anurag SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Chronic Otitis Media Types, Investigations, TreatmentDocument43 pagesChronic Otitis Media Types, Investigations, TreatmentPrasanna DattaNo ratings yet
- Ear ProblemDocument52 pagesEar ProblemLaurensia MassariNo ratings yet
- Tinnitus Grand Rounds: Edward Buckingham, M. D. Jeff Vrabec, M. D., Faculty Sponcer Francis Quinn, M.D., Series EditorDocument61 pagesTinnitus Grand Rounds: Edward Buckingham, M. D. Jeff Vrabec, M. D., Faculty Sponcer Francis Quinn, M.D., Series EditorShauki AliNo ratings yet
- Common Ent DisordersDocument20 pagesCommon Ent DisordersattaheeraNo ratings yet
- Journal Reading Traumatic Ossicle Extrusion Into The External Auditory CanalDocument15 pagesJournal Reading Traumatic Ossicle Extrusion Into The External Auditory CanalAdrian Prasetya SudjonoNo ratings yet
- Middle Ear CHR DiseasesDocument157 pagesMiddle Ear CHR DiseasesAdi SitaruNo ratings yet
- Affection of EarDocument43 pagesAffection of EarDr Anais AsimNo ratings yet
- ENT Approach To The External EarDocument2 pagesENT Approach To The External EarVanessa HermioneNo ratings yet
- Bool NotresDocument7 pagesBool NotresrohNo ratings yet
- Ucd Oe OmDocument28 pagesUcd Oe OmFaiq Syukri Bin SaparudinNo ratings yet
- Endodontics (31 Questions) : Pulpal DiseaseDocument51 pagesEndodontics (31 Questions) : Pulpal DiseaseTayaba Naim KhanNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Methods To Analyze The Severe Obesity in Romania and Its Impact Over Public Administration Health ExpendituresDocument13 pagesQuantitative Methods To Analyze The Severe Obesity in Romania and Its Impact Over Public Administration Health ExpendituresLiviu LivaxNo ratings yet
- Obesity and Health-Related Lifestyle Factors in The General Population in Romania: A Cross Sectional StudyDocument9 pagesObesity and Health-Related Lifestyle Factors in The General Population in Romania: A Cross Sectional StudyLiviu LivaxNo ratings yet
- Cheats Game StrategyDocument3 pagesCheats Game StrategyLiviu LivaxNo ratings yet
- HIT Netherlands PDFDocument275 pagesHIT Netherlands PDFLiviu LivaxNo ratings yet
- HIT Netherlands PDFDocument275 pagesHIT Netherlands PDFLiviu LivaxNo ratings yet
- Course 4 - Otitele MediiDocument45 pagesCourse 4 - Otitele MediiLiviu LivaxNo ratings yet
- Euro Million Lottery StrategyDocument1 pageEuro Million Lottery StrategyLiviu LivaxNo ratings yet
- MusicDocument26 pagesMusicamme77No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan: Gyan Bharati School Saket, New DelhiDocument6 pagesLesson Plan: Gyan Bharati School Saket, New DelhiDivanshi ShakyaNo ratings yet
- By MBBS Gang: ENT Examination ProcedureDocument23 pagesBy MBBS Gang: ENT Examination ProcedureYour DaddyNo ratings yet
- Ear - WikipediaDocument15 pagesEar - WikipediadearbhupiNo ratings yet
- Ent Past Years Question According To TopicsDocument32 pagesEnt Past Years Question According To Topicsmohamed100% (1)
- WavesDocument65 pagesWavesMelanie Tagudin TrinidadNo ratings yet
- Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Notes: Vestibular System-Peripheral MechanismsDocument4 pagesMedical Neuroscience Tutorial Notes: Vestibular System-Peripheral MechanismsHenrique De Figueiredo MariscoNo ratings yet
- Hearing Loss - Ear, Nose, and Throat Disorders - MSD Manual Professional EditionDocument14 pagesHearing Loss - Ear, Nose, and Throat Disorders - MSD Manual Professional Editiondr.aliceNo ratings yet
- Scala SC 53 TMDocument2 pagesScala SC 53 TMMBAlexNo ratings yet
- AP Psychology - Myers Module 17-22 VocabularyDocument7 pagesAP Psychology - Myers Module 17-22 VocabularyJaakkiiee YungNo ratings yet
- Bi Lobar Post Auricular Skin Flap For Reconstruction of The EarlobeDocument3 pagesBi Lobar Post Auricular Skin Flap For Reconstruction of The Earlobedrgurpal74No ratings yet
- Lesson1health6 200628035049Document15 pagesLesson1health6 200628035049FernandoNo ratings yet
- Lopez - Neil - Case StudyDocument17 pagesLopez - Neil - Case StudyNeil LopezNo ratings yet
- Eyes EarsDocument6 pagesEyes EarsSk Laila AyeshaNo ratings yet
- Journal Diagnosis and Management of A Tympanic Membrane HemangiomaDocument9 pagesJournal Diagnosis and Management of A Tympanic Membrane HemangiomaAndriyani YaniNo ratings yet
- 2019 ENT Nursing Exam 1Document7 pages2019 ENT Nursing Exam 1KAUH EducationNo ratings yet
- Revision StapedectomyDocument21 pagesRevision Stapedectomyapi-19500641100% (1)
- Coordination BioHackDocument9 pagesCoordination BioHackMohammed HamedNo ratings yet
- CSOMDocument32 pagesCSOMDarwin LlanesNo ratings yet
- Notes50 - PEDIATRIC VISION OR HEARING DISORDERSDocument9 pagesNotes50 - PEDIATRIC VISION OR HEARING DISORDERSTJ ZamarroNo ratings yet
- Sensation and Perception Flash CardsDocument164 pagesSensation and Perception Flash Cardsapi-318932038No ratings yet
- Checklist Exam of EarDocument4 pagesChecklist Exam of EarCes Melisse DNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 f3Document113 pagesChapter 1 f3FAthiyah Abdul RahimNo ratings yet
- Level1 PHYSICAL-ASSESSMENTDocument11 pagesLevel1 PHYSICAL-ASSESSMENTShyra Mae Riano MarinNo ratings yet
- CSF OttorheaDocument8 pagesCSF OttorheaImam AdiNo ratings yet