Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ENT Approach To The External Ear
Uploaded by
Vanessa Hermione0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views2 pagesThe external ear is composed of the auricle and external auditory meatus. The auricle develops from the first and second branchial arches and is formed by elastic cartilage covered in skin. The external auditory meatus is a tube connecting the auricle to the tympanic membrane, with an outer cartilaginous portion and inner bony portion. The nerve supply of the external ear includes the trigeminal, facial, and vagus cranial nerves. Diseases of the external ear include congenital abnormalities, infections, tumors, metabolic conditions like gout, and wax impaction.
Original Description:
Original Title
ENT Approach to the External Ear
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe external ear is composed of the auricle and external auditory meatus. The auricle develops from the first and second branchial arches and is formed by elastic cartilage covered in skin. The external auditory meatus is a tube connecting the auricle to the tympanic membrane, with an outer cartilaginous portion and inner bony portion. The nerve supply of the external ear includes the trigeminal, facial, and vagus cranial nerves. Diseases of the external ear include congenital abnormalities, infections, tumors, metabolic conditions like gout, and wax impaction.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views2 pagesENT Approach To The External Ear
Uploaded by
Vanessa HermioneThe external ear is composed of the auricle and external auditory meatus. The auricle develops from the first and second branchial arches and is formed by elastic cartilage covered in skin. The external auditory meatus is a tube connecting the auricle to the tympanic membrane, with an outer cartilaginous portion and inner bony portion. The nerve supply of the external ear includes the trigeminal, facial, and vagus cranial nerves. Diseases of the external ear include congenital abnormalities, infections, tumors, metabolic conditions like gout, and wax impaction.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
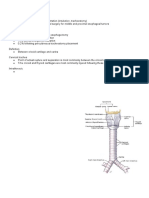
Approach to the External Ear
Clinical Anatomy
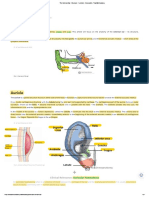
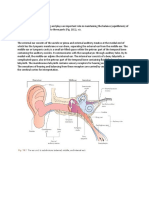
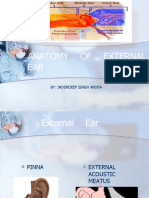
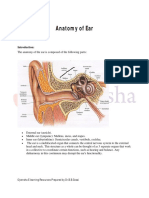
The external ear is composed of the auricle(pinna) and the external
auditory meatus. Its function is to collect and transmit sound to the
tympanic membrane.
Auricle
Develops from 6 nodules from 1st 2 branchial arches and the
overlying skin
Formed by a skeleton of yellow elastic cartilage covered in skin
External Auditory Meatus
Tube connecting the conchal bowl to the tympanic membrane
Outer 1/3 is cartilaginous, Inner 2/3 is bony
24 – 25mm long in adults
Skin of outer third of meatus is hair-bearing and contains wax and
sebaceous glands (which are absent in inner bony meatus)
The 2 portions of the meatus have slightly different directions – the
cartilaginous part goes upwards and backwards, the bony part goes
forward and downward
Nerve Supply of the External Ear
Knowledge of the nerve supply is important as patients may present with
otalgia caused by stimulation of the nerves elsewhere in their course.
Auriculotemporal Most of the anterior half of the auricle and the
branch of trigeminal EAM
nerve
Greater auricular Posterior and cranial side of the auricle
nerve (C2, C3)
Branches from
lesser occipital
nerve (C2)
Small sensory Around concha and posterior meatus
branches of CN IX Near the tympanic membrane
and X It is these branches that when stimulated during
examination of the ear, especially in children),
can cause an episode of coughing due to vagal
stimulation (recurrent laryngeal n.)
The skin of the lateral surface of the tympanic membrane and ear canal is
unusual. It is not simply shed as is the skin from the rest of the body, but it
is migratory and travels radially outwards from the ear drum and thence
out along the ear canal. Thus, the ear canal is largely sefl-cleaning.
Causes of Referred Otalgia Diseases of the External Ear
Parotid, TMJ, Sinuses, Teeth, Congenital (micro/macrotia,
Tongue base, Tonsil, Larynx, meatal stenosis/atresia, bat ears)
Pharynx, Upper esophagus, Cervical Traumatic
spine Infective/inflammatory
Neoplastic
Metabolic (gouty tophi)
Idiopathic (wax impaction)
You might also like
- A Simple Guide to the Ear and Its Disorders, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to the Ear and Its Disorders, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- 10 - Anatomy of The Ear (Edited)Document26 pages10 - Anatomy of The Ear (Edited)Enlighten usNo ratings yet
- Simply Put - ENT EAR LECTURE NOTESDocument48 pagesSimply Put - ENT EAR LECTURE NOTESCedric KyekyeNo ratings yet
- Adhi Wardana 405120042: Blok PenginderaanDocument51 pagesAdhi Wardana 405120042: Blok PenginderaanErwin DiprajaNo ratings yet
- Blank-2023-09-16 22-28-41Document6 pagesBlank-2023-09-16 22-28-41adham bani younesNo ratings yet
- ENT Prelims TransDocument45 pagesENT Prelims TransRaven CocjinNo ratings yet
- EarDocument33 pagesEarHikmat UllahNo ratings yet
- Diseases of The External Ear 2Document57 pagesDiseases of The External Ear 2Mimo HemadNo ratings yet
- Surgical Ear Diseases of The Dog - An OverviewDocument9 pagesSurgical Ear Diseases of The Dog - An OverviewPavel VokrouhlíkNo ratings yet
- Anatomy EarDocument44 pagesAnatomy Earrinaldy agungNo ratings yet
- 25 Middle Ear, Ossicles, Eustachian Tube (Done)Document17 pages25 Middle Ear, Ossicles, Eustachian Tube (Done)osamaeNo ratings yet
- Anatomy EarDocument44 pagesAnatomy Earrinaldy agungNo ratings yet
- By DR Manah Chandra Changmai MBBS MSDocument31 pagesBy DR Manah Chandra Changmai MBBS MSKalaivaany RamachandranNo ratings yet
- EAR-4 Year PresentationDocument133 pagesEAR-4 Year Presentationeiuj497No ratings yet
- Otalgia & TinnitusDocument19 pagesOtalgia & Tinnitushonda matizNo ratings yet
- Sensory Organs - EarsDocument37 pagesSensory Organs - Earsapi-324160601No ratings yet
- Anatomy of Middle Ear: BY Kuriachan JosephDocument15 pagesAnatomy of Middle Ear: BY Kuriachan Josephallen chrysoNo ratings yet
- Diseases of External EarDocument66 pagesDiseases of External Earalmazmulu76100% (1)
- Organs of Head&neckDocument143 pagesOrgans of Head&neckraphaelyohana140No ratings yet
- LO SSS Week 5Document8 pagesLO SSS Week 5Tony StarkNo ratings yet
- Acuteotitismedia1 180118101452 PDFDocument57 pagesAcuteotitismedia1 180118101452 PDFWael ShamyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Ent.Document60 pagesLecture 1 Ent.kiprotich weldonNo ratings yet
- Evaluationandmanagement Ofotalgia: Tiffany Peng Hwa,, Jason A. BrantDocument14 pagesEvaluationandmanagement Ofotalgia: Tiffany Peng Hwa,, Jason A. BrantLeo CortesNo ratings yet
- Ent Image BankDocument140 pagesEnt Image Bankanitaabreu123No ratings yet
- Nursing Management of Patient With Disorders of Ent Third YrDocument26 pagesNursing Management of Patient With Disorders of Ent Third YrShreyas Walvekar100% (3)
- The EarDocument13 pagesThe EarOjambo FlaviaNo ratings yet
- Demo Class of EarDocument54 pagesDemo Class of EarMegha BhengraNo ratings yet
- Middle Ear, Ossicles, Eustachian Tube (Done)Document17 pagesMiddle Ear, Ossicles, Eustachian Tube (Done)Dr-Firas Nayf Al-ThawabiaNo ratings yet
- 15-Sensory OrgansDocument23 pages15-Sensory OrgansMilad HabibiNo ratings yet
- The Ear AnatomyDocument23 pagesThe Ear AnatomyyasinoNo ratings yet
- Case Report CSOMDocument13 pagesCase Report CSOMNashria RusdhyNo ratings yet
- Ent Diagnosis (Kaneez-E-Zahra)Document16 pagesEnt Diagnosis (Kaneez-E-Zahra)hamzaw213No ratings yet
- Chronic Otitis Media (Mesotympanitis. Epitympanitis) - Otogenous Intracranial ComplicationsDocument53 pagesChronic Otitis Media (Mesotympanitis. Epitympanitis) - Otogenous Intracranial Complicationssimi yNo ratings yet
- Ear 1, 2Document9 pagesEar 1, 2Nnbbh HggyyNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Ear FinalDocument61 pagesAnatomy of Ear FinalRavi KushwahaNo ratings yet
- The External Ear - Structure - Function - Innervation - TeachMeAnatomyDocument3 pagesThe External Ear - Structure - Function - Innervation - TeachMeAnatomywzt2001No ratings yet
- RAJIV DHAWAN ENT FMG RR Watermark Final Corrected 09.11.23Document69 pagesRAJIV DHAWAN ENT FMG RR Watermark Final Corrected 09.11.23Wahib ZaidiNo ratings yet
- Exterior and Middle EarDocument26 pagesExterior and Middle EarAndra BauerNo ratings yet
- Ear - Islam AssiDocument21 pagesEar - Islam AssiIslam AssiNo ratings yet
- Diseases of The Middle EarDocument32 pagesDiseases of The Middle EarMimo HemadNo ratings yet
- ورق مذاكره PDFDocument100 pagesورق مذاكره PDFsalamred100% (1)
- 23 External Ear (Done)Document4 pages23 External Ear (Done)osamaeNo ratings yet
- Referat Othematom Auricular DeviDocument22 pagesReferat Othematom Auricular DeviGigin Sandria100% (1)
- Anatomy and Physiology THT - Dr. AriefDocument88 pagesAnatomy and Physiology THT - Dr. AriefGilbert Sterling OctaviusNo ratings yet
- Potongan CSOM Part 2Document12 pagesPotongan CSOM Part 2Athanasius WrinNo ratings yet
- CsomDocument4 pagesCsomMitch C.No ratings yet
- 5 Anatomi Organ Dan Sistem Pendengaran-1Document63 pages5 Anatomi Organ Dan Sistem Pendengaran-1Naafi RizkiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The EarDocument63 pagesAnatomy of The EargabrielNo ratings yet
- ENT Notes For Med StudentsDocument4 pagesENT Notes For Med Studentsnikki100% (1)
- DR - Rimpy Bhuyan Trihms.Document63 pagesDR - Rimpy Bhuyan Trihms.DIKSHA RANI DEKANo ratings yet
- EarDocument10 pagesEarfatimaawan8989No ratings yet
- Anatomy of External EarDocument49 pagesAnatomy of External EarInderdeep AroraNo ratings yet
- Radio Study of Middle EarDocument44 pagesRadio Study of Middle EarDOC AJNo ratings yet
- Jurnal ReadingDocument32 pagesJurnal ReadingEva Ratnasari DinNo ratings yet
- Referat Ready To AccDocument66 pagesReferat Ready To AccGebrina AmandaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of External Ear, Middle Ear and MastoidDocument66 pagesAnatomy of External Ear, Middle Ear and Mastoiddebdeepbhattacharya411No ratings yet
- 15 Ear - DR - GosaiDocument9 pages15 Ear - DR - GosaiDr.B.B.GosaiNo ratings yet
- Kuliah THT FKUI TK 4 Kapita SelektaDocument39 pagesKuliah THT FKUI TK 4 Kapita SelektaSri HartatiNo ratings yet
- IL2-Describing Variation in DataDocument7 pagesIL2-Describing Variation in DataVanessa HermioneNo ratings yet
- IL3-Understanding and Using Observational Studies in EpidemiologyDocument5 pagesIL3-Understanding and Using Observational Studies in EpidemiologyVanessa HermioneNo ratings yet
- IL4-Measures of Risk and Association 1 PDFDocument4 pagesIL4-Measures of Risk and Association 1 PDFVanessa HermioneNo ratings yet
- IL1-Measures of Disease FrequencyDocument5 pagesIL1-Measures of Disease FrequencyVanessa HermioneNo ratings yet
- Pocket Manual in Critical CareDocument356 pagesPocket Manual in Critical CareTahir Uddin Qazi86% (7)
- Joms Guide To SuturingDocument68 pagesJoms Guide To SuturingSundeep Sharma100% (3)
- Cancer Registry Annual Report 2015 - WebDocument43 pagesCancer Registry Annual Report 2015 - WebVanessa HermioneNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Mediastinum and Imaging ModalitiesDocument11 pagesAnatomy of The Mediastinum and Imaging ModalitiesVanessa HermioneNo ratings yet
- PY CARD 004 AMI Program Policy Updated 8thMArch 2017 PDFDocument14 pagesPY CARD 004 AMI Program Policy Updated 8thMArch 2017 PDFVanessa HermioneNo ratings yet
- Piis1078588418300807 PDFDocument62 pagesPiis1078588418300807 PDFPrasojo JojoNo ratings yet
- OBGYN Invasive Cervical Cancer ArticleDocument7 pagesOBGYN Invasive Cervical Cancer ArticleVanessa HermioneNo ratings yet
- Managemen of Vascular Graft and Endograft Infections Mar 2020Document46 pagesManagemen of Vascular Graft and Endograft Infections Mar 2020Vanessa HermioneNo ratings yet
- Disease of Mesenteric Arteries and Veins 2017Document51 pagesDisease of Mesenteric Arteries and Veins 2017Vanessa HermioneNo ratings yet
- Tracheobronchial InjuriesDocument1 pageTracheobronchial InjuriesVanessa HermioneNo ratings yet
- ACLS Simulation ScenariosDocument14 pagesACLS Simulation ScenariosVanessa HermioneNo ratings yet
- ENT Nose Examination ScriptDocument1 pageENT Nose Examination ScriptVanessa HermioneNo ratings yet
- ENT Ear Examination ScriptDocument2 pagesENT Ear Examination ScriptVanessa HermioneNo ratings yet
- ENT Approach To Thyroid MassesDocument2 pagesENT Approach To Thyroid MassesVanessa HermioneNo ratings yet
- ENT Approach To Deep Space Neck InfectionsDocument3 pagesENT Approach To Deep Space Neck InfectionsVanessa HermioneNo ratings yet
- Protocol For Ordering Treadmill Before Cardiology ConsultDocument2 pagesProtocol For Ordering Treadmill Before Cardiology ConsultVanessa HermioneNo ratings yet
- Skin Pathology NotesDocument2 pagesSkin Pathology NotesVanessa HermioneNo ratings yet
- ENT Annotated Neck Mass NotesDocument11 pagesENT Annotated Neck Mass NotesVanessa HermioneNo ratings yet
- Not Consistent With ACS ? Acs Very Consistent With ACS (Based On Clinical Features and ECG)Document1 pageNot Consistent With ACS ? Acs Very Consistent With ACS (Based On Clinical Features and ECG)Vanessa HermioneNo ratings yet
- PSYCH Conduct Disorder OSCE ScriptDocument1 pagePSYCH Conduct Disorder OSCE ScriptVanessa Hermione0% (1)
- PSYCH Autism OSCE ScriptDocument1 pagePSYCH Autism OSCE ScriptVanessa HermioneNo ratings yet
- PY CARD 004 AMI Program Policy Updated 8thMArch 2017 PDFDocument14 pagesPY CARD 004 AMI Program Policy Updated 8thMArch 2017 PDFVanessa HermioneNo ratings yet
- Protocol 13: Chest Pain: A&E DoctorDocument4 pagesProtocol 13: Chest Pain: A&E DoctorVanessa HermioneNo ratings yet
- Bronchospasm During Anaesthesia Update 2011Document5 pagesBronchospasm During Anaesthesia Update 2011Vanessa HermioneNo ratings yet
- H 11 FactorsDocument10 pagesH 11 FactorsSonia RogersNo ratings yet
- Skin Pathology NotesDocument2 pagesSkin Pathology NotesVanessa HermioneNo ratings yet
- The Role of Leadership On Employee Performance in Singapore AirlinesDocument42 pagesThe Role of Leadership On Employee Performance in Singapore Airlineskeshav sabooNo ratings yet
- Purchase Spec. For Bar (SB425)Document4 pagesPurchase Spec. For Bar (SB425)Daison PaulNo ratings yet
- Student Exploration: Magnetism (Find Gizmo Icon On Eclass)Document4 pagesStudent Exploration: Magnetism (Find Gizmo Icon On Eclass)Abdel Majeed Tuffaha0% (1)
- SFC PresentationDocument51 pagesSFC PresentationjmtriggerzNo ratings yet
- GutsDocument552 pagesGutsroparts cluj100% (1)
- Cracking Passwords GuideDocument45 pagesCracking Passwords GuideKorben100% (6)
- Wayne A. Thorp - Analyzing Supply & Demand Using Point & Figure Charts PDFDocument5 pagesWayne A. Thorp - Analyzing Supply & Demand Using Point & Figure Charts PDFSrinivasNo ratings yet
- Introduction To SAP: Venkat Emani FICO Certified Consultant / TrainerDocument22 pagesIntroduction To SAP: Venkat Emani FICO Certified Consultant / TrainerVenkat EmaniNo ratings yet
- Doyennés Et Granges de L'abbaye de Cluny (A. Guerreau)Document45 pagesDoyennés Et Granges de L'abbaye de Cluny (A. Guerreau)theseus11No ratings yet
- Unit 5, Orders and Cover Letters of Orders For StsDocument13 pagesUnit 5, Orders and Cover Letters of Orders For StsthuhienNo ratings yet
- Vertical Transportation: Commercial, Hotel, Hospital, Etc)Document5 pagesVertical Transportation: Commercial, Hotel, Hospital, Etc)fdarchitectNo ratings yet
- 1422-Article Text-3684-1-10-20211104Document57 pages1422-Article Text-3684-1-10-20211104f.kpobi1473No ratings yet
- Daftar PustakaDocument1 pageDaftar PustakaUlul Azmi Rumalutur NeinaNo ratings yet
- N Mon Visualizer OverviewDocument27 pagesN Mon Visualizer OverviewClaudioQuinterosCarreñoNo ratings yet
- How To Do Nothing - Jenny Odell - MediumDocument67 pagesHow To Do Nothing - Jenny Odell - MediumWilmer Rodriguez100% (4)
- Selling AIESEC To Your TargetsDocument7 pagesSelling AIESEC To Your TargetspijoowiseNo ratings yet
- Theoretical & Conceptual Framework (RESEARCH)Document3 pagesTheoretical & Conceptual Framework (RESEARCH)Rizza Manabat PacheoNo ratings yet
- Buzan, Barry - Security, The State, The 'New World Order' & BeyondDocument15 pagesBuzan, Barry - Security, The State, The 'New World Order' & Beyondyossara26100% (3)
- Chinese MedicineDocument16 pagesChinese MedicineTrisNo ratings yet
- Service Instruction Selection of Suitable Operating Fluids For ROTAX Engine Type 916 I (Series), 915 I (Series), 912 I (Series), 912 and 914 (Series)Document15 pagesService Instruction Selection of Suitable Operating Fluids For ROTAX Engine Type 916 I (Series), 915 I (Series), 912 I (Series), 912 and 914 (Series)Martin PilatiNo ratings yet
- 5 Waves AnswersDocument2 pages5 Waves AnswersNoor Ulain NabeelaNo ratings yet
- ErtlDocument64 pagesErtlManpreet SinghNo ratings yet
- Register A Custom Table in Apps SchemaDocument5 pagesRegister A Custom Table in Apps SchemaIapps ErpSolutionsNo ratings yet
- Impact of Technology On Our LivesDocument3 pagesImpact of Technology On Our LivesKim ErandioNo ratings yet
- Far Eastern University Mba - Thesis 060517Document2 pagesFar Eastern University Mba - Thesis 060517Lex AcadsNo ratings yet
- IELTS Materials ReadingDocument9 pagesIELTS Materials ReadingßläcklìsètèdTȜè0% (1)
- Chem 152 Lab ReportDocument21 pagesChem 152 Lab Reportapi-643022375No ratings yet
- Mind'S Nest Review Center Inc.,: Criteria of A Good Research Problem: Easibility Nterest EsearchabilityDocument21 pagesMind'S Nest Review Center Inc.,: Criteria of A Good Research Problem: Easibility Nterest EsearchabilitySherlyn Pedida100% (1)
- Baltrushes2006 PDFDocument46 pagesBaltrushes2006 PDFsilikondioksidaNo ratings yet
- Ringleman Chart FlareDocument12 pagesRingleman Chart FlareguhadebasisNo ratings yet