Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The A Algorithm: Héctor Muñoz-Avila
Uploaded by
AnkitOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The A Algorithm: Héctor Muñoz-Avila
Uploaded by
AnkitCopyright:
Available Formats
The A* Algorithm
Hctor Muoz-Avila
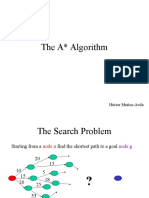
The Search Problem
Starting from a node n find the shortest path to a goal node g
10
15
20
?
20
15
5
18
25
33
Consider the following weighted undirected graph:
5
2
7
10
18
22
66
20
Shortest Path
10
20
16
4
6
8
24
20
6
9
We want: A path 5 v1 v2 20
Such that g(20) = cost(5v1) + cost(v1 v2) + + cost ( 20)
is minimum
Djikstra Algorithm
Greedy algorithm: from the candidate nodes select the one
that has a path with minimum cost from the starting node
10
15
20
?
20
15
5
18
25
33
Djikstra Algorithm
T
Given a Graph G = (V,E) and T a subset of V, the fringe of T, is
defined as:
Fringe(T) = { (w,x) in E : w T and x V T}
Djikstras algorithm
pick the edge v in
Fringe(T) that has
minimum distance to
the starting node
g(v) is minimum
Example
5
2
7
10
18
22
66
20
10
20
16
4
6
8
24
20
6
9
Properties
Dijkstras is a greedy algorithm
Why Dijkstras Algorithm works?
T
V T
The path from u to every node in T is the minimum path
w
u
r
s
v
6
20
20
x
7
15
Example
What does Djikstras algorithm will do? (minimizing g(n))
Problem: Visit too many nodes, some clearly out of the question
Complexity
Actual complexity is O(|E|log
2
|E|)
Is this good?
Actually it is bad for very large graphs!
Branching
factor: b
.
.
# nodes = b
(# levels)
Another Example: think of the search space in chess
Better Solution: Make a hunch!
Use heuristics to guide the search
Heuristic: estimation or hunch of how to search for a
solution
We define a heuristic function:
h(n) = estimate of the cost of the cheapest path from
the starting node to the goal node
Lets Try A Heuristic
Heuristic: minimize h(n) = Euclidean distance to destination
Problem: not optimal (through Rimmici Viicea and Pitesti is shorter)
The A* Search
Difficulty: we want to still be able to generate the path
with minimum cost
A* is an algorithm that:
Uses heuristic to guide search
While ensuring that it will compute a path with
minimum cost
A* computes the function f(n) = g(n) + h(n)
actual cost
estimated cost
A*
f(n) = g(n) + h(n)
g(n) = cost from the starting node to reach n
h(n) = estimate of the cost of the cheapest path from n
to the goal node
10
15
20
20
15
5
18
25
33
n
g(n)
h(n)
Example
A*: minimize f(n) = g(n) + h(n)
Properties of A*
A* generates an optimal solution if h(n) is an admissible
heuristic and the search space is a tree:
h(n) is admissible if it never overestimates the cost to
reach the destination node
A* generates an optimal solution if h(n) is a consistent
heuristic and the search space is a graph:
h(n) is consistent if for every node n and for every
successor node n of n:
h(n) c(n,n) + h(n)
n
n
d
h(n)
c(n,n)
h(n)
If h(n) is consistent then h(n) is admissible
Frequently when h(n) is admissible, it is also consistent
Admissible Heuristics
A heuristic is admissible if it is too optimistic, estimating
the cost to be smaller than it actually is.
Example:
In the road map domain,
h(n) = Euclidean distance to destination
is admissible as normally cities are not connected by
roads that make straight lines
How to Create Admissible Heuristics
Relax the conditions of the problem
This will result in admissible heuristics!
Lets look at an 8-puzzle game:
http://www.permadi.com/java/puzzle8/
Possible heuristics?
Example: Admissible Heuristics in 8-
Puzzle Game
Heuristic: a tile A can be moved to any tile B
H1(n) = number of misplaced tiles in board n
Heuristic: a tile A can be moved to a tile B if B is adjacent to A
H2(n) = sum of distances of misplaced tiles to goal positions
in board n
Some experimental results reported in Russell & Norvig (2002):
A* with h2 performs up to 10 times better than A* with h1
A* with h2 performs up to 36,000 times better than a classical
uninformed search algorithm (iterative deepening)
Using A* in Planning
A
C
B
A B C
A C
B
C
B
A
B
A
C
B
A
C
B C
A
C
A
B
A
C
B
B
C
A
A B
C
A
B
C
A
B
C
h(n) = # of goals remaining to be satisfied g(n) = # of steps so far
A* in Games
Path finding (duh!)
We will have several presentations on the topic
We will see that sometimes even A* speed
improvements are not sufficient
Additional improvements are required
A* can be used for planning moves computer-controlled
player (e.g., chess)
F.E.A.R. uses A* to plan its search
You might also like
- The A Algorithm: Héctor Muñoz-AvilaDocument20 pagesThe A Algorithm: Héctor Muñoz-AvilaBinoy NambiarNo ratings yet
- A StarDocument20 pagesA StartoncuvasileNo ratings yet
- AstarDocument20 pagesAstarPetter PNo ratings yet
- AstarDocument20 pagesAstarPetter PNo ratings yet
- Lec5 6Document35 pagesLec5 6MazharulislamNo ratings yet
- Informed SearchDocument36 pagesInformed SearchDUDEKULA VIDYASAGARNo ratings yet
- Outline: Informed Search and Exploration For AgentsDocument7 pagesOutline: Informed Search and Exploration For AgentsEhsan GhasisinNo ratings yet
- Lecture 10 11Document38 pagesLecture 10 11ALi SaLman RahatNo ratings yet
- Ut - 1 - T - 4 A Star SearchDocument44 pagesUt - 1 - T - 4 A Star SearchDhivya Bharathi pNo ratings yet
- Informed Search AlgorithmsDocument39 pagesInformed Search AlgorithmsmmminishaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 08 Informed Search Strategies-IDocument45 pagesLecture 08 Informed Search Strategies-IHassan RazaNo ratings yet
- Informed Search AlgorithmsDocument39 pagesInformed Search Algorithmsviraj guptaNo ratings yet
- AI File - 5 PDFDocument46 pagesAI File - 5 PDFNahim's kitchenNo ratings yet
- L04 Search (MoreSearchStrategies)Document23 pagesL04 Search (MoreSearchStrategies)KofiNo ratings yet
- Search AlgorithmsDocument44 pagesSearch AlgorithmsHassan VilniusNo ratings yet
- A.I.: Informed Search Algorithms: Chapter III: Part DeuxDocument35 pagesA.I.: Informed Search Algorithms: Chapter III: Part DeuxAriel AsunsionNo ratings yet
- AI Unit-2Document75 pagesAI Unit-2Zaidali 050No ratings yet
- In From Ed SearchDocument24 pagesIn From Ed Searchapi-3854551No ratings yet
- Informed Search Algorithms: UNIT-2Document35 pagesInformed Search Algorithms: UNIT-2Tariq IqbalNo ratings yet
- Informed Search ProblemsDocument38 pagesInformed Search ProblemsTayyab NaveedNo ratings yet
- Informed Search Algorithms: Team Teaching AI (Created by Dewi Liliana) PTIIK 2012Document41 pagesInformed Search Algorithms: Team Teaching AI (Created by Dewi Liliana) PTIIK 2012Shatria KaniputraNo ratings yet
- Lecture-3.1 Heuristic SearchDocument131 pagesLecture-3.1 Heuristic SearchmusaNo ratings yet
- AI-03 Informed SearchDocument26 pagesAI-03 Informed SearchDebashish DekaNo ratings yet
- Optimal Searching: - AdvantagesDocument37 pagesOptimal Searching: - AdvantagesTamal Dey3335No ratings yet
- M04-Heuristics Informed SearchDocument41 pagesM04-Heuristics Informed SearchchakravarthyashokNo ratings yet
- AI Final PDFDocument9 pagesAI Final PDFJessi KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Lec 07Document37 pagesLec 07Sourabh ShahNo ratings yet
- Rec2 SolDocument6 pagesRec2 Solm22ai569No ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document75 pagesChapter 4Mohammad Omar FaruqNo ratings yet
- L8 HeuristicsDocument11 pagesL8 Heuristicsshini s gNo ratings yet
- SP14 CS188 Lecture 3 - Informed SearchDocument69 pagesSP14 CS188 Lecture 3 - Informed Searchimoptra143No ratings yet
- Informed Search (CMU)Document30 pagesInformed Search (CMU)WENXIN LIANGNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence: Informed SearchDocument21 pagesArtificial Intelligence: Informed SearchDede Ari HidayatullohNo ratings yet
- Informed SearchDocument37 pagesInformed SearchtauraiNo ratings yet
- A General Introduction To Artificial IntelligenceDocument55 pagesA General Introduction To Artificial IntelligenceÁnh PhạmNo ratings yet
- Scsa1702 - Ai - Unit IiDocument42 pagesScsa1702 - Ai - Unit IiLolakapuri Ananth VardhanNo ratings yet
- 4 Best First Search A StarDocument24 pages4 Best First Search A Stardivyalakshmi81889897No ratings yet
- Heuristic-Search PDF PracticeDocument4 pagesHeuristic-Search PDF PracticePankaj ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Module 3Document26 pagesModule 3Yashwanth NNo ratings yet
- CPSC 352 - Artificial Intelligence Notes: A Algorithm Admissibility, Monotonicity, InformednessDocument4 pagesCPSC 352 - Artificial Intelligence Notes: A Algorithm Admissibility, Monotonicity, InformednessshuvasalvaNo ratings yet
- Informed Search and Exploration: Berlin ChenDocument77 pagesInformed Search and Exploration: Berlin Chenlogic_laoshirNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence: Informed SearchDocument25 pagesArtificial Intelligence: Informed SearchPrasidha PrabhuNo ratings yet
- A Search Algorithm: Krishna Kumar (IT2018/122) Kishan Raj (IT2018/025) Aavriti Dutta (IT2018/101)Document14 pagesA Search Algorithm: Krishna Kumar (IT2018/122) Kishan Raj (IT2018/025) Aavriti Dutta (IT2018/101)Jessi KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Solving Problems by Searching Solving Problems by Searching: 14 Jan 2004 CS 3243 - Blind Search 1Document25 pagesSolving Problems by Searching Solving Problems by Searching: 14 Jan 2004 CS 3243 - Blind Search 1Gomathi ShanmugamNo ratings yet
- 03 InformedHeuristicSearchDocument80 pages03 InformedHeuristicSearchHaroonRashidNo ratings yet
- AI&ML Module 2Document114 pagesAI&ML Module 2Its MeNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence: Informed Search and ExplorationDocument52 pagesArtificial Intelligence: Informed Search and ExplorationVarun YadavNo ratings yet
- Solving Problems by Searching: 14 Jan 2004 CS 3243 - Blind Search 1Document25 pagesSolving Problems by Searching: 14 Jan 2004 CS 3243 - Blind Search 1Gomathi ShanmugamNo ratings yet
- Heuristic Algorithm LectureDocument13 pagesHeuristic Algorithm LectureAwais AliNo ratings yet
- Set 3: Informed Heuristic Search: ICS 271 Fall 2014 Kalev KaskDocument78 pagesSet 3: Informed Heuristic Search: ICS 271 Fall 2014 Kalev KaskmadhavNo ratings yet
- Informed Search: CS 4804 Fall 2020Document27 pagesInformed Search: CS 4804 Fall 2020TryerNo ratings yet
- Informed Search NewDocument71 pagesInformed Search NewAshish_Chawla_518No ratings yet
- Heuristic SearchDocument46 pagesHeuristic SearchbangarrajuNo ratings yet
- Heuristic SearchDocument7 pagesHeuristic SearchKadali Lakshmi NirmalaNo ratings yet
- CSM6120 Introduction To Intelligent Systems: Informed SearchDocument58 pagesCSM6120 Introduction To Intelligent Systems: Informed SearchreemNo ratings yet
- Informed HeuristicSearchDocument39 pagesInformed HeuristicSearchRaghu SomuNo ratings yet
- PATH FINDING - Dijkstra's and A Algorithm'sDocument15 pagesPATH FINDING - Dijkstra's and A Algorithm'sMarisol Triple SNo ratings yet
- Heuristic Searching: A Search: Nazmul HasanDocument5 pagesHeuristic Searching: A Search: Nazmul HasanInternational Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)No ratings yet
- Programme Name: BCS (HONS) Course Code: CSC 3200 Course Name: Artificial IntelligenceDocument4 pagesProgramme Name: BCS (HONS) Course Code: CSC 3200 Course Name: Artificial IntelligenceAnil khatriNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Programming Longest Common SubsequenceDocument3 pagesDynamic Programming Longest Common SubsequenceAnkitNo ratings yet
- LshortDocument171 pagesLshortCXBBANo ratings yet
- Lab Manual CS4500 Artificial Intelligence Lab Fall Session 2013, 1434 With Lab SessionDocument23 pagesLab Manual CS4500 Artificial Intelligence Lab Fall Session 2013, 1434 With Lab SessionAnkit100% (1)
- Lisp Tutorial: CS157 April 9, 2004Document27 pagesLisp Tutorial: CS157 April 9, 2004Nizam DeenNo ratings yet
- Lab Assignment of Computer Networks: Submitted By: Ankit Enroll: 167/11 Roll No.: 48 Branch: CSE Semester: 6Document7 pagesLab Assignment of Computer Networks: Submitted By: Ankit Enroll: 167/11 Roll No.: 48 Branch: CSE Semester: 6AnkitNo ratings yet
- VHDL Simulation Tutorials (INFN Torino Wiki)Document15 pagesVHDL Simulation Tutorials (INFN Torino Wiki)AnkitNo ratings yet
- JS1K Demo - The Making of - AckoDocument12 pagesJS1K Demo - The Making of - AckoAnkitNo ratings yet
- Naruto Shippuden UNS Generations Ninja Tools UnlockDocument4 pagesNaruto Shippuden UNS Generations Ninja Tools UnlockAnkitNo ratings yet
- Control Systems TheoryDocument331 pagesControl Systems Theorycorsairsan100% (1)
- Naruto Shippuden UNS Generations Ninja Tools UnlockDocument4 pagesNaruto Shippuden UNS Generations Ninja Tools UnlockAnkitNo ratings yet
- Data Structures WikibooksDocument120 pagesData Structures WikibooksAnkitNo ratings yet
- 1 Hw6 SolutionsDocument8 pages1 Hw6 SolutionsdavejaiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4b Urban Transportation Planning (Part 2) PDFDocument93 pagesLecture 4b Urban Transportation Planning (Part 2) PDFBhanuKhannaNo ratings yet
- R22-M.tech Curriculum and SyllabusDocument85 pagesR22-M.tech Curriculum and SyllabusVivekanandhan VijayanNo ratings yet
- Subtask2: A Maze Simulation: 1 Problem StatementDocument3 pagesSubtask2: A Maze Simulation: 1 Problem StatementAkash SuryawanshiNo ratings yet
- Ai Unit-1Document41 pagesAi Unit-1Sreeprada VNo ratings yet
- E. O. Frimpong Tee PDFDocument73 pagesE. O. Frimpong Tee PDFAna JanakievskaNo ratings yet
- Graphs: CS 302 - Data Structures Section 9.3Document78 pagesGraphs: CS 302 - Data Structures Section 9.3Jazib AlikhanNo ratings yet
- Design Analysis and Algorithms: (Unit I Question Bank)Document7 pagesDesign Analysis and Algorithms: (Unit I Question Bank)abcjohnNo ratings yet
- 5 GraphsDocument6 pages5 GraphsNguyen Tien Dat (K18 HL)No ratings yet
- Routing of Branched Water Distribution Networks Us PDFDocument6 pagesRouting of Branched Water Distribution Networks Us PDFAna JanakievskaNo ratings yet
- Link State RoutingDocument11 pagesLink State RoutingPav TechnicalsNo ratings yet
- Artificial IntelligenceDocument7 pagesArtificial IntelligenceManjil KarmacharyaNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 1Document13 pagesProblem Set 1redNo ratings yet
- Alg Part ADocument22 pagesAlg Part AHamid ArashNo ratings yet
- Rump Jalan TambangDocument9 pagesRump Jalan TambangAndre AlistinNo ratings yet
- MIT6 006F11 Quiz2 Sol PDFDocument15 pagesMIT6 006F11 Quiz2 Sol PDFAnjali GhoshNo ratings yet
- Programming Homework HelpDocument9 pagesProgramming Homework HelpProgramming Homework HelpNo ratings yet
- DAA Interview Questions and AnswersDocument9 pagesDAA Interview Questions and AnswersPranjal KumarNo ratings yet
- Solid Waste CollectionDocument70 pagesSolid Waste CollectionssasaduNo ratings yet
- Ai03 Classical Search Part1 Posthandouts PDFDocument63 pagesAi03 Classical Search Part1 Posthandouts PDFEnisa MEHMEDINo ratings yet
- Shortest-Route AlgorithmsDocument18 pagesShortest-Route Algorithmsأوكيتش شمشونNo ratings yet
- Art of Programming Contest Part13Document7 pagesArt of Programming Contest Part13karndeNo ratings yet
- Algorithms and Data Structures: Study Manual v2021.2Document8 pagesAlgorithms and Data Structures: Study Manual v2021.2Serkan SezinNo ratings yet
- STL2Document13 pagesSTL2Romee PanchalNo ratings yet
- 11199A048 - DAA Lab ExercisesDocument19 pages11199A048 - DAA Lab ExercisesAyapilla Sri hari PranavNo ratings yet
- Dijkstra Algorithm: Unit 03.03.02 CS 5220: Computer CommunicationsDocument12 pagesDijkstra Algorithm: Unit 03.03.02 CS 5220: Computer Communicationsarafath uzzamanNo ratings yet
- BSC C.S (H) 6th Semester SyllabusDocument6 pagesBSC C.S (H) 6th Semester Syllabusnyksolution rimitNo ratings yet
- Solving Problems by Searching: Chapter 3 - Unit 2Document70 pagesSolving Problems by Searching: Chapter 3 - Unit 28mk5n2q8ptNo ratings yet
- L01-02 - 8.11.2022 - Introduction To Algorithms and Roadmap of This CourseDocument48 pagesL01-02 - 8.11.2022 - Introduction To Algorithms and Roadmap of This CourseSamia RahmanNo ratings yet
- M.E. Cse.Document62 pagesM.E. Cse.janu130% (1)