Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Presentation On Human Resourcemanagement Practices in India
Uploaded by
Kumar Amit0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
39 views10 pagesE-recruitment: Newspaper advertisements will specify age and gender requirements. Training (future orientation): Education is extremely valued, and training is an extension of it. In-house training centers are a common feature in india.
Original Description:
Original Title
Amit Kumar
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentE-recruitment: Newspaper advertisements will specify age and gender requirements. Training (future orientation): Education is extremely valued, and training is an extension of it. In-house training centers are a common feature in india.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
39 views10 pagesPresentation On Human Resourcemanagement Practices in India
Uploaded by
Kumar AmitE-recruitment: Newspaper advertisements will specify age and gender requirements. Training (future orientation): Education is extremely valued, and training is an extension of it. In-house training centers are a common feature in india.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 10
PRESENTATION ON
HUMAN RESOURCEMANAGEMENT PRACTICES
IN INDIA
Prepared By:
Amit Kumar
MBA 2
nd
sem
Staffing Practices
Resumes seek strong educational background.
Employee referrals (predominantly used for middle and
senior management).
Succession planning (predominantly used for middle and
senior management).
Elaborate employment tests related to the job, especially at
entry level.
E-recruitment: Naukri.com was the first e-portal
established in 1998 (naukri means job in Hindi ).
2
Staffing Practices
Newspaper advertisements are used to brand the company
to potential applicants.
Newspaper advertisements will specify age and gender
requirements.
Personal questions will be asked in interviews/resumes
about:
Age
Marital status
Family plans (women planning to start a family)
Family background
Caste background
Photos to be included
Verification of educational certificates
3
Training Practices
Training (future orientation):
Education is extremely valued, and training is an
extension of it.
Entry point training programs (3 to12 months of
orientation).
Ongoing training programs.
Development programs (promotions involve training).
In-house training centers are a common feature in
Indian organizations.
Deductive learning style in training: Known as top-
down approach where learning principles start with
general concepts and move toward specific
application.
4
Performance Appraisal
Cultural dimensions of collectivism and power distance
make objective appraisals a challenge.
Supervisors and subordinates develop close relationships.
Organizational loyalty is as important as work performance.
Employee promotions are frequently based on seniority.
Annual performance appraisals.
Supervisors provide performance ratings that are
frequently inflated due to personal relationships.
Employment at will does not exist in India. Employment
termination carries a social stigma.
Compensation and Benefits
In addition to a base salary, compensation includes:
House rent allowance (HRA*).
Medical allowance.
Dearness allowance (DA*).
Leave travel allowance (LTA*).
Commuter allowance.
* These allowances are frequently referred by their acronyms
Several categories of leave (vacation) exist:
Sick leave: 7 days (medical certificate required).
Casual leave: 7 days (for personal and family emergencies,
requires prior permission of boss). Employees can take
maximum 2 days at a time
Annual leave: 3 weeks (after one year of employment).
Federal holidays: About 20 days.
Compensation and Benefits
Retirement age:
55-60 years (private sector);.
60 years (public sector).
Retirement Benefits: Employees receive two lump-sum payments
when they retire:
Provident Fund (similar to 401(k))
Typical contributions: 10-12 percent of base salary
(employer and employee).
Payable on retirement, voluntary separation, death.
Gratuity
Only employer contributes (15 days salary per year of
service).
Tax-exempt for employees.
Payable on retirement, voluntary separation, death.
Compensation and Benefits
Organizations are seen as an extension of the family.
Provide both short-term and long-term personal loans.
Personal loans for housing, car, home maintenance and family
emergencies.
Loan amounts vary by position and level in organization.
All employees after their probation (confirmation) period are
eligible.
Many medium and large organizations have cafeterias with
subsidized lunch facilities.
Compensation and Benefits
Executives receive special benefits to reflect status such as:
Club memberships.
Overseas training.
Company housing.
Company cars.
Provided with drivers.
International cars.
Operational and maintenance costs.
Phone bill reimbursements.
Organizations provide business and cell phones.
THANK YOU
You might also like
- Comparison of HRD PracticesDocument45 pagesComparison of HRD PracticesruhanadarlingNo ratings yet
- Important! PDFDocument9 pagesImportant! PDFSanja GorgievaNo ratings yet
- Mba Assignment (Mb0043) - Arun MishraDocument17 pagesMba Assignment (Mb0043) - Arun MishraPushpanjali MishraNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument10 pagesCase StudyAayush khatriNo ratings yet
- Final Assigment Essentials of HRM Dec 22Document7 pagesFinal Assigment Essentials of HRM Dec 22Le JagNo ratings yet
- Hrmcecppdsem 2 200818131847Document24 pagesHrmcecppdsem 2 200818131847Praveen JangidNo ratings yet
- Jyothi Madam PCX - ReportDocument40 pagesJyothi Madam PCX - ReportbagyaNo ratings yet
- Yogyata Singh BBA 4TH A (ROLL NO.61)Document24 pagesYogyata Singh BBA 4TH A (ROLL NO.61)Kunal SinghNo ratings yet
- BST P-3Document7 pagesBST P-3iresh kumarNo ratings yet
- NTCCDocument19 pagesNTCCPreeti AnandNo ratings yet
- Hindustan Unilever Project ReportDocument9 pagesHindustan Unilever Project ReportAbhishek Singh Raghuvanshi100% (1)
- Itc Net ContentDocument10 pagesItc Net ContentSarika JhaNo ratings yet
- Hindustan Unilever Project ReportDocument13 pagesHindustan Unilever Project ReportRani JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Objectives and Importance of Human Resource ManagementDocument5 pagesObjectives and Importance of Human Resource Managementnani66215487No ratings yet
- Assignment - 01/02Document11 pagesAssignment - 01/02Mercy DsouzaNo ratings yet
- HRM MergedDocument134 pagesHRM MergedShaikh Ahsan AliNo ratings yet
- Essentials of HRM Answer - 1: Today, Human Resources Management Deals WithDocument8 pagesEssentials of HRM Answer - 1: Today, Human Resources Management Deals Withhemangi patelNo ratings yet
- Compensation Management 1Document27 pagesCompensation Management 1Rekha NehaNo ratings yet
- ProjectDocument8 pagesProjectaarshiawadhwa15No ratings yet
- M-1 Intoduction To HRMDocument50 pagesM-1 Intoduction To HRMritwikNo ratings yet
- What Is HR Practice?: We Can Divide Scope of Human Resource Practice in Three Part. 1 Personal AspectDocument3 pagesWhat Is HR Practice?: We Can Divide Scope of Human Resource Practice in Three Part. 1 Personal AspectDeep AdesaraNo ratings yet
- HRMDocument54 pagesHRMAhsan ImtiazNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Management ASSIGNMENT 1 AND 2 ANSWER SHEETDocument12 pagesHuman Resource Management ASSIGNMENT 1 AND 2 ANSWER SHEETarifNo ratings yet
- Report On Compensation and BenefitsDocument64 pagesReport On Compensation and BenefitsShilpa VaralwarNo ratings yet
- What Are The Five Tools That A Company Can Use To Keep GoodDocument4 pagesWhat Are The Five Tools That A Company Can Use To Keep GoodKingFaithNo ratings yet
- 8.reporter em 206Document35 pages8.reporter em 206Niel Vincent CatapangNo ratings yet
- Compensation Management at Care HospitalDocument65 pagesCompensation Management at Care Hospitalammukhan khanNo ratings yet
- Jesika HRM and MarketingDocument42 pagesJesika HRM and MarketingAnonymous BWMGGSNo ratings yet
- Review of LiteratureDocument9 pagesReview of LiteratureVISHNU PRIYA P 1927754No ratings yet
- Recruitment and Selection in IT CompanyDocument9 pagesRecruitment and Selection in IT Companyajay2726No ratings yet
- What Are Examples of How Staffing Activities Are Influenced by Training Activities? Compensation Activities?Document7 pagesWhat Are Examples of How Staffing Activities Are Influenced by Training Activities? Compensation Activities?Clinton RegerstNo ratings yet
- " A Comparative Study of Recruitment & Selection, Training and Development Policies in Indian Mncs and Foreign M..Document16 pages" A Comparative Study of Recruitment & Selection, Training and Development Policies in Indian Mncs and Foreign M..AKANKSHA PREETINo ratings yet
- Module 1,2,3Document56 pagesModule 1,2,3PawanNo ratings yet
- Accenture Reward Management SystemDocument20 pagesAccenture Reward Management SystemParthsarthi Sinha60% (5)
- Sneha KaleDocument18 pagesSneha KaleSneha kaleNo ratings yet
- SPB HRDocument11 pagesSPB HRKuamresan KrishnanNo ratings yet
- HR PPT FinalDocument21 pagesHR PPT Finalpayal_pNo ratings yet
- A Project Report On A Comparative Study On Awareness and Utilization of Employee Benefits Strategic Compensation ManagementDocument30 pagesA Project Report On A Comparative Study On Awareness and Utilization of Employee Benefits Strategic Compensation ManagementshilpaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 IntrtroductionDocument27 pagesChapter 1 IntrtroductionChethan B HNo ratings yet
- Compensation and Benefits AdministrationDocument15 pagesCompensation and Benefits Administrationcluadine dinerosNo ratings yet
- Recruitment and Selection Project ReportDocument45 pagesRecruitment and Selection Project Reportnemchand100% (1)
- Article On CompensationDocument9 pagesArticle On CompensationAhmadNo ratings yet
- Definitions New PrintDocument6 pagesDefinitions New PrintTauqeer IqbalNo ratings yet
- Human Capita MGMTDocument9 pagesHuman Capita MGMTRituparna HotaNo ratings yet
- Assignment of HRMDocument11 pagesAssignment of HRMShadab RashidNo ratings yet
- Compensation Management: Dr. Anuraag Awasthi 9810068709Document35 pagesCompensation Management: Dr. Anuraag Awasthi 9810068709Parihar BabitaNo ratings yet
- Unilever HRMDocument8 pagesUnilever HRMAdeel OmarNo ratings yet
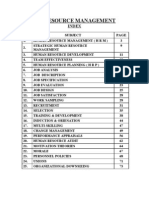
- Human Resource Management: IndexDocument72 pagesHuman Resource Management: IndexSahil KapoorNo ratings yet
- Name Roll No Learning Centre Subject Assignment No Date of Submission at The Learning CentreDocument12 pagesName Roll No Learning Centre Subject Assignment No Date of Submission at The Learning CentreVikash AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Project On Employee BenefitsDocument16 pagesProject On Employee BenefitsDarsana Borkakoty0% (1)
- Group Work Project On Human Resource Management Practices in The Organizations of BangladeshDocument21 pagesGroup Work Project On Human Resource Management Practices in The Organizations of BangladeshsiamNo ratings yet
- Aditya Birla GroupDocument22 pagesAditya Birla GroupAkshita ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Compensation ManagementDocument67 pagesCompensation Managementsodesai100% (1)
- Career PlanningDocument30 pagesCareer PlanningAdil MustafaNo ratings yet
- Question BankDocument7 pagesQuestion Banksuchitasingh1106No ratings yet
- Talent ManagementDocument24 pagesTalent ManagementAbhishek jhaNo ratings yet
- Model Answer: Literature review on Employee motivation, rewards and performanceFrom EverandModel Answer: Literature review on Employee motivation, rewards and performanceNo ratings yet
- Our Terms and ConditionsDocument1 pageOur Terms and ConditionsKumar AmitNo ratings yet
- Mba - Job Dddetails With RequirementDocument1 pageMba - Job Dddetails With RequirementKumar AmitNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Office Word DocumentDocument1 pageNew Microsoft Office Word DocumentKumar AmitNo ratings yet
- "Evaluting Consumer Satisfaction From Hero Motorcycle": A Project Report ONDocument59 pages"Evaluting Consumer Satisfaction From Hero Motorcycle": A Project Report ONKumar Amit100% (1)
- "Evaluting Consumer Satisfaction From Hero Motorcycle": A Project Report ONDocument59 pages"Evaluting Consumer Satisfaction From Hero Motorcycle": A Project Report ONKumar Amit100% (1)
- FDSXDocument4 pagesFDSXKumar AmitNo ratings yet
- Samsung C3322IDocument3 pagesSamsung C3322IKumar AmitNo ratings yet
- Blue Collar WorkforceDocument2 pagesBlue Collar WorkforceAdemuwagun EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- Entrep Module 9 - Managing The Human Resource P2Document4 pagesEntrep Module 9 - Managing The Human Resource P2JOHN PAUL LAGAONo ratings yet
- Swamy's Books: S.No Name of The Book Rate TotalDocument1 pageSwamy's Books: S.No Name of The Book Rate Totalनरोत्तमवत्सNo ratings yet
- ContractTypes PDFDocument2 pagesContractTypes PDFHaider ShahNo ratings yet
- Impact of Covid-19 On Employment Opportunities For Fresh Graduates in Hospitality &tourism IndustryDocument8 pagesImpact of Covid-19 On Employment Opportunities For Fresh Graduates in Hospitality &tourism IndustryInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- Questionnaire 2Document5 pagesQuestionnaire 2jeanlauraqueen100% (1)
- Poverty Reduction Strategy Paper On SindhDocument104 pagesPoverty Reduction Strategy Paper On SindhInnovative Development Strategies (Pvt.) LtdNo ratings yet
- Week 13 Chapter 12: Training For HospitalityDocument11 pagesWeek 13 Chapter 12: Training For HospitalityechxNo ratings yet
- Organizational Behaviour II: Assignment-Ii Section - C Group-5Document6 pagesOrganizational Behaviour II: Assignment-Ii Section - C Group-5Arnab BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- 6 Steps To Creating A Talent Pool Based Successsion Planning Process PDFDocument1 page6 Steps To Creating A Talent Pool Based Successsion Planning Process PDFmanik_elaNo ratings yet
- Internship Report On Human Resource Management Practices On Prime Bank LimitedDocument49 pagesInternship Report On Human Resource Management Practices On Prime Bank LimitedÃñûshkâ SûmãñNo ratings yet
- Final Research MR KadangoDocument30 pagesFinal Research MR KadangoJAPHET NKUNIKANo ratings yet
- Item 22 and 23-Annual Medical Report and Program For Drugfree WorkplaceDocument35 pagesItem 22 and 23-Annual Medical Report and Program For Drugfree WorkplaceJoyce JimenezNo ratings yet
- Termination CasesDocument47 pagesTermination CasesSheilah Mae PadallaNo ratings yet
- Payslip - 2021 03 29Document1 pagePayslip - 2021 03 29Loan LoanNo ratings yet
- 3 National Federation of Labor Vs CADocument11 pages3 National Federation of Labor Vs CAAnonymous kCX0FoNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Associate Diploma People Management Feb2021 - tcm18 88827Document88 pagesSyllabus Associate Diploma People Management Feb2021 - tcm18 88827mayabi matete89No ratings yet
- The Impact of Job Stress On Employee Job SatisfactionDocument7 pagesThe Impact of Job Stress On Employee Job SatisfactionChristopher BurnsNo ratings yet
- Gender Stereotyping (A Human Resource Management Quandary)Document7 pagesGender Stereotyping (A Human Resource Management Quandary)MarriumNo ratings yet
- CFR 2013 Title29 Vol5 Part1910 Subpart FDocument41 pagesCFR 2013 Title29 Vol5 Part1910 Subpart Fgpax42No ratings yet
- Gdce JR Clerk ApplicationDocument1 pageGdce JR Clerk ApplicationJonesNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Human Resource ManagementDocument17 pagesIntroduction To Human Resource Managementolivia hoNo ratings yet
- EXISTING RECRUITMENT PROCESS OF ABC (PVT.) LTD PDFDocument14 pagesEXISTING RECRUITMENT PROCESS OF ABC (PVT.) LTD PDFHappy RNo ratings yet
- Geography of TourismDocument7 pagesGeography of TourismBima AjiNo ratings yet
- Impact of Job Stress On Job Satisfaction and Turnover Intention With Moderating Imact of OBSeDocument11 pagesImpact of Job Stress On Job Satisfaction and Turnover Intention With Moderating Imact of OBSeAnees Ur RehmanNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Union Budget by Ayussh SanghiDocument9 pagesAnalysis of Union Budget by Ayussh SanghiRavi Agrahari100% (2)
- Ocean 88 PresentationDocument26 pagesOcean 88 PresentationChristian PetinesNo ratings yet
- Managing Workplace Monitoring and SurveillanceDocument10 pagesManaging Workplace Monitoring and SurveillanceSpit FireNo ratings yet
- Coca-Cola Taleo RecruitmentDocument16 pagesCoca-Cola Taleo RecruitmentNitinMaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Integrity Trade Services, Inc. v. Integrity Employment Partners, LLCDocument48 pagesIntegrity Trade Services, Inc. v. Integrity Employment Partners, LLCJohn TaggartNo ratings yet