Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Coronary Artery Disease: Presented by
Uploaded by
anusarannyaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Coronary Artery Disease: Presented by
Uploaded by
anusarannyaCopyright:
Available Formats
PRESENTED BY:
MS.ANU SARANNYA
M.SC(N) II YEAR
APOLLO COLLEGE OF NURSING
1
Coronary Artery & their Branches
Coronary arteries arises form coronary
sinus at the base of the aorta
LCA
Left Anterior Descending (LAD)
Marginal Artery
Circumflex Artery
RCA
Marginal Artery
Posterior descending Branch
2
Coronary Arteries
3
CORONARY BLOOD FLOW
Coronary blood flow in Humans at rest is
about 225-250 ml/minute, about 5% of
cardiac output.
At rest, the heart extracts 60-70% of
oxygen from each unit of blood delivered
to heart [other tissue extract only 25% of
O
2
.
4
CORONARY BLOOD FLOW
Why heart is extracting 60-70% of O
2
?
Because heart muscle has more
mitochondria, up to 40% of cell is occupied
by mitochondria, which generate energy for
contraction by aerobic metabolism,
therefore, heart needs O
2
.
When more oxygen is needed e.g.
exercise, O
2
can be increased to heart only
by increasing blood flow.
5
Blood flow to Heart during
Systole & Diastole
During systole when heart muscle
contracts it compresses the
coronary arteries therefore blood
flow is less to the left ventricle
during systole and more during
diastole.
To the subendocardial portion of
Left ventricle it occurs only during
diastole
6
Phasic changes in coronary bld flow
Effect of cardiac muscle contraction
7
Coronary blood flow to the right side is
not much affected during systole.
Reason---Pressure difference
between aorta and right ventricle is
greater during systole than during
diastole, therefore more blood flow to
right ventricle occurs during systole.
8
CORONARY
BLOOD
FLOW
DURING
SYSTOLE
AND
DIASTOLE
9
Factors Affecting Blood Flow to
CORONARY ARTERIES
-Pressure in aorta
-Chemical factors
-Neural factors
NOTECoronary blood flow
shows considerable Autoregulation.
10
Chemical factors affecting
Coronary blood flow
Chemical factors causing
Coronary vasodilatation
(Increased coronary blood flow)
NOTE Adenosine, which is formed
from ATP during cardiac metabolic
activity, causes coronary
vasodilatation.
11
Neural factors affecting Coronary Blood
Flow
1. -Effect of Sympathetic stimulation
2. -Effect of Parasympathetic stimulation
Sympathetic stimulation
Coronary arteries have
Alpha Adrenergic receptors which mediate
vasoconstriction
Beta Adrenergic receptors which mediate
vasodilatation
12
Effect of Parasympathetic stimulation
-Vagus nerve stimulation (Parasympathetic)
causes coronary vasodilatation
13
CARDIAC MUSCLE METABOLISM
Heart uses primarily free fatty acids and
to lesser extent glucose and lactate for
metabolism.
in ischemic / anaerobic conditions
Derives energy from
Anaerobic glycolysis
Forms lactic acid (one of cause of
cardiac pain )
14
CORONARY ARTERY HEART
DISEASE
ISCHEMIC HEART DISEASE (IHD) (ANGINA
PECTORIS)
MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION
ANGINA PECTORIS:
THERE IS REDUCED CORONARY ARTERY
BLOOD FLOW DUE TO ATHEROSCLEROSIS
(CHOLESTROL DEPOSITION
SUBENDOCARDIALLY -- Plaque)
15
RISK FACTORES OF IHD:
CIGARETTE SMOKING
HYPERTENSION
DIABETES MELLITUS
INCREASED LIPIDS ( CHOLESTROL)
OTHER FACTORS: LACK OF
EXERCISE, ANXIETY etc.
16
IHD:
IHD IS USED TO DESCRIBE DISCOMFORT IN
THE CHEST DUE TO DECREASED CORONARY
BLOOD FLOW (TRANSIENT MYOCARDIAL
ISCHEMIA).
PATIENT COMPLAINS OF TIGHTNESS OR PAIN
IN THE MIDDLE OF CHEST (RETROSTERNAL)
FOR FEW MINUTES. PAIN OFTEN RADIATES
TO INNER SIDE OF LEFT ARM.
PAIN IS PRECIPETED BY EFFORT AND
RELIEVED BY REST.
17
MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION (MI):
IT IS DUE TO OBSTRUCTION TO THE
CORONARY BLOOD FLOW, ATLEAST 75 % OF
LUMEN OF CORONARY ARTERY IS BLOCKED
BY THROMBUS.
MI IS THE COMMON CAUSE OF DEATH.
18
Applied Aspect
THE C A D.
19
20
Electrocardiographic changes during
exercise test. Upper trace significant
horizontal ST segment depression during
exercise.
21
22
INVESTIGATIONS:
ECG
CARDIAC ENZYMES e.g. CK, LDH, TROPONIN
etc.
ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY
TREADMILL EXERCISE TEST
THALLIUM STRESS TEST
CORONARY ANGIOGRAPHY
NOTE:
ECG CHANGES IN IHD:
ST DEPRESSION OCCURS IN ECG IN RESPECTIVE LEADS
ECG CHANGES IN MI:
ST ELEVATION OCCURS IN ECG IN RESPECTIVE LEADS
23
TREATMENT:
CORONARY DILATORS E.g. NITRATES
BETA-BLOCKERS
ANGIOPLASTY (DILATE AREA OF
CONSTRICTION)
STENT
BYPASS SURGERY
24
25
Percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty (PTCA). (a)
Coronary angiography demonstrates a severe stenosis in the
proximal left anterior descending artery. (b) During PTCA a soft
guidewire is passed across the stenosis and then a balloon is
expanded that dilates the stenosis. (c) Post-PTC
26
An intracoronary stent.
27
CORONARY ARTERY
BYPASS SURGERY
28
NAME :Mrs.Indirani
AGE :71 years
DEMOGRAPHIC DATA
DIABETES MELLITUS- 15 years
HYPERTENSION - 2 years
CAD - 2 months
Has family history of diabetes mellitus
Diet history- non vegetarian( junk food
consumption, fat rich diet )
Life style- sedentary life style
HISTORY COLLECTION-HIGHLIGHTS
TRIPLE VESSEL DISEASE
GRAFT SITE
CORONARY ARTERY BYPASS
GRAFT
Thanks
34
You might also like
- Full EHR Implementation Roadmap 02082006Document13 pagesFull EHR Implementation Roadmap 02082006kexon100% (1)
- Case Reflection FormatDocument9 pagesCase Reflection Formatanusarannya100% (5)
- Microsurgery BookDocument335 pagesMicrosurgery BookProforVictor100% (2)
- 03-07 Lecture Coronary CirculationDocument29 pages03-07 Lecture Coronary Circulationaspalavista50% (2)
- Rajan Industrial Safety Assessment - Internship ReportDocument17 pagesRajan Industrial Safety Assessment - Internship ReportanusarannyaNo ratings yet
- Coronary Circulation FDocument36 pagesCoronary Circulation FjefferyNo ratings yet
- Coronary CirculationDocument47 pagesCoronary CirculationSuresh KumarNo ratings yet
- Coronary Circulation PhysiologyDocument25 pagesCoronary Circulation PhysiologyDerrick Ezra Ng100% (1)
- Day 7 Cardiac Perfussion Coronaria - KoronerDocument38 pagesDay 7 Cardiac Perfussion Coronaria - KoronerNiluh Putu NurindahNo ratings yet
- Patofisiologi Syok Hemoragik PDFDocument30 pagesPatofisiologi Syok Hemoragik PDFjsagayNo ratings yet
- Circulatory Response To ExerciseDocument31 pagesCirculatory Response To ExerciseFarhad GulNo ratings yet
- Cardiogenic Shock - SWDocument41 pagesCardiogenic Shock - SWAyu LuthfiyahNo ratings yet
- CirculationDocument18 pagesCirculationasimm9hamedNo ratings yet
- Heart Pump and Cardiac Cycle: Faisal I. Mohammed, MD, PHDDocument41 pagesHeart Pump and Cardiac Cycle: Faisal I. Mohammed, MD, PHDUsama SadiqNo ratings yet
- 8 Coronary CirculationDocument31 pages8 Coronary CirculationAhmed AliNo ratings yet
- The Cardiovascular System Parts of The Cardiovascular SystemDocument7 pagesThe Cardiovascular System Parts of The Cardiovascular SystemBrent AnosNo ratings yet
- 1.1 CV PhysiologyDocument34 pages1.1 CV PhysiologygilangbpNo ratings yet
- Syok HemoragicDocument22 pagesSyok HemoragicFebiFascinateD'meeanNo ratings yet
- Myocardial Protection and CardioplegiaDocument56 pagesMyocardial Protection and CardioplegiaArhanNo ratings yet
- AnaesDocument16 pagesAnaessindujasaravananNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Perfussion Coronaria - KoronerDocument55 pagesCardiac Perfussion Coronaria - KoronerMuhammad RamadhanNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System1Document50 pagesCardiovascular System1Justin Ahorro-DionisioNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System PhysiologyDocument109 pagesCardiovascular System PhysiologyKing kakaNo ratings yet
- Content 2partial FisioejDocument119 pagesContent 2partial Fisioejruth sanchezNo ratings yet
- Coronary Blood Flow Regulation and DeterminantsDocument4 pagesCoronary Blood Flow Regulation and Determinantsjordandenise2No ratings yet
- K 29 Sirkulasi Koroner - CVS K29Document16 pagesK 29 Sirkulasi Koroner - CVS K29Jane Andrea Christiano DjianzonieNo ratings yet
- 4. CHF and HTDocument120 pages4. CHF and HTcreativejoburgNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Assessment LectureDocument116 pagesCardiovascular Assessment LectureJohnryl FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of the Coronary CirculationDocument60 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of the Coronary CirculationNithya SekarNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 21 - Coronary CirculationDocument5 pagesCHAPTER 21 - Coronary Circulationg_komolafeNo ratings yet
- Management of ShockDocument18 pagesManagement of ShockObongsamuel IdiongNo ratings yet
- Coronary Circulation and Cardiac FailuresDocument67 pagesCoronary Circulation and Cardiac FailuresMonica CaballesNo ratings yet
- Cvs 6Document30 pagesCvs 6Kim Sa-buNo ratings yet
- Physiologic and Pathophysiologic Function of The Heart: Cardiac Cycle Graphs, Curves, Loops and CO CalculationsDocument40 pagesPhysiologic and Pathophysiologic Function of The Heart: Cardiac Cycle Graphs, Curves, Loops and CO CalculationsMarc Imhotep Cray, M.D.100% (1)
- Shock: Differential Diagnosis and Hemodynamic MonitoringDocument21 pagesShock: Differential Diagnosis and Hemodynamic MonitoringtataranyNo ratings yet
- Acute Cardiac Crisis: Recognizing Heart FailureDocument77 pagesAcute Cardiac Crisis: Recognizing Heart FailureJudy Anne PatricioNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Output: Presented by N.Perumal Bot 4 TH YearDocument21 pagesCardiac Output: Presented by N.Perumal Bot 4 TH YearNithya SekarNo ratings yet
- Emd166 Slide Shock-1Document53 pagesEmd166 Slide Shock-1THuthi MUktiNo ratings yet
- Drugs Acting in CVSDocument63 pagesDrugs Acting in CVSMeghan Norico Cristuta100% (1)
- Coronary Circulation: by Sridip HaldarDocument19 pagesCoronary Circulation: by Sridip HaldarPercy JacksonNo ratings yet
- Exercise PhysiologyDocument24 pagesExercise PhysiologyMohammed AlharbiNo ratings yet
- Circulation Study Guide Chapters 14-24Document3 pagesCirculation Study Guide Chapters 14-24raanja2No ratings yet
- Coronary CirculationDocument33 pagesCoronary CirculationAayushman YadavNo ratings yet
- Cardiogenic ShockDocument31 pagesCardiogenic ShockLovelights ZamoraNo ratings yet
- Congestive Heart Failure (CHF): Causes, Symptoms and PathophysiologyDocument10 pagesCongestive Heart Failure (CHF): Causes, Symptoms and PathophysiologyAnna VilceaNo ratings yet
- Crnry CrclatnDocument26 pagesCrnry CrclatnSherene Jacob Mathew VaidyanNo ratings yet
- Cardiogenic Shock: Sparsh Goel 77Document28 pagesCardiogenic Shock: Sparsh Goel 77Sparsh GoelNo ratings yet
- Case 2 SlosDocument7 pagesCase 2 SlosNamarNo ratings yet
- Congestive Cardiac Failure GuideDocument61 pagesCongestive Cardiac Failure GuideYAMINIPRIYANNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Muscle Physiology and Cardiovascular System FunctionDocument183 pagesCardiac Muscle Physiology and Cardiovascular System FunctionArdhian Yudha CandraNo ratings yet
- Cardiology DR Osama MahmoudDocument138 pagesCardiology DR Osama MahmoudIsmail Habib100% (4)
- Congestive Heart FailureDocument4 pagesCongestive Heart FailureZosmita Shane GalgaoNo ratings yet
- Regional Circulation: Prof. K. SivapalanDocument23 pagesRegional Circulation: Prof. K. SivapalanjikookNo ratings yet
- 4.shock & MonitoringDocument21 pages4.shock & MonitoringDr.G.Bhanu PrakashNo ratings yet
- Shock PathophysiologyDocument63 pagesShock PathophysiologyRani OktasariNo ratings yet
- Circulație CoroarăDocument2 pagesCirculație CoroarăAurelia AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Shock Syndrome: DR Melkamu BDocument62 pagesShock Syndrome: DR Melkamu BAsteway MesfinNo ratings yet
- ANP 1105 Blood VesselsDocument72 pagesANP 1105 Blood VesselsMathios TigerosNo ratings yet
- Perfusion for Congenital Heart Surgery: Notes on Cardiopulmonary Bypass for a Complex Patient PopulationFrom EverandPerfusion for Congenital Heart Surgery: Notes on Cardiopulmonary Bypass for a Complex Patient PopulationRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Guide to Canine and Feline ElectrocardiographyFrom EverandGuide to Canine and Feline ElectrocardiographyRuth WillisNo ratings yet
- Nurse As Change AgentDocument18 pagesNurse As Change AgentanusarannyaNo ratings yet
- Conceptual FrameworkDocument1 pageConceptual FrameworkanusarannyaNo ratings yet
- Labor Laws and UnionsDocument149 pagesLabor Laws and UnionsanusarannyaNo ratings yet
- RHDDocument57 pagesRHDanusarannyaNo ratings yet
- HAND OUT-haemodynamic MonitoringDocument1 pageHAND OUT-haemodynamic MonitoringanusarannyaNo ratings yet
- Care of Patients Undergoing Valvular Heart SurgerryDocument62 pagesCare of Patients Undergoing Valvular Heart SurgerryanusarannyaNo ratings yet
- CADDocument20 pagesCADanusarannyaNo ratings yet
- Ajitha EndocarditisDocument66 pagesAjitha EndocarditisanusarannyaNo ratings yet
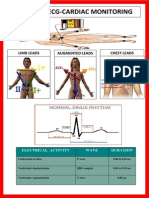
- 12-Lead ECG Guide: Limb, Augmented & Chest LeadsDocument1 page12-Lead ECG Guide: Limb, Augmented & Chest LeadsanusarannyaNo ratings yet
- Study of X - Ray's in ErDocument38 pagesStudy of X - Ray's in EranusarannyaNo ratings yet
- Study of X - Ray's in ErDocument38 pagesStudy of X - Ray's in EranusarannyaNo ratings yet
- Assignment: Fundamental of ElementsDocument7 pagesAssignment: Fundamental of ElementsanusarannyaNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Rehab for COPD PatientsDocument6 pagesPulmonary Rehab for COPD PatientsanusarannyaNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Rehab for COPD PatientsDocument6 pagesPulmonary Rehab for COPD PatientsanusarannyaNo ratings yet
- Professional Advancement & Role and Scope of NursingDocument15 pagesProfessional Advancement & Role and Scope of Nursinganusarannya100% (5)
- Nutri ProbDocument9 pagesNutri ProbanusarannyaNo ratings yet
- Assignment: Fundamental of ElementsDocument7 pagesAssignment: Fundamental of ElementsanusarannyaNo ratings yet
- Horizon Medical Health Insurance Claim Form: Please Read This Important InformationDocument2 pagesHorizon Medical Health Insurance Claim Form: Please Read This Important InformationBrianReagerNo ratings yet
- INTRODUCTION A Cerebrovascular Accident (CVA), An Ischemic Stroke or "BrainDocument30 pagesINTRODUCTION A Cerebrovascular Accident (CVA), An Ischemic Stroke or "BrainCherie May100% (5)
- Daftar Pustaka: Therapeutics: The Clinical Use of Drugs.Document4 pagesDaftar Pustaka: Therapeutics: The Clinical Use of Drugs.putri_lakaNo ratings yet
- Ikterus NeonatorumDocument10 pagesIkterus NeonatorumHerryanto AgustriadiNo ratings yet
- CholedocholithiasisDocument6 pagesCholedocholithiasisprincess0fdeath0% (1)
- A Practical Approach To Rhinoplasty.35Document22 pagesA Practical Approach To Rhinoplasty.35andrew kilshawNo ratings yet
- Prodedural Coding CPT and HCPCSDocument38 pagesProdedural Coding CPT and HCPCSdonna8compton8harmon83% (6)
- National Rural Health MissionDocument37 pagesNational Rural Health MissionSanjeev SinghNo ratings yet
- Disseminated Intravascular CoagualationDocument47 pagesDisseminated Intravascular CoagualationIshaBrijeshSharmaNo ratings yet
- Guideline Chronic Stable AnginaDocument21 pagesGuideline Chronic Stable AnginarinadillaNo ratings yet
- Dispensing 2 - 5 Medication ReviewDocument3 pagesDispensing 2 - 5 Medication ReviewAlyssa Erika AzoresNo ratings yet
- Resume - Alanna SteeleDocument4 pagesResume - Alanna Steeleapi-280544985No ratings yet
- Abnormal Psychology TestDocument7 pagesAbnormal Psychology TestCamae Snyder GangcuangcoNo ratings yet
- PHC Project Concept DRAFT - 0924Document6 pagesPHC Project Concept DRAFT - 0924Gio Glen GrepoNo ratings yet
- BOLT StudyDocument11 pagesBOLT Studytiago_nelson100% (1)
- Deborah Stover RN ResumeDocument2 pagesDeborah Stover RN Resumeapi-479158a34fNo ratings yet
- Reflex Anal Dilatation An Observational Study On Non-Abused ChildrenDocument5 pagesReflex Anal Dilatation An Observational Study On Non-Abused Childrenaniendyawijaya0% (1)
- Hospital Disaster Management: Triage, Response and PreparednessDocument44 pagesHospital Disaster Management: Triage, Response and PreparednessrizqiNo ratings yet
- Brochure Cairo 2013Document9 pagesBrochure Cairo 2013Hanan AhmedNo ratings yet
- Medication Error Reporting Form Pindaan 2Document2 pagesMedication Error Reporting Form Pindaan 2hanselMD100% (2)
- ANTI FungalDocument7 pagesANTI FungalSteve ShirmpNo ratings yet
- Amputation LevelsDocument9 pagesAmputation Levelskrissh20No ratings yet
- Priming IV TubingDocument10 pagesPriming IV Tubinglainey101No ratings yet
- Mental RetardationDocument42 pagesMental RetardationAmmar YusopNo ratings yet
- App 1Document80 pagesApp 1Edmond JacquesNo ratings yet
- Berita MMA April 2016Document48 pagesBerita MMA April 2016Long Tuan MastazaminNo ratings yet
- Couvy Duchesne 2018Document12 pagesCouvy Duchesne 2018spaciugNo ratings yet
- Antidepressant DrugsDocument41 pagesAntidepressant DrugsSashaKay100% (5)