SURFACE RUNOFF
DEFINITION
EXPLAIN
CALCULATE
1. Direct Runoff
2. Base Flow
3. Hydrograph
4. Effective Rain
5. Loss
1. Stream Flow Hydrograph
2. Direct Runoff Hydrograph
3. Equation Of Direct Runoff
Depth With Effective Rain
Volume of direct
runoff from
direct runoff
hydrograph
Calculate stream
Discaharge using
Velocity-area
method
Estimate loss with
phi-index method
Next
Direct runoff
from data of
Stream flow &
Base flow
Direct runoff depth based
on volume of direct runoff
and catchment width
INTRODUCTION
If the amount of water
falling on the ground is
greater than the infiltration
rate of the surface, runoff
or overland flow will occur.
Runoff specifically refers to
the water leaving an area of
drainage and flowing
across the land surface to
points of lower elevation.
Runoff flowing into a
stormwater drain
Direct Runoff
Water that flows over the ground surface
or through the ground directly into
streams, rivers, and lakes.
Direct runoff originally from excess rain.
Direct runoff magnitude and excess rain is
the same
Base flow (also called drought flow, groundwater
recession flow, low flow, and sustained or fair-
weather runoff) is the portion of stream flow that
comes from "the sum of deep subsurface flow
and delayed shallow subsurface flow". It should
not be confused with groundwater flow.
Stream discharge derived from groundwater
sources as differentiated from surface runoff.
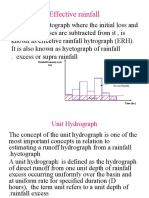
A hydrograph is a graph showing the rate
of flow (discharge) versus time past a
specific point in a river, or other channel or
conduit carrying flow. The rate of flow is
typically expressed in cubic meters or
cubic feet per second (cms or cfs).
is the remaining quantity of rainfall after
subtracting losses. These losses consist in
interception, storage within depressions,
infiltration and evapotranspiration.
Effective rainfall corresponds to the intensity of
residual rain, after a portion of the total depth of
rainfall provided by the storm has been
dissipated by hydrological processes of
infiltration and evapotranspiration.
FACTORS WHICH INFLUENCED DIRECT
RUNOFF
Climatic Factor
Type of precipitation
Rainfall intensity
Rainfall Duration
Rainfall distribution
Storm Direction of motion
Other (loss & Evapotranspiration)
Catchment Area physical factor
Next
Catchment Area Physical Factor
Also need to consider the storm
duration and time of concentration.
CATCHMENTS NATURE WHICH
INFLUENCED RUNOFF
Catchment Area
Major River Distance
Catchment Area Gradient
Catchment Orientation
Average Annual Excess Rainfall
Stream Frequency
Base Flow Index
Lake Area And Reservoir
Soil Humidity Rate
Next Map
Stream flow hydrograph
0
100
200
300
400
500
600
700
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
Time (hour)
Q
(
c
f
s
)
Direct runoff hydrograph
DRO
Time
Equation Of Direct Runoff Depth
With Effective Rain
Calculate direct runoff from stream flow
& base flow data
Direct runoff = stream flow base flow
Schedule below shows observation data from stream flow with base flow
depth in catchment's area 250 km2. from that data , get direct runoff
magnitude.
Time (hour) Stream flow, Q (m
3
/s) Base Flow, (m
3
/s)
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
40
45
50
55
60
65
70
75
1.37
1.25
1.12
5.00
12.00
15.60
17.15
14.40
8.80
6.80
5.50
4.10
2.75
2.00
1.20
0.65
0.15
0.32
0.62
1.25
1.28
1.35
1.42
1.65
1.82
1.88
2.05
2.55
1.91
1.53
1.15
0.28
e
x
a
m
p
l
e
Baseflow Separation
Baseflow separation is used to partition
the streamflow hydrograph into the:
baseflow component
direct runoff component
Methods (for this course):
Straight line method
Horizontal line
Digital filter
Figure 1 : Graphical baseflow separation techniques
including
1. (1a) constant discharge method
2. (1b) constant slope method and
3. (1c) concave method (Linsley et al. 1958)
Calculate Direct Runoff Volume From Direct
Runoff Hydrograph
Volume Direct Runoff From hydrograph =
Total DRO (m
3
/s) x Time (s)
Calculate Direct Runoff Depth Base On Volume
DRO And Cathment Area.
DRO Depth,r
d
= V
d
A
DIMANA;
V
d
= RUNOFF VOLUME = Qn
t
A = CATCHMENT WIDE
Qn = HYDROGRAPH ORDINATE
t
= HYDROGRAPHY TIME INTERVAL
Calculate runoff volume and excess rain depth
to a 7 acres catchment's area. Schedule below
show a direct runoff data resultant from one
precipitation
Time
(minute)
Flow, Q (cfs)
0
2
4
6
8
10
0
0
9
21
17
13
E
X
A
M
P
L
E
How to measured:
STATION ARE REQUIRED TO FILL UP CONDITION;
1. Reach of the river must be straight to ensure velocity
that uniform from point in upstream to observation
station.
2. Having depth that is suitable. Depend upon velocity
measuring tool that want to be used. Flow meter need
at least depth 30 cm
3. Free station from any interference (garbage, trunk, tree
etc ) that could be distracting the river flow velocity.
4. Cross section must be perpendicular with river flow
direction.
The procedure is to:
1. Choose a suitable site along the stream with a straight reach, uniform laminar flow
conditions and relatively constant depth and width. Sites with extreme turbulence,
protruding obstructions, eddies, stagnant zones or divided channels should be
avoided.
2. Set up tagline consisting of a tape measure perpendicular across the stream to be
used for locating the velocity/depth measurements. Measurements are taken along
10-20 verticals across the stream transect. Each vertical should partition stream flow
equally, so that verticals should be closer together where water is faster or deeper.
3. At each site, use a current meter to measure stream velocity and a graduated pole to
measure stream depth. Typically, flow is measured at a depth considered to reflect
average velocity conditions (0.6 of the stream depth measured downward from the
surface). Other approaches such as two measurements taken and averaged for each
vertical, at 0.2 and 0.8 of the water depth are used (refer Table 1)
4.The stream flow can be calculated.
A current meter
Exercise 4:
Given V = 0.3N + 0.05 m/ s. Determine streamflow discharge using velocity-
area method.
Distance
from
Datum
(m)
Stream
depth
(m)
Current meter reading
0.6D 0.2D 0.8D
Rotation Duration
(s)
Rotation Duration
(s)
Rotation Duration
(s)
3 1.2 10 60
6 3.0 35 62 20 65
9 5.7 42 65 28 62
12 8.5 50 68 25 64
15 4.6 57 65 30 68
18 3.8 40 60 32 60
21 2.5 34 62 25 65
24 1.5 15 60