Professional Documents
Culture Documents
LTE EPS Architecture Overview
Uploaded by
telecomwormOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
LTE EPS Architecture Overview
Uploaded by
telecomwormCopyright:
Available Formats
LTE EPS
ARCHITECTURE
OVERVIEW
LTE requirements
WCDMA Architecture
EPS OVERVIEW
Network Components
EPS NODES
MME (Mobility Management Entity)
NAS signaling (eMM, eSM) and security, AS security, tracking area
list management, PDN GW and S-GW selection, handovers (intra-
and inter-LTE), authentication, bearer management.
S-GW
The local mobility anchor point for inter-e NodeB handover;
downlink packet buffering and initiation of network-triggered
service requests, lawful interception, accounting on user and
QCIgranularity, UL/DL charging per UE.
P-GW
UE IP address allocation, packet filtering and PDN connectivity, UL
and DL service-level charging, gating and rate enforcement.
EPS NODES
HSS (Home Subscriber Server)
The HSS contains the database holding subscription information
for UE subscribing to the EPS network. The HSS stores, for
example, the location of the UE (on MME node level), and
authentication parameters.
PCRF (Policy & Charging Rules Function)
Quality of Service (QoS) policy
Charging rules from Policy and Charging
EPC AND E-UTRAN NODES
AND INTERFACES
EPS, GERAN and UTRAN
architecture One Tunnel
Approach
SAE/LTE Combined
SGSN/MME
SAE/LTE INTERFACES
Gi: It is the interface to external packet data networks (e.g.,
Internet) and contains the end-users IP point of presence
S1: It is the interface between eNBs and MME and S-GW.
X2: It is the interface between eNBs. The interface is mainly used to
support active mode UE mobility
S3: It is a control interface between the MME and 2G/3G SGSNs
S4: It is the interface between the P-GW and 2G/3G SGSNs
S11: It is the interface between the MME and S-GW
S10: It is a control interface between the MMEs
S5/S8: S5/S8 is the interface between the S-GW and P-GW
THANK YOU
You might also like
- What Is New in LTEDocument23 pagesWhat Is New in LTEvikramjeetsinghNo ratings yet
- Lte System ArchitectureDocument27 pagesLte System ArchitectureVladut PirvanNo ratings yet
- College Report of Optical Burst SwitchingDocument21 pagesCollege Report of Optical Burst Switchingimcoolsha999No ratings yet
- Multiplex Section Protection Vs SNCPDocument1 pageMultiplex Section Protection Vs SNCPSanthosh MadhuNo ratings yet
- Optical NetworksDocument46 pagesOptical NetworksJaviNo ratings yet
- WCDMA Air InterfaceDocument54 pagesWCDMA Air InterfaceArindam BhattacharayaNo ratings yet
- GPRS EDGE 3G LTE Overview EricssonDocument1 pageGPRS EDGE 3G LTE Overview EricssonMoosa KhalidNo ratings yet
- DATA CommunicationsUNIT 3Document69 pagesDATA CommunicationsUNIT 3Anonymous l0bNv6G0% (1)
- Optisystem PresentationDocument16 pagesOptisystem PresentationzainabNo ratings yet
- WSN - IntroductionDocument48 pagesWSN - IntroductionVaishnavi BalasubramanianNo ratings yet
- 02 Sn2cvxzv010eu13sn 0002 System Overview EwsdDocument126 pages02 Sn2cvxzv010eu13sn 0002 System Overview Ewsdiboorose7No ratings yet
- Sigtran Protocols-M3ua M2paDocument9 pagesSigtran Protocols-M3ua M2paJawahar SinhaNo ratings yet
- LTE Overview TitusDocument41 pagesLTE Overview TitusVepur SrikanthNo ratings yet
- Study Guide Test#1Document11 pagesStudy Guide Test#1GypsyNo ratings yet
- OFDMADocument55 pagesOFDMAamelalic75% (4)
- Lesson 14: Qos in Ip Networks: Intserv and Diffserv: Slide Supporting MaterialDocument52 pagesLesson 14: Qos in Ip Networks: Intserv and Diffserv: Slide Supporting MaterialSallam SallakhoNo ratings yet
- Bandwidth CalculationDocument3 pagesBandwidth CalculationAriev IkankNo ratings yet
- TJ 1400 OLT BrochureDocument2 pagesTJ 1400 OLT BrochureShine JosephNo ratings yet
- IEEE1588 PTP Sync in Electric UtilitiesDocument8 pagesIEEE1588 PTP Sync in Electric UtilitiesGustavo AguayoNo ratings yet
- Department of Electronics and Telecommunication: Pillai College of Engineering New Panvel - 410 206Document16 pagesDepartment of Electronics and Telecommunication: Pillai College of Engineering New Panvel - 410 206Venkatraman SubramanianNo ratings yet
- GSM System OverviewDocument12 pagesGSM System Overviewvemala vandanaNo ratings yet
- Very-High-Speed Digital Subscriber Lines: BY Mostafa Jamal M.S.Cs of Network of ComputerDocument10 pagesVery-High-Speed Digital Subscriber Lines: BY Mostafa Jamal M.S.Cs of Network of ComputerMostafa J AlneamyNo ratings yet
- Gpon Vs EponDocument17 pagesGpon Vs Eponkflim100% (1)
- 3.3G Cellular, WMAN (WIMAX), WLAN (WIFI), WPAN (Bluetooth and UWB), Mobile Ad Hoc Networks (MANET), and Wireless Sensor NetworksDocument36 pages3.3G Cellular, WMAN (WIMAX), WLAN (WIFI), WPAN (Bluetooth and UWB), Mobile Ad Hoc Networks (MANET), and Wireless Sensor Networksekhy29No ratings yet
- G.709 Intro v2Document74 pagesG.709 Intro v2Sivakumar MohanNo ratings yet
- NSN BTS Operation and Maintenance: Target Group: Following Are The Target Audience For This Training ProgramDocument1 pageNSN BTS Operation and Maintenance: Target Group: Following Are The Target Audience For This Training ProgramGauravSwamiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Wireless IP Network Architectures: Jyh-Cheng Chen and Tao ZhangDocument148 pagesChapter 2: Wireless IP Network Architectures: Jyh-Cheng Chen and Tao ZhangPrakarn KorkiatcharoonNo ratings yet
- Omer Khalid (Resume)Document3 pagesOmer Khalid (Resume)omerkamirNo ratings yet
- TJ1400-P Brochure GlobalDocument2 pagesTJ1400-P Brochure GlobalVince CentenoNo ratings yet
- NMS Course Modified)Document89 pagesNMS Course Modified)Srikanth VudutaNo ratings yet
- Frame Structure Frame Characteristic RSOH (Regenerator Section Overhead) MSOH (Multiplex Section Overhead) ReferencesDocument3 pagesFrame Structure Frame Characteristic RSOH (Regenerator Section Overhead) MSOH (Multiplex Section Overhead) ReferencesRaviNo ratings yet
- Timing and Synchronization in Packet Networks: White PaperDocument12 pagesTiming and Synchronization in Packet Networks: White Papermymothman69No ratings yet
- 3.quantization and Transmission of AudioDocument10 pages3.quantization and Transmission of AudioNatnel TsehayeNo ratings yet
- Presentation On: Rajat Singla It-B 274109Document25 pagesPresentation On: Rajat Singla It-B 274109Garima KapoorNo ratings yet
- DSLDocument20 pagesDSLZatin Gupta100% (1)
- Swe2002 Computer-Networks Eth 1.0 37 Swe2002Document4 pagesSwe2002 Computer-Networks Eth 1.0 37 Swe2002Naveen VnvNo ratings yet
- Mobile Communication: Unit-I Two Marks Q&ADocument20 pagesMobile Communication: Unit-I Two Marks Q&AKarthika NarasimanNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 - Wireless NetworkDocument13 pagesUnit 3 - Wireless NetworkZappYNo ratings yet
- IR829 COnfig GuideDocument116 pagesIR829 COnfig Guidelashanj2No ratings yet
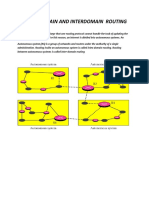
- Difference INTRA and INTER Domain RoutingDocument2 pagesDifference INTRA and INTER Domain RoutingSumit Kamble100% (2)
- MSC PoolDocument5 pagesMSC Poolle_linh_53No ratings yet
- ANT Mod5Document100 pagesANT Mod5DmanNo ratings yet
- CV - Experienced NGN and Voip EngineerDocument3 pagesCV - Experienced NGN and Voip EngineeramirNo ratings yet
- Comparison LTE WiMax CiscoDocument7 pagesComparison LTE WiMax Ciscozbalouch15No ratings yet
- 3G RF Planning OptimizationDocument1 page3G RF Planning OptimizationShalua YonahNo ratings yet
- Fault Tolerant Ethernet Delivers Robust Networking Solution For Experion PKSDocument6 pagesFault Tolerant Ethernet Delivers Robust Networking Solution For Experion PKSKhalid AliNo ratings yet
- HUAWEI CloudEngine Switch Quick Reference Guide PDFDocument36 pagesHUAWEI CloudEngine Switch Quick Reference Guide PDFHussein DhafanNo ratings yet
- LTE RRC Layer State DiagramDocument2 pagesLTE RRC Layer State DiagramMuthulingamNo ratings yet
- A Review: Wireless Sensor Networks and Its Application, Platforms, Standards and ToolsDocument7 pagesA Review: Wireless Sensor Networks and Its Application, Platforms, Standards and ToolsseventhsensegroupNo ratings yet
- LTE Interview Questions P1Document5 pagesLTE Interview Questions P1Mohamed AlaaNo ratings yet
- Ason/Gmpls: Development and Deployment: Young Lee Huawei, USADocument25 pagesAson/Gmpls: Development and Deployment: Young Lee Huawei, USA7kkhsNo ratings yet
- Mentum Planet 5 7 LTE PDFDocument168 pagesMentum Planet 5 7 LTE PDFJuan Carlos Zapata GarciaNo ratings yet
- Indoor Wireless CoverageDocument4 pagesIndoor Wireless Coveragefiqur1No ratings yet
- Proof Of Concept A Complete Guide - 2021 EditionFrom EverandProof Of Concept A Complete Guide - 2021 EditionRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- Day1 Session1Document75 pagesDay1 Session1MohsenNo ratings yet
- ASTRIX ProductDocument2 pagesASTRIX ProductLe ProfessionistNo ratings yet
- 3G TechnologyDocument13 pages3G Technologyrahulrashmi103658No ratings yet
- WC-Lect 12 Thu 30 April Part TwoDocument16 pagesWC-Lect 12 Thu 30 April Part TwoFahad MehmoodNo ratings yet