The Core Competence of the
Corporation
By C.K. Prahalad and Garry Hamel Harvard Business Review
May-June 1990
Group 7
Minh Nguyen
Tanin Pinket
Pannada Lertsaengpetch
Sutta Nitikankool
Gina Herrera
MKTG 5320
February 03, 2009
Texas A & M University Corpus Christi
�GTE and NEC (early 1980s)
GTE :
- Positioned to become a major player in the IT
industry
- Specialized in a variety of business (telephone,
semiconductors, defense systems, switching
and transmission systems, etc)
NEC :
- Had an equivalent technological base and
computer businesses
- Had no experience in telecom operating field
�GTE and NEC (1988)
GTE :
Became a telephone operating company
Positioned in defense and lighting products
Closed down semiconductors
NEC :
Became the world leader in semiconductors
First-tier player in telecommunications & CPU
Top five of the world in revenue in
telecommunications, semiconductors, and
mainframes
�Comparing sales
1980
1988
% Sales Increase
GTE
$9.98 Billion
$16.46 Billion
65%
NEC
$3.8 Billion
$21.89 Billion
476%
(Source : The Core Competence of the Corporation by C.K. Prahalad and Gary Hamel
Harvard Business Review May-June 1990)
�GTE and NEC
Lesson from GTE and NEC
GTE : - Had no clear strategic intent
- Focused on managing independent
business units
NEC : - Had an effective strategic architecture
- Focused on developing core
competencies
�Rethinking the Corporation
In a quickly changing market, companies have
changed their focus from strategic business
units (SBUs) at end products to core
competencies
=> Require a primary change in the
management of a corporation :
- Top managements must bear the
responsibility in acquiring core competencies
- Core competencies must be developed
throughout the corporation
�Rethinking the Corporation
NEC example
NEC s top managers built an appropriate strategic
architecture to strengthen its core products and develop its core
competencies
NEC targeted 3 markets :
- Computing market
- Communication market
- Component market
Identifying semiconductors as one of the most important core
products, NECs core competencies during 1970s - 1980s was
a much quicker and cheaper use of foreign technology
without a necessity to develop new idea
�Roots of Competitive Advantage
A short-term competitiveness of a corporation can be
the price/performance of current products
A long-term competitiveness of a corporation is an
ability :
- To build core competencies creating unanticipated
products
- To strengthen core products
=> Need a managements ability to reinforce core skills
and integrate them into core competencies that can
empower business units to adapt quickly to the
changing market.
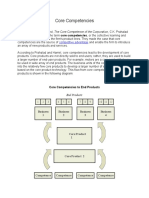
�Core Competency
(Source : The Core Competence of the Corporation by C.K. Prahalad and Gary Hamel
Harvard Business Review May-June 1990)
�Core Competency
The collective learning maintained within an
organization
Integration into technology, work
organization, value delivery
Communication, involvement and an
engagement to working at the entire corporate
level
Not decline with use but be enhanced during
the time of applying and sharing within the
corporation
Need to be cultivated and preserved
�How Not to Think of Competence
Not just making products
But finding core competencies by overseeing the
portfolio of business including customers, distribution
channels, merchandising strategy, etc
NEC Digital Technology especially VLSI
Honda Engines and Power Trains
Canon Optics, Imaging, and Microprocessor
Controls
Philips Optical-Media(Laser Disc)
�How Not to Think of Competence
Not just making products
But finding core competencies by overseeing the
portfolio of business including customers, distribution
channels, merchandising strategy, etc
Developing Core Competencies does not mean:
Outspending competitors on R&D
Sharing manufacturing and operating costs
Vertical Integration
�Identifying Core Competencies
Provide gateway to a wide variety of markets
Casio Hand-Held TV Market
Contribute super value to end products that
benefit consumers
Honda Esteemed Product
Be complex to imitate :
Complicated harmonization of technologies
and production skills
JVC vs. RCA
�Losing Core Competencies
Competitiveness relying on the
price/performance of end products
Outsourcing and OEM Cost Centers
(Chrysler vs. Honda)
Suppliers become competitors
Lack of people-embodied skills
Lack of a clear goal in building core competencies
->Intelligent alliance or sourcing strategy
Forgoing opportunities to develop competencies
that are growing in existing businesses
Give up with the existing competencies
�Costs of Losing Core
Competencies
Hardly to predict in advance
Difficult to enter an emerging market
�Core Products
The brand share
only in end product
markets
The manufacturing share
in any core product
To maintain the market =
leadership
To maximize the companys
manufacturing share in core
products
�Core Products
JVCs decision in the mid-70s :
JVC
established
VCR supply relationships with
the electronics companies
in Europe and USA
The core product of JVC was VCR in the electronics machine
which sustained the market share for JVC in Asia, Europe,and
USA.
�Focus on rivals in the market
Stress on business units performance
The Tyranny of the SBU
Decentralize commanding by each business
Allocate a lot of money to advertise brand name
�Two Concepts of the Corporation:
SBU vs. Core Competence
SBU
Basic for
competition
Corporate
structure
Status of the
business unit
Focus on competitiveness of
todays product
Core Competence
Try to build competence with
the inter-firm competition
Portfolio of businesses related in Portfolio of competencies,
product-market terms
core products, and businesses
Autonomy is inviolable and
SBU owns all resources other
than cash
SBU is only a potential
reservoir of core competencies
Resource
allocation
Each businesses is like the unit,
so capital is allocated business
by business
Businesses and competencies
are the unit of analysis, so
allocation is the overall picture
Value added of
top management
Optimizing corporate returns
through capital allocation tradeoffs among businesses
Enunciating strategic
architecture and building
competencies to secure the
future
(Source : The Core Competence of the Corporation by C.K. Prahalad and Gary Hamel Harvard Business
Review May-June 1990)
�The disadvantages to corporation from
the SBUs distortion
SBUs distortion
Underinvestment in Developing
Core Competencies & Core Products
�Vickers
The Origin of Vickers
A division of Trinova Corporation
The Elements of Transformation
Technologies
Customer Needs
The New Concepts Goals
Development of the Capability of Competition
Certainty of the present market in the future
The new market preemption
�Strategic Architecture
Help to identify which core competencies to
build.
Motivate companies in learning from
alliances and create efforts for internal
development
Provide a logic for product and market
diversification.
Help organizations to identify and engage in
the technical and production linkages across
SBUs creating competitive advantage
�Strategic Architecture
Different for every company
Must be clear with resource allocation
priorities within the organization
Difficult to be imitated by competitors
�Strategic Architecture
A tool for
communicating
with customers
and other external
relative units.
�Deploying Core Competencies
Core competencies are from companys
resources and reallocated by board of
governance
People carrying core competencies are
corporate assets to be utilized by corporate
management, not by any particular business
unit
Contribution of SBU managers should be clear
in equality across the company
�Deploying Core Competencies
Process of building core competencies must be
recorded and appreciated
Core competencies should be shared and
employed within the organization
Responsibility of top management in
establishing strategic architecture to build core
competence
�Conclusion
Suggestions from Prahalad and Hamel
Core competence should be recognized and
concentrated in a corporate strategy
Companies need to acknowledge the hierarchy of
core competence, core product, and business units
with market focus in a strategy with an aim of
strengthening capabilities to compete in a quickly
changing market
It is the responsibility of top management to build a
strategic architecture for a direction in acquiring core
competencies
�Question ???