50% found this document useful (2 votes)
12K views21 pagesQuantum Computing
This presentation provides an overview of quantum computing, including its history, key concepts, advantages over classical computing, applications, and challenges. It was submitted by Anurag Anand, an undergraduate student at the Department of Electronics and Communication, under the guidance of Dr. Rajeswari. The presentation covers topics such as the basics of quantum computers, how they use quantum mechanics principles like superposition and entanglement, their potential for massive parallel processing power, applications in cryptography and artificial intelligence, and challenges like error correction and decoherence.
Uploaded by
Anurag AnandCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
50% found this document useful (2 votes)
12K views21 pagesQuantum Computing
This presentation provides an overview of quantum computing, including its history, key concepts, advantages over classical computing, applications, and challenges. It was submitted by Anurag Anand, an undergraduate student at the Department of Electronics and Communication, under the guidance of Dr. Rajeswari. The presentation covers topics such as the basics of quantum computers, how they use quantum mechanics principles like superposition and entanglement, their potential for massive parallel processing power, applications in cryptography and artificial intelligence, and challenges like error correction and decoherence.
Uploaded by
Anurag AnandCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Introduction
- History
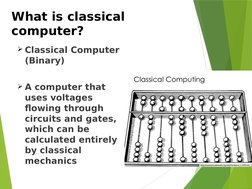
- What is Quantum Computer?
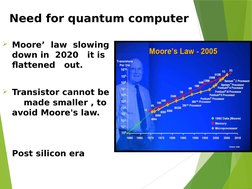
- Need for Quantum Computer
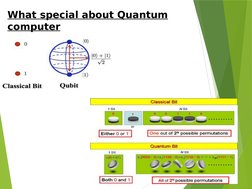
- What Special About Quantum Computer
- Quantum Computing Power
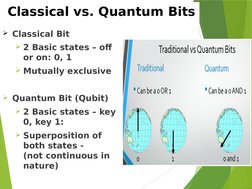
- Classical vs Quantum
- The Need For Speed
- Applications of Quantum Computer
- Challenges and Limitations
- Summary
- References