Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cement
Cement
Uploaded by
vinay0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views15 pagesThe document discusses cement stabilization of soils. The primary reaction when cement is added to soil is hydration, forming cementitious materials. This reaction occurs independently of soil type. Hydrated lime released by cement can cause secondary pozzolanic reactions with clay in soil, producing additional cementitious products. Cement reduces moisture susceptibility and develops bonds between soil particles, improving tensile strength and stiffness. The properties of cement-soil mixes depend on factors like soil type, cement content, mixing/compaction method, curing conditions, and additives. Design mixes are typically based on compressive strength tests or durability tests like wet-dry or freeze-thaw cycling.
Original Description:
ground improvement techniques
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses cement stabilization of soils. The primary reaction when cement is added to soil is hydration, forming cementitious materials. This reaction occurs independently of soil type. Hydrated lime released by cement can cause secondary pozzolanic reactions with clay in soil, producing additional cementitious products. Cement reduces moisture susceptibility and develops bonds between soil particles, improving tensile strength and stiffness. The properties of cement-soil mixes depend on factors like soil type, cement content, mixing/compaction method, curing conditions, and additives. Design mixes are typically based on compressive strength tests or durability tests like wet-dry or freeze-thaw cycling.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views15 pagesCement
Cement
Uploaded by
vinayThe document discusses cement stabilization of soils. The primary reaction when cement is added to soil is hydration, forming cementitious materials. This reaction occurs independently of soil type. Hydrated lime released by cement can cause secondary pozzolanic reactions with clay in soil, producing additional cementitious products. Cement reduces moisture susceptibility and develops bonds between soil particles, improving tensile strength and stiffness. The properties of cement-soil mixes depend on factors like soil type, cement content, mixing/compaction method, curing conditions, and additives. Design mixes are typically based on compressive strength tests or durability tests like wet-dry or freeze-thaw cycling.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 15
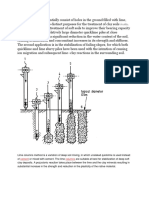
CEMENT STABILIZATION
CONCEPT OF CEMENT SOIL MIX
The primary reaction is the hydration leads to the
formation of cementitious material (calcium silicate
and aluminium hydrates as in concrete).
These reactions occur almost independently of the
nature of the soil.
The hydration reaction releases hydrated lime
(about 30% by mass of the added cement) which
can cause secondary reactions with any pozzolans
(usually clay) within the soil.
The secondary reaction produces cementitious
products similar to those from the primary reaction.
equations
Pozzolanic reactions are usually slow but continue
over a long period provided that adequate moisture
is present. Reactions are also temperature sensitive,
the rate of reaction increasing with increasing
temperature.
Cement has two important effects
on soil behavior
It greatly reduces the moisture
susceptibility of some soils, giving
enhanced volume and strength stability
under variable moisture conditions.
It can cause the development of
interparticle bonds in granular
materials, endowing the stabilized
material with tensile strength and high
elastic modulus.
FACTORS INFLUENCING PROPERTIES OF SOIL CEMENT
MIX
Soil
Cement
Pulverization and mixing
Compaction
Curing
Additives
SOIL
Particle size distribution, clay content,
LL, PI affect the properties of mix.
Cement content:
Increase in cement content causes increase
in strength and durability.
For satisfactory stabilization, amount of
cement depends on type of soil.
Cement requirement increases with specific
surface area of the soil.
Pulverization and mixing
Presence of unpulverised dry lumps of soil
reduces strength and durability of mix
Compaction
Dry density of mix can be increased by increasing the amount of
compaction.
Curing
Higher temperature of curing accelerates the rate of gain in
strength, strength also increases with age.
Additives
Sodium hydroxide, sodium carbonate and calcium chloride are some
of useful chemical additives to soil cement mix
Note :Organic material and sulphates may cause retardation of the reaction
DESIGN MIX
Most commonly used methods
British method
(based on compressive strength of specimens cured
for 7 days)
PCA method
(Based on durability of mix to withstand wet-dry
cycles and freeze-thaw cycles.)
Strength of various soils stabilised with general purpose cement
(cured for7 days at 25C and constant moisture content
You might also like
- Eco-efficient Rendering Mortars: Use of Recycled MaterialsFrom EverandEco-efficient Rendering Mortars: Use of Recycled MaterialsNo ratings yet
- Chemical StabilizationDocument7 pagesChemical StabilizationKarwitha MutwiriNo ratings yet
- Research On Soil-CementDocument6 pagesResearch On Soil-CementhuhuhuhuNo ratings yet
- Stabilization of Soil Using AdmixtureDocument17 pagesStabilization of Soil Using AdmixtureVarun Singh ChandelNo ratings yet
- Soil Stabilization Using Lime: Presented By: Harshit Agarwal Rahul Sharma Ashish ChakroborthyDocument19 pagesSoil Stabilization Using Lime: Presented By: Harshit Agarwal Rahul Sharma Ashish ChakroborthyRahulSharmaNo ratings yet
- Soil Stabilisation & Compaction MethodsDocument44 pagesSoil Stabilisation & Compaction MethodsKURUBA SARAN RAJ SamNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Soil Stabilization:: M Baqir Ismail 2017-UET-QET-SWL-CIVIL-23Document10 pagesIntroduction of Soil Stabilization:: M Baqir Ismail 2017-UET-QET-SWL-CIVIL-23M Baqir IsmailNo ratings yet
- Soil Improvement With Lime: Parampreet Kaur, Gurdeep SinghDocument3 pagesSoil Improvement With Lime: Parampreet Kaur, Gurdeep Singhtyas_pramesthiNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2 of Thesis On Stabilization RahulDocument5 pagesCHAPTER 2 of Thesis On Stabilization RahulSanjay TiwariNo ratings yet
- Construction TechnologyDocument9 pagesConstruction TechnologyAparnaNo ratings yet
- Method of Soil StabilizationDocument29 pagesMethod of Soil StabilizationAbhi WanwadeNo ratings yet
- SUGAR:-Construction Activities Are Accomplished Through Laid Down Procedures andDocument37 pagesSUGAR:-Construction Activities Are Accomplished Through Laid Down Procedures andJakeer SharifNo ratings yet
- GIT Unit-5Document8 pagesGIT Unit-5himabindugvsd71No ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Durability PDFDocument5 pagesFactors Affecting Durability PDFApoorvaAppiNo ratings yet
- Setting:-: Concrete Technology (I) Lecture 5Document10 pagesSetting:-: Concrete Technology (I) Lecture 5Mahmoud HosnyNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two Literature ReviewDocument19 pagesChapter Two Literature ReviewVictor ImehNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument43 pagesDocumentGajanan JafrabadkarNo ratings yet
- Silica Fume As An Admixture in ConcreteDocument15 pagesSilica Fume As An Admixture in ConcreteNithya Gowda100% (1)
- Admixtures in Concrete - NotesDocument55 pagesAdmixtures in Concrete - Notesnital poteNo ratings yet
- Concrete 2Document11 pagesConcrete 2Anirban MazumderNo ratings yet
- Concrete Technology - 2 Lecture - 4-1Document17 pagesConcrete Technology - 2 Lecture - 4-1Muhammad Ahmad JamilNo ratings yet
- Gi - 5Document3 pagesGi - 5Nehja ShajahanNo ratings yet
- Soil Stablization Methods: PGCM 44 Special Construction Methods and TechnologyDocument32 pagesSoil Stablization Methods: PGCM 44 Special Construction Methods and TechnologySagar0% (1)
- Final BodyDocument63 pagesFinal BodyAbubakar MusaNo ratings yet
- CMT BasicDocument11 pagesCMT BasicElle EnolbaNo ratings yet
- CMT BasicDocument11 pagesCMT BasicElle EnolbaNo ratings yet
- Technical Note: Mrthomps@uiuc - EduDocument10 pagesTechnical Note: Mrthomps@uiuc - EduHadi BendjNo ratings yet
- Concret Technology 2 Mark QaDocument11 pagesConcret Technology 2 Mark Qasaty1049No ratings yet
- Chapter Five HW IIDocument24 pagesChapter Five HW IIHenok YalewNo ratings yet
- Ijs DR 2009016Document6 pagesIjs DR 2009016عبدالرحمن العليميNo ratings yet
- Soilstabilisation1 151228083503 PDFDocument92 pagesSoilstabilisation1 151228083503 PDFabhayNo ratings yet
- Unit 17Document12 pagesUnit 17swaraj deshpande123No ratings yet
- Git NotesDocument19 pagesGit NotesZahid0% (1)
- Abdulsalam, Mayowa Basit.Document12 pagesAbdulsalam, Mayowa Basit.Abdulsalam MayowaNo ratings yet
- Concrete Material and MixtureDocument51 pagesConcrete Material and MixtureAina Aqilah100% (1)
- ADMIXTURES FOR CONCRETE and Hardened ConcreteDocument13 pagesADMIXTURES FOR CONCRETE and Hardened ConcreteMwaniki WilNo ratings yet
- Soilstabilisation1 151228083503Document92 pagesSoilstabilisation1 151228083503Carmel Buniel SabadoNo ratings yet
- Admixture Stabilization 1Document35 pagesAdmixture Stabilization 1SaulatJillani100% (2)
- Soil Stabilization by Using: Fly AshDocument12 pagesSoil Stabilization by Using: Fly AshRavi HirulkarNo ratings yet
- Light Weight ConcreteDocument46 pagesLight Weight ConcreteJay BadiyaniNo ratings yet
- Studying of Effect The High Range Water Reducer Super Plasticizer Retarding Admixture On Properties of ConcreteDocument5 pagesStudying of Effect The High Range Water Reducer Super Plasticizer Retarding Admixture On Properties of ConcreteKing MKNo ratings yet
- Module-1 Cement: What Are The Properties of Cement?Document10 pagesModule-1 Cement: What Are The Properties of Cement?Jincy JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 2 - Concrete Works at Construction SiteDocument43 pagesChapter - 2 - Concrete Works at Construction Sitepritti_naa83% (6)
- Cement FDVDocument6 pagesCement FDVJinyan YangNo ratings yet
- Points For PPT On AdmixturesDocument9 pagesPoints For PPT On AdmixturesAvinash MaratheNo ratings yet
- Irjet V4i6529 PDFDocument3 pagesIrjet V4i6529 PDFShankar Dev GourNo ratings yet
- RPDocument24 pagesRPईशान्त शर्माNo ratings yet
- Presented BY: Ashok KumarDocument50 pagesPresented BY: Ashok KumarashoknrNo ratings yet
- Replacement of Clinker With Dune SandDocument18 pagesReplacement of Clinker With Dune SandRehan RaviNo ratings yet
- Concrete Materials: CIEN 30023 S.Y. 2ND SEM 2019-2020Document49 pagesConcrete Materials: CIEN 30023 S.Y. 2ND SEM 2019-2020Mhervin Bisis100% (1)
- Admixtures, Nanoconcrete, Glenium ConcreteDocument99 pagesAdmixtures, Nanoconcrete, Glenium Concretejitesh dhuleNo ratings yet
- Construction Quality Management: NCP 27 Prof.B.RavinderDocument60 pagesConstruction Quality Management: NCP 27 Prof.B.RavinderGopinadh NidraNo ratings yet
- Naga 1Document31 pagesNaga 1Siddharth RavuriNo ratings yet
- Bituminous Soil Stabilization AssignmentDocument5 pagesBituminous Soil Stabilization AssignmentScott MuthuriNo ratings yet
- Admixtures Types of Admixtures: Engineering MaterialsDocument11 pagesAdmixtures Types of Admixtures: Engineering Materialsanne chandraNo ratings yet
- 15-Concrete 3rd HandoutDocument14 pages15-Concrete 3rd HandoutZELALEMNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document40 pagesChapter 5ADHAM SAFINo ratings yet
- Water Reducing - Retarding AdmixturesDocument17 pagesWater Reducing - Retarding AdmixturesAbdullah PathanNo ratings yet
- Plain & Reinforced Cement - 1 PBL Activity-1Document6 pagesPlain & Reinforced Cement - 1 PBL Activity-1Umair AshrafNo ratings yet