Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Design Datapath Controllers (DPC
Uploaded by
Thắng HuỳnhOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Design Datapath Controllers (DPC
Uploaded by
Thắng HuỳnhCopyright:
Available Formats
Unit 4 Design and Synthesis of
Datapath Controllers
Department of Communication
Engineering, NCTU
Digital CAS
Sau-Hsuan
Wu
Digital systems
Unit 4 : Design of Datapath
Controllers
Control-dominated systems :
being reactive systems responding to external events, such
as traffic controllers, elevator controllers, etc
Data-dominated systems :
requiring high throughput data computation and transport
such as telecommunications and signal processing
Sequential machines are commonly partitioned into data
path units and control units
Datapath Logic
Control inputs
Clock
FSM
Control
signals
Datapath
Registers
Department of Communication Engineering,
Digital CAS
Arithmetic units :
Arithmetic and logic units (ALU)
Storage registers
Logic for moving data :
through the system
between the computation units and internal registers
to and from the external environments
Control units are commonly modeled by
Sau-Hsuan
Wu
Datapath units consist of:
Unit 4 : Design of Datapath
Controllers
State transition graphs (STGs)
Algorithm state machine (ASM) charts for FSM
A combined control-dataflow sequential machine is
modeled by ASM and datapath (ASMD) charts
Department of Communication Engineering,
Digital CAS
Sau-Hsuan
Wu
Algorithm State Machine (ASM) Charts
Unit 4 : Design of Datapath
Controllers
State transition graphs only indicate the transitions that
result from inputs
Not only does ASM display the state transitions, it also
models the evolution of states under the application of input
datas
An ASM chart is formed with three fundamental elements
Department of Communication Engineering,
Digital CAS
Unit 4 : Design of Datapath
Controllers
Sau-Hsuan
Wu
Both Mealy and Moore machines can be represented by
ASM
The outputs of a Moore machine are listed inside a state box
Conditional outputs (Mealy outputs) are placed in
conditional output boxes
Start
En
C <= C+1
Department of Communication Engineering,
Digital CAS
Unit 4 : Design of Datapath
Controllers
Sau-Hsuan
Wu
A sequential machine is partitioned into a controller and a
datapath, and the controller is described by an ASM
The ASM chart can be modified to link to the datapath
that is under control of the ASM
The modified ASM is referred to as the algorithm state
machine and datapath (ASMD) chart
ASMD is different from ASM in that :
each of the transition path of an ASM is annotated with
the associated concurrent register operations of datapath
Department of Communication Engineering,
Digital CAS
Unit 4 : Design of Datapath
Controllers
Sau-Hsuan
Wu
An ASMD chart for a up-down counter
Up-down counter
with asynchronous reset
Up-down counter
with synchronous reset
Count <= 0
Reset
Count <= 0
Count <= Count - 1
Start
Up
Start
Count <= Count + 1
Clr
Count <= Count - 1
Up
Count <= Count + 1
Department of Communication Engineering,
Digital CAS
Unit 4 : Design of Datapath
Controllers
Sau-Hsuan
Wu
ASM v.s. ASMD charts for a counter with enable
ASM chart
representation
ASMD chart
representation
Start
Start
En
En
C <= C+1
Enable DP
Department of Communication Engineering,
Count <= Count + 1
Unit 4-1 UART Design
Department of Communication
Engineering, NCTU
Digital CAS
Unit 4 : Design of Datapath
Controllers
Sau-Hsuan
Wu
Most computers and microcontrollers have one or more
serial data ports used to communicate with serial
input/output devices
The serial communication interface, which receive serial
data, is often called a UART (Universal Asynchronous
Receiver-Transmitter)
One application of a UART is the modem (modulatordemodulator) that communicates via telephone lines
Department of Communication Engineering,
10
Digital CAS
Unit 4 : Design of Datapath
Controllers
Sau-Hsuan
Wu
Features of UARTs
There is no clock for UARTs
Data (D) is transmitted one bit at a time
When no data is being transmitted, D remains high
To mark the transmission, D goes low for one bit time,
which is referred to as the start bit
When text is being transmitted, ASCII code is usually used
ASCII is 7-bit in length the 8th bit is used for parity check
Department of Communication Engineering,
11
Digital CAS
Unit 4 : Design of Datapath
Controllers
Sau-Hsuan
Wu
After 8 bits are transmitted, D must go high for at least one
bit time
When receiving, the UART detects the start bit, receives the
8 data bits, and converts the data to parallel form when it
detects the stop bit
The UART must synchronize the incoming bit stream with
the local clock
The number of bits transmitted per second is often
referred to the BAUD rate
Department of Communication Engineering,
12
Digital CAS
Unit 4 : Design of Datapath
Controllers
Sau-Hsuan
Wu
Design of a simplified UART
TDR : transmit data register, TSR : transmit shift register
RDR : receive data register, RSR : receive shift register
SCCR : serial communication control register
SCSR : serial communications status register
Department of Communication Engineering,
13
Digital CAS
Unit 4 : Design of Datapath
Controllers
Sau-Hsuan
Wu
Procedure for the data transmission of the UART :
(TDRE is set when TDR is empty)
A microcontroller waits TDRE=1 load TDR TDRE=0
The UART moves data from TDR to TSR and TDRE=1
Output a start bit (0) shift right TSR stop bit (1)
Department of Communication Engineering,
14
Digital CAS
Unit 4 : Design of Datapath
Controllers
Sau-Hsuan
Wu
ASM for TX
Department of Communication Engineering,
15
Digital CAS
Unit 4 : Design of Datapath
Controllers
Sau-Hsuan
Wu
The operation of the UART receiver :
When detecting a start bit, the UART starts reading the
remaining bits serially and shifts them into the RSR
When the stop bit is received, load RSR to RDR and RDRF=1
If RDRF=1, the microcontroller read RDR and RDRF = 0
Department of Communication Engineering,
16
Digital CAS
Unit 4 : Design of Datapath
Controllers
Sau-Hsuan
Wu
Key points for designing a UART receiver
The bit stream is not synchronized with the local Bclk
The bit rate of the incoming RxD differs from Bclk by a small
amount could end up reading some bits at the wrong time
To avoid this problem, sample RxD eight times each bit time
When RxD first goes to 0, check for four consecutive 0s. If
this is true waits for 8 more BclkX8 star reading the 1st
bit waits for 8 more BclkX8 read 2nd bit and so on
Department of Communication Engineering,
17
Digital CAS
Unit 4 : Design of Datapath
Controllers
Department of Communication Engineering,
Sau-Hsuan
Wu
18
Digital CAS
Unit 4 : Design of Datapath
Controllers
Sau-Hsuan
Wu
BAUD generator
Suppose the system clock 8 MHz and we want BAUD rates
300, 600, 1200, 2400, 4800, 9600, 19200 and 38400
Selection for BAUD rates (Notice!! set default rate at
38462)
Department of Communication Engineering,
19
Digital CAS
Unit 4 : Design of Datapath
Controllers
Sau-Hsuan
Wu
Input/Output (I/O) interface
TIE and RIE are set by the microcontroller (uC)
SCI_IRQ is generated for uC when RDRF or OE =1
When TIE =1, SCI_IRQ is generated when TDRE =1
Data BUS RDR, SCSR and hi-Z
Data BUS TDR and SCCR
Department of Communication Engineering,
20
Digital CAS
Unit 4 : Design of Datapath
Controllers
Sau-Hsuan
Wu
Input/Output (I/O) interface
Memory mapping of controller registers
ADDR WR Action
00
0
DBUS RDR
00
1
TDR DBUS
01
0
DBUS SCSR
01
1
DBUS hi-Z
1x
0
DBUS SCCR
1x
1
SCCR DBUS
Notice that the port to DBUS must be tri-state buffered and
held hi-Z whenever not outputting data to DBUS
Department of Communication Engineering,
21
Digital CAS
Unit 4 : Design of Datapath
Controllers
Sau-Hsuan
Wu
Transmit FIFO controller
Generate a synchronous FIFO of 16 bytes
q
Data In
used_dw
TX
FIFO16
wr_req
rd_req
CLK
Addr
DBUS
Full
WR
Empty
CS
Reset_N
TX
UART
RX
UART_IRQ
CLK
Department of Communication Engineering,
Reset_N
22
Digital CAS
Unit 4 : Design of Datapath
Controllers
Sau-Hsuan
Wu
TXFIFO16 timing
Department of Communication Engineering,
23
Digital CAS
Unit 4 : Design of Datapath
Controllers
Sau-Hsuan
Wu
Transmit FIFO controller
Generate a synchronous FIFO of 16 bytes
q
Data In
used_dw
TX
FIFO16
wr_req
rd_req
CLK
Addr
DBUS
Full
WR
Empty
CS
Reset_N
TX
UART
RX
UART_IRQ
CLK
Department of Communication Engineering,
Reset_N
24
Digital CAS
Unit 4 : Design of Datapath
Controllers
Department of Communication Engineering,
Sau-Hsuan
Wu
25
You might also like
- Unit 4 Design and Synthesis of Datapath Controllers: Department of Communication Engineering, NCTUDocument25 pagesUnit 4 Design and Synthesis of Datapath Controllers: Department of Communication Engineering, NCTUPerumal NamasivayamNo ratings yet
- ASMD Based Design: UART TransmitterDocument19 pagesASMD Based Design: UART Transmittermisss123100% (1)
- Serial CommunicationsDocument23 pagesSerial CommunicationsPhuoc Trung Tran100% (1)
- Dire Dawa University Institute of TechnologyDocument28 pagesDire Dawa University Institute of TechnologyAsed ZakirNo ratings yet
- Project 2Document19 pagesProject 2Gaurav BaluNo ratings yet
- 6-Iriset S28 PDFDocument109 pages6-Iriset S28 PDFAnjaliTripathi75% (4)
- Baud Rate Generator:: Homework Assignment # 4Document5 pagesBaud Rate Generator:: Homework Assignment # 4Badrinath Balasubramanian100% (1)
- Computer OrganizationDocument18 pagesComputer OrganizationBolaji AwokiyesiNo ratings yet
- C6713 DSP Lab Mannual 2Document40 pagesC6713 DSP Lab Mannual 2dangvuduongNo ratings yet
- WE Project Report Moiz, AliDocument17 pagesWE Project Report Moiz, AliMoiz HussainNo ratings yet
- Design of The Data Acquisition System Based On STM32: Information Technology and Quantitative Management (ITQM2013)Document7 pagesDesign of The Data Acquisition System Based On STM32: Information Technology and Quantitative Management (ITQM2013)Nguyễn Trọng TuyếnNo ratings yet
- Datalogger, Aws, Acd, TPWS, Etcs PDFDocument55 pagesDatalogger, Aws, Acd, TPWS, Etcs PDFvaranasilkoNo ratings yet
- UARTDocument27 pagesUARTNaveen Kumar100% (1)
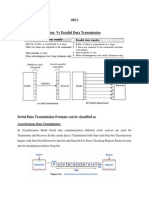
- Serial Data Transmission Vs Parallel Data Transmission: Unit 5Document16 pagesSerial Data Transmission Vs Parallel Data Transmission: Unit 5achuu1987No ratings yet
- Es Notes Unit 5Document33 pagesEs Notes Unit 51balamanianNo ratings yet
- Design and Implementation of UartDocument21 pagesDesign and Implementation of Uartbhanu455No ratings yet
- Design of The Data Acquisition System Based On STM32: Information Technology and Quantitative Management (ITQM2013)Document7 pagesDesign of The Data Acquisition System Based On STM32: Information Technology and Quantitative Management (ITQM2013)Josue Manuel Pareja ContrerasNo ratings yet
- PC Interfacing Fourth Level Lecture Six: Serial To Parallel and Parallel To Serial InterfaceDocument5 pagesPC Interfacing Fourth Level Lecture Six: Serial To Parallel and Parallel To Serial Interfaceأسامة المياحيNo ratings yet
- AR1719 AbstractDocument12 pagesAR1719 AbstractSarika KarwandeNo ratings yet
- Intellignt Instrumentation NotesDocument13 pagesIntellignt Instrumentation NotesBarun DhimanNo ratings yet
- Abstract 2. Circuit Diagram 3. Explanation 4. Working 5. Program Code 6. PCB Layout Fabrication and Assembly 8. Conclusion 9. Reference 10. DatasheetDocument22 pagesAbstract 2. Circuit Diagram 3. Explanation 4. Working 5. Program Code 6. PCB Layout Fabrication and Assembly 8. Conclusion 9. Reference 10. Datasheetaditya_pundirNo ratings yet
- ADS8412 As A Serial ADC - ALTERA PDFDocument11 pagesADS8412 As A Serial ADC - ALTERA PDFhieuhuech1No ratings yet
- Introduction To Microprocessor-Based ControlDocument42 pagesIntroduction To Microprocessor-Based ControlAhdan FawwazNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document30 pagesChapter 4udgam pandeyNo ratings yet
- Data Acquisition System Components and FunctionsDocument10 pagesData Acquisition System Components and FunctionsBarun DhimanNo ratings yet
- FPGA Implementation of Universal Asynchronous Receiver and Transmitter (UART)Document13 pagesFPGA Implementation of Universal Asynchronous Receiver and Transmitter (UART)VaseaPupchinNo ratings yet
- Master-Slave DSP Board for Digital Control SystemsDocument5 pagesMaster-Slave DSP Board for Digital Control Systemsfurious143No ratings yet
- Research Paper On 8086 MicroprocessorDocument7 pagesResearch Paper On 8086 Microprocessorfzqs7g1d100% (1)
- Shift Registrs and UartDocument13 pagesShift Registrs and UartSarath ChandraNo ratings yet
- UARTDocument26 pagesUARTShantanu Tripathi100% (2)
- MAR Notes 3 - ATMega328PDocument6 pagesMAR Notes 3 - ATMega328PYupniatsNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document55 pagesUnit 2Shubhankit SinghNo ratings yet
- Datalogger TPWSDocument64 pagesDatalogger TPWSNagendra PrasadNo ratings yet
- 8251A USART - Programmable Communication InterfaceDocument15 pages8251A USART - Programmable Communication InterfaceShreerama Samartha G BhattaNo ratings yet
- IJAER Ok 23043-23052Document10 pagesIJAER Ok 23043-23052vijayNo ratings yet
- Buses or Data Highways. Since An Interface Bus Is A Parallel Assembly of Connections, Data IsDocument13 pagesBuses or Data Highways. Since An Interface Bus Is A Parallel Assembly of Connections, Data Isranbeer1991No ratings yet
- Reference Material For EXP - 1Document26 pagesReference Material For EXP - 1Jatin YadavNo ratings yet
- Types of Registers in a Computer SystemDocument17 pagesTypes of Registers in a Computer SystemManju JangirNo ratings yet
- Input-Output Interfaces and Communication ProtocolsDocument21 pagesInput-Output Interfaces and Communication ProtocolsBlackk SpydoNo ratings yet
- Prof. Dr. Ahmet İhsan KUTLAR Prof. Dr. Nihat YILDIRIM Res. Assit - Eren ÖZKURDocument23 pagesProf. Dr. Ahmet İhsan KUTLAR Prof. Dr. Nihat YILDIRIM Res. Assit - Eren ÖZKURxxxNo ratings yet
- Embedded Systems Architecture Device Drivers - Part 3 On Board Bus Device Drivers PDFDocument7 pagesEmbedded Systems Architecture Device Drivers - Part 3 On Board Bus Device Drivers PDFsergeysergey1No ratings yet
- Distributed Control SystemsDocument24 pagesDistributed Control SystemsPraveen Madhusoodhanan100% (1)
- 8251A USART Chip GuideDocument15 pages8251A USART Chip GuideselvaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 16 Bit Microprocessors 8086/8088Document33 pagesUnit 2 16 Bit Microprocessors 8086/8088Asha GusainNo ratings yet
- Introduction To MicroprocessorDocument39 pagesIntroduction To MicroprocessorDeepika BansalNo ratings yet
- A Design of Network Remote Control SystemDocument4 pagesA Design of Network Remote Control SystemPurush ArunNo ratings yet
- معمارية 2Document13 pagesمعمارية 2firasvtNo ratings yet
- 8051 CH10Document93 pages8051 CH10Murali KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Experiment #8 Serial Communication Using The Asynchronous Communications Interface Adapter (Acia)Document29 pagesExperiment #8 Serial Communication Using The Asynchronous Communications Interface Adapter (Acia)Felipe DiasNo ratings yet
- Uart Receiver Verilog CodeDocument31 pagesUart Receiver Verilog CodeSannena Govinda80% (5)
- High Speed Data Logging and Control SystemDocument59 pagesHigh Speed Data Logging and Control SystemmknunwalNo ratings yet
- ECE448 S12 In-Class MidtermDocument3 pagesECE448 S12 In-Class Midtermbilalhabib2001No ratings yet
- CS1104: Computer Organisation: School of ComputingDocument49 pagesCS1104: Computer Organisation: School of ComputingvkthikNo ratings yet
- Juniper Mx960 - FisicoDocument9 pagesJuniper Mx960 - FisicoAdrian CarmonaNo ratings yet
- DSPDocument13 pagesDSPSayoshni Ghosh100% (1)
- Digital Electronics and MicrocomputersDocument37 pagesDigital Electronics and Microcomputersrejie magnayeNo ratings yet
- Preliminary Specifications: Programmed Data Processor Model Three (PDP-3) October, 1960From EverandPreliminary Specifications: Programmed Data Processor Model Three (PDP-3) October, 1960No ratings yet
- Practical Reverse Engineering: x86, x64, ARM, Windows Kernel, Reversing Tools, and ObfuscationFrom EverandPractical Reverse Engineering: x86, x64, ARM, Windows Kernel, Reversing Tools, and ObfuscationNo ratings yet
- Quick Start Guide For Fpra PDFDocument24 pagesQuick Start Guide For Fpra PDFWladimirGonzálezContrerasNo ratings yet
- Atmel 7647 Automotive Microcontrollers ATmega16M1 32M1 64M1 32C1 64C1 DatasheetDocument318 pagesAtmel 7647 Automotive Microcontrollers ATmega16M1 32M1 64M1 32C1 64C1 DatasheetakshatNo ratings yet
- Confidential Power Electronics TestDocument9 pagesConfidential Power Electronics TestMuhammad NabilNo ratings yet
- Dynamic BTS Power ControlDocument14 pagesDynamic BTS Power ControlSameh GalalNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Typical Solved ProblemsDocument10 pagesPower Electronics Typical Solved Problemsaprilswapnil0% (1)
- LG CE-29Q90ID Color TV Service ManualDocument41 pagesLG CE-29Q90ID Color TV Service ManualJan DettlaffNo ratings yet
- M Tech Industrial Power Automation SyllabusDocument55 pagesM Tech Industrial Power Automation SyllabusZaher V Abdul RahamanNo ratings yet
- Weekend VHF Uhf Power AmplifierDocument5 pagesWeekend VHF Uhf Power AmplifierEm GomezNo ratings yet
- MK32P VE_MULTIDocument2 pagesMK32P VE_MULTIEvgenyPetrovich0% (1)
- Manual de Service para TV LED PhilipsDocument108 pagesManual de Service para TV LED Philipstavillo1980No ratings yet
- Soft-Switching Current-Fed Push-Pull Converter For PV ApplicationDocument6 pagesSoft-Switching Current-Fed Push-Pull Converter For PV ApplicationDebdeep MondalNo ratings yet
- p80c51bh IntelDocument21 pagesp80c51bh Intelyash_pachauryNo ratings yet
- SSD 9971Document4 pagesSSD 9971Popa GabrielNo ratings yet
- Design A Logamp RF Pulse DetectorDocument5 pagesDesign A Logamp RF Pulse DetectorEric SorensenNo ratings yet
- Android 3.1 USB HostDocument20 pagesAndroid 3.1 USB HostBa DanNo ratings yet
- Development of JTAG Verification IP in UVM MethodologyDocument3 pagesDevelopment of JTAG Verification IP in UVM MethodologyKesavaram ChallapalliNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering Thesis SamplesDocument4 pagesElectrical Engineering Thesis Samplesazyxppzcf100% (2)
- Class Notes - Components of Numerical Relay & Anti-aliasing FilterDocument8 pagesClass Notes - Components of Numerical Relay & Anti-aliasing FilterbiswajitsahooNo ratings yet
- Apu Carc 03 LMCDocument34 pagesApu Carc 03 LMCRamrekha AkshayNo ratings yet
- Simulation Study of A Three Phase Transmission LineDocument21 pagesSimulation Study of A Three Phase Transmission LineAsith SavindaNo ratings yet
- Abstract-An Analog Circuit For The Fitzhugh-Nagumo Equations IsDocument5 pagesAbstract-An Analog Circuit For The Fitzhugh-Nagumo Equations Isneel1237No ratings yet
- Sirio Dualband Ant CatalogDocument10 pagesSirio Dualband Ant Catalog10sd156No ratings yet
- Milli Volt DropDocument2 pagesMilli Volt Dropkazishah100% (1)
- Module 4 - Number Systems and Boolean AlgebraDocument8 pagesModule 4 - Number Systems and Boolean AlgebraSuyog ChavanNo ratings yet
- Simulation and Implementation of FC-TCR: Sumit K Rathor (IEEE Member), Chintan Patel, Mithila S ZodapeDocument10 pagesSimulation and Implementation of FC-TCR: Sumit K Rathor (IEEE Member), Chintan Patel, Mithila S Zodapehamza mandlwiNo ratings yet
- Programmable DPM RISH: Data SheetDocument5 pagesProgrammable DPM RISH: Data SheetMartin SanabriaNo ratings yet
- TK-25 05-18 RHDocument1 pageTK-25 05-18 RHDhruba DasNo ratings yet
- ITC-Chapter 02-System Unit 39847 663Document21 pagesITC-Chapter 02-System Unit 39847 663Baktash AhmadiNo ratings yet
- MB Manual Ga-890fxa Ud5 v2Document120 pagesMB Manual Ga-890fxa Ud5 v2dsonic2007No ratings yet
- SST26VF064BDocument76 pagesSST26VF064Bmar_barudjNo ratings yet