0% found this document useful (0 votes)
235 views22 pagesOverview of Immunoglobulins and Their Structure
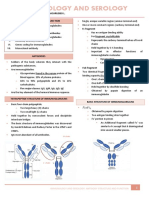
Immunoglobulins, also known as antibodies, are Y-shaped glycoproteins produced by plasma cells that recognize and bind to specific antigens. There are 5 classes of immunoglobulins - IgG, IgA, IgM, IgD, and IgE - which have the same basic antibody structure of two light chains and two heavy chains. The variable regions of the light and heavy chains form the antigen binding site that is specific to each antibody's target antigen.
Uploaded by
lianazulakCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
235 views22 pagesOverview of Immunoglobulins and Their Structure
Immunoglobulins, also known as antibodies, are Y-shaped glycoproteins produced by plasma cells that recognize and bind to specific antigens. There are 5 classes of immunoglobulins - IgG, IgA, IgM, IgD, and IgE - which have the same basic antibody structure of two light chains and two heavy chains. The variable regions of the light and heavy chains form the antigen binding site that is specific to each antibody's target antigen.
Uploaded by
lianazulakCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd