0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2K views22 pagesLensing Scheme
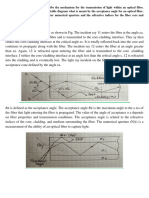
1) This chapter discusses various methods of coupling light between optical sources and fibers, as well as fiber-to-fiber coupling, including launching light into fibers from LEDs and lasers, fiber splicing, and fiber connectors.
2) It provides equations to calculate coupling efficiency between a source and fiber based on their radiance profiles and numerical apertures.
3) When coupling between fibers, losses are influenced by mechanical alignment, longitudinal offsets, end face defects, and modal distributions between the fibers. Splicing and connectors are discussed as demountable connection methods.
Uploaded by
nandiniCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2K views22 pagesLensing Scheme
1) This chapter discusses various methods of coupling light between optical sources and fibers, as well as fiber-to-fiber coupling, including launching light into fibers from LEDs and lasers, fiber splicing, and fiber connectors.
2) It provides equations to calculate coupling efficiency between a source and fiber based on their radiance profiles and numerical apertures.
3) When coupling between fibers, losses are influenced by mechanical alignment, longitudinal offsets, end face defects, and modal distributions between the fibers. Splicing and connectors are discussed as demountable connection methods.
Uploaded by
nandiniCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd