Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Amazon Web Services: The Blue Book Pages 19 Onwards
Uploaded by
Kamran Bhatti0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2K views12 pagesAmazone web service
Original Title
AWS Presentation
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentAmazone web service
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2K views12 pagesAmazon Web Services: The Blue Book Pages 19 Onwards
Uploaded by
Kamran BhattiAmazone web service
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 12
Amazon Web Services
The Blue Book pages 19 onwards
References
http://developer.amazonwebservices.com/
connect/forumindex.jspa
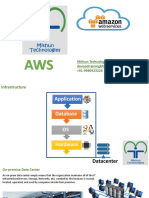
An overview of AWS
AWS is Amazons umbrella description of all
of their web-based technology services.
Mainly infrastructure services:
Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2)
Amazon Simple Storage Service (S3)
Amazon Simple Queue Service (SQS)
Amazon CloudFront
Amazon SimpleDB
Amazon EC2 is hiring
http://aws.amazon.com/ec2-jobs/
Amazon EC2
EC2 provides web services API for
provisioning, managing, and deprovioning
virtual servers inside amazon cloud.
Applications anywhere on the Internet
can launch a virtual server in the amazon
cloud with a single web services call
(either REST or SOAP WS call)
Where is SOAP API? For example,
http://docs.amazonwebservices.com/AmazonEC2/dg/2006-06-26/using-soap-api.html
Storage
Instance store : disappears with the
instance (transient)
Block storage: SAN-like, persists across
time
S3 is independent of an instance: for
archival purposes: vault: store it now and
retrieve it at a later date
Amazon: SimpleDB: Relational database
better than MySQl or Oracle for
reliability.
Amazon Cloud-front
Cloud-based content distributing network
enables you to place the content at the
edges of the network for rapid delivery.
Place the contents in S3 and run the
application from anywhere and the
content is moved to where the
application is (to the edges).
S3
Amazon web services API support the ability to:
Find buckets and objects
Discover their meta data
Create new buckets
Upload new objects
Delete existing buckets and objects
When manipulating the buckets you can optionally
specify where they should be stored.
Use REST API preferably something that abstracts out
even that: Jets3t; s3cmd (command line)
BitTorrent access to S3 is also available
Bucket Naming
Flat namespace
Names may contain only lowercase
letters, numbers, periods, underscores,
and dashes, and must start with a number
or letter
Create your own namespace with your
own bcukets
EC2 concepts
See figure 2.1
Instance: virtual server running a guest os
of your choice
AMI: Pristine image of your server so that
you can launch any number of instance
from this. Minimally machine image will
operating systems + pre-installed tools.
Elastic IP address: Not static not dynamic
but elastic; an IP reserved for your use;
disappears once the server is terminated.
EC2 (contd.)
Availability zone: Any two availability zones are
guaranteed to share any common points of
failure ( US, EU, Asia/Pacific)
Security group: define the firewall/security.
Defines what can talk to your instances. (Ex;
http, and not sftp etc.)
Snap shot: You can take snapshots of block
volume (that can be formatted etc) and is
stored in S3 for later use or for rollback etc.
What is the difference between instances and
machine images?
How to access Ec2?
AWS console
http://console.aws.amazon.com
The ElasticFox firefox plugin
The amazon command line tool
Typical Use in an organization
Maintain a library of AMIs for the business
May contain legacy systems or company-specific
systems
Harden AMIs using such software as Bastille
Launch instances for non-technical but domain
experts to work with.
What will you provide them so that they can start
working?
Use S3 for archival storage and shared storage
You might also like
- Amazon EC2Document13 pagesAmazon EC2Saranya ThangarajNo ratings yet
- Masterclass Webinar - Amazon EC2Document111 pagesMasterclass Webinar - Amazon EC2Ngoc Dong QuanNo ratings yet
- Amazon Web Services TrainingDocument5 pagesAmazon Web Services TrainingvisualpathNo ratings yet
- Azure Stack HciDocument1,600 pagesAzure Stack HciPt BuddhakirdNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing and Microsoft Azure - FAQ'sDocument23 pagesCloud Computing and Microsoft Azure - FAQ'spraveenmpkNo ratings yet
- AWS-New PPTSDocument110 pagesAWS-New PPTSpavani2571No ratings yet
- Jenkins: Continuous Integration - Written in JavaDocument54 pagesJenkins: Continuous Integration - Written in Javaatul bhardwajNo ratings yet
- 1 AwsDocument30 pages1 AwsAslam AnsariNo ratings yet
- Installing Ansible - Ansible DocumentationDocument14 pagesInstalling Ansible - Ansible Documentationjlieghton7157No ratings yet
- AzureARM Handout M5&6-1Document1 pageAzureARM Handout M5&6-1Vijay BalanNo ratings yet
- Course Content: AWS ConceptsDocument3 pagesCourse Content: AWS ConceptsSujeendra kumarNo ratings yet
- GCP Collated Version1Document22 pagesGCP Collated Version1Sivakumar Bala100% (1)
- Azure, Powershell, and SQL Server Virtual Machines: Rob VolkDocument17 pagesAzure, Powershell, and SQL Server Virtual Machines: Rob VolkKuppurasu NagarajNo ratings yet
- DevopsDocument13 pagesDevops05-Neha Kadam100% (1)
- Introduction To ServersDocument32 pagesIntroduction To ServersGlezelBayubayNo ratings yet
- Amazon S3 Essentials - Sample ChapterDocument13 pagesAmazon S3 Essentials - Sample ChapterPackt PublishingNo ratings yet
- Resume JCPAUKCloudCDocument2 pagesResume JCPAUKCloudCLuis Carlos Covilla YarceNo ratings yet
- Azure Devops Get Started Azure DevopsDocument521 pagesAzure Devops Get Started Azure DevopsJalalNo ratings yet
- Control M Jobs - An OverviewDocument14 pagesControl M Jobs - An Overviewputtu1No ratings yet
- AmazonElasticComputeCloud-Getting Started With EC2Document19 pagesAmazonElasticComputeCloud-Getting Started With EC2Konstantinos ChatziamallosNo ratings yet
- Amazon Elastic Compute CloudDocument8 pagesAmazon Elastic Compute CloudsohelsunNo ratings yet
- Aws LinuxAcademyDocument8 pagesAws LinuxAcademymitiwanaNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computin G: Sanjay Gandhi Institute of Engineering & TechnologyDocument27 pagesCloud Computin G: Sanjay Gandhi Institute of Engineering & TechnologyadityaphoolpurNo ratings yet
- Artifactory With Amazon Ecs On The Aws Cloud PDFDocument37 pagesArtifactory With Amazon Ecs On The Aws Cloud PDFKevin MadhuNo ratings yet
- Combine PDFDocument113 pagesCombine PDFsanjayNo ratings yet
- AWS Amazon VPC Connectivity Options PDFDocument31 pagesAWS Amazon VPC Connectivity Options PDFShantanu MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Azure Stack HCI Overview WhitepaperDocument12 pagesAzure Stack HCI Overview Whitepaperjohnlondon125No ratings yet
- Website On AWSDocument20 pagesWebsite On AWSmydatasyncNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Cloud CoumptingDocument21 pagesIntroduction To Cloud Coumpting28 POOJA POOJANo ratings yet
- Cloud ComputingDocument18 pagesCloud ComputingQazi AliNo ratings yet
- Devops Master Program Syllabus: Mithun Software Solutions BangaloreDocument12 pagesDevops Master Program Syllabus: Mithun Software Solutions BangaloreRamakant SinghNo ratings yet
- Presentation On: Cloud ComputingDocument18 pagesPresentation On: Cloud ComputingMadhusudan MujawdiyaNo ratings yet
- Azure Online TrainingDocument4 pagesAzure Online TrainingashapriyaNo ratings yet
- AWS Solution Architect Associate Agenda PDFDocument6 pagesAWS Solution Architect Associate Agenda PDFSamaram SamNo ratings yet
- MicroDegree AWS NotesDocument85 pagesMicroDegree AWS NotesAshwiniNo ratings yet
- Lab-6 Ec2 InstanceDocument11 pagesLab-6 Ec2 InstanceEswarchandra PinjalaNo ratings yet
- Aws Odd Interview QuestionsDocument36 pagesAws Odd Interview QuestionsZubair AhmadNo ratings yet
- SQL Capacity PlaningDocument7 pagesSQL Capacity PlaningMadhan MohanNo ratings yet
- Troubleshoot Windows Ad Auth PDFDocument39 pagesTroubleshoot Windows Ad Auth PDFJoseph SamuelNo ratings yet
- AWS Admin AWS Account Creation and Navigation by Kv. ReddyDocument22 pagesAWS Admin AWS Account Creation and Navigation by Kv. ReddyRavi SankasrNo ratings yet
- Amazon Elastic File SystemDocument180 pagesAmazon Elastic File SystemshiivangNo ratings yet
- Cognixia 360° MASTERS TRAINING PROGRAM IN AWSDocument25 pagesCognixia 360° MASTERS TRAINING PROGRAM IN AWSshivNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Notes 1Document12 pagesCloud Computing Notes 1Roshan JhaNo ratings yet
- 2 AWS StorageDocument16 pages2 AWS StorageAslam AnsariNo ratings yet
- Using Terraform in The Context of AWS Multi-Account SetupsDocument25 pagesUsing Terraform in The Context of AWS Multi-Account SetupsTonyNo ratings yet
- Create A Web Server and An Amazon RDS DatabaseDocument22 pagesCreate A Web Server and An Amazon RDS DatabaseAnshul KathetNo ratings yet
- Azure ConceptsDocument6 pagesAzure ConceptsNew sonNo ratings yet
- Automating Infrastructure Deployments in The Cloud With Terraform and Azure PipelinesDocument12 pagesAutomating Infrastructure Deployments in The Cloud With Terraform and Azure PipelinesabacusdotcomNo ratings yet
- Terraform NotesDocument7 pagesTerraform NotesRavi Teja100% (2)
- 110+ Devops Interview Questions and Answers For 2023: 1. What Do You Know About Devops?Document74 pages110+ Devops Interview Questions and Answers For 2023: 1. What Do You Know About Devops?SYED IFTAQAR HUSSAINNo ratings yet
- AWS Solution Architect Syllabus - by Murali P N, Besant TechnologiesDocument7 pagesAWS Solution Architect Syllabus - by Murali P N, Besant Technologiesakash sheelvanthNo ratings yet
- DockerDocument25 pagesDockerBiplab ParidaNo ratings yet
- Module 7: Data Management Backup, DR, Test/Dev EnvironmentsDocument9 pagesModule 7: Data Management Backup, DR, Test/Dev EnvironmentssrinubasaniNo ratings yet
- ConceptsDocument500 pagesConceptsHarsha DEVOPSNo ratings yet
- AKS BookletDocument12 pagesAKS BookletRonald ValdésNo ratings yet
- 15 Reasons To Use Redis As An Application Cache: Itamar HaberDocument9 pages15 Reasons To Use Redis As An Application Cache: Itamar Haberdyy dygysd dsygyNo ratings yet
- Hands-On Lab: Building A VPC From ScratchDocument5 pagesHands-On Lab: Building A VPC From ScratchAnuj MittalNo ratings yet
- Mastering Azure Kubernetes ServiceDocument8 pagesMastering Azure Kubernetes Serviceamitmaurya1No ratings yet
- Azure Vs Amazon EC2Document35 pagesAzure Vs Amazon EC2robin69hNo ratings yet
- Running Neo4j Graph Databases On AWSDocument26 pagesRunning Neo4j Graph Databases On AWSpark hyoNo ratings yet
- External Configuration 5.2.5 - PDFDocument689 pagesExternal Configuration 5.2.5 - PDFEphrem AlemuNo ratings yet
- Sns DGDocument249 pagesSns DGRobin LiNo ratings yet
- AWS EC2 Interview Questions - MindMajixDocument27 pagesAWS EC2 Interview Questions - MindMajixjgovindaraajNo ratings yet
- AWS Best PracticesDocument7 pagesAWS Best PracticesYogesh raoNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing: Post Graduate Program inDocument19 pagesCloud Computing: Post Graduate Program indipeshNo ratings yet
- Product & Solutions Overview: Ananda Rajagopal VP, Product Line ManagementDocument37 pagesProduct & Solutions Overview: Ananda Rajagopal VP, Product Line ManagementCCIE DetectNo ratings yet
- Hierarchy of Faysal Bank - Editable Diagram Template On CreatelyDocument5 pagesHierarchy of Faysal Bank - Editable Diagram Template On CreatelyAli RajpootNo ratings yet
- Chapter3 M1Document36 pagesChapter3 M1kgolchha2204No ratings yet
- Aws TYSonDocument15 pagesAws TYSonPradeesh S AINo ratings yet
- Log Collection Into Splunk With Control TowerDocument25 pagesLog Collection Into Splunk With Control ToweraalejoNo ratings yet
- Ejemplo 2 Factura Amz PDFDocument3 pagesEjemplo 2 Factura Amz PDFValeriaNo ratings yet
- CIS Question BankDocument3 pagesCIS Question BankGhggNo ratings yet
- 2 D Storage On AWSDocument61 pages2 D Storage On AWSpablogarlandeiraNo ratings yet
- Data and Analytics Skills TrackerDocument23 pagesData and Analytics Skills TrackerMuhammad FaizanNo ratings yet
- Edureka AWS EbookDocument24 pagesEdureka AWS EbookRanjan Yadav100% (3)
- AWS Lab Practice Guide by WWW - Server-Computer - Com - v1Document86 pagesAWS Lab Practice Guide by WWW - Server-Computer - Com - v1ayman IbaidaNo ratings yet
- Caltech - PG Program in Cloud ComputingDocument22 pagesCaltech - PG Program in Cloud ComputingkaperumaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Fundamentals of Cloud ComputingDocument29 pagesUnit 1 Fundamentals of Cloud ComputingShriprasad JadhavNo ratings yet
- The Forrester Wave™ - Cloud Data Warehouse, Q1 2021Document15 pagesThe Forrester Wave™ - Cloud Data Warehouse, Q1 2021Carlos Alonso Fernandez100% (1)
- Forester 2020 Wave WAFDocument17 pagesForester 2020 Wave WAFM.A. FaisalNo ratings yet
- An Introdcution To AWS Cloud Security-ETDADocument33 pagesAn Introdcution To AWS Cloud Security-ETDAkavinduNo ratings yet
- Amazon Web Services - WikipediaDocument16 pagesAmazon Web Services - Wikipediasai vishnu vardhanNo ratings yet
- Amazon Web Services (Aws)Document13 pagesAmazon Web Services (Aws)shanmathi100% (1)
- Aws SDK Java DGDocument167 pagesAws SDK Java DGmahesh_rampalliNo ratings yet
- GitHub - SkullTech - Aws-Solutions-Architect-Associate-Notes - My Notes For AWS Solutions Architect AssociateDocument19 pagesGitHub - SkullTech - Aws-Solutions-Architect-Associate-Notes - My Notes For AWS Solutions Architect Associateaznabi100% (1)
- Santosh Goud - Senior AWS Big Data EngineerDocument9 pagesSantosh Goud - Senior AWS Big Data EngineerPranay GNo ratings yet
- AWS Architect Associate Document - Part 1 13367566 2023 03-02-00 07Document408 pagesAWS Architect Associate Document - Part 1 13367566 2023 03-02-00 07ateeqrahman032582No ratings yet
- Amazon Web Services Certforall Saa-C03 Vce Download 2022-Dec-27 by Martin 138q VceDocument19 pagesAmazon Web Services Certforall Saa-C03 Vce Download 2022-Dec-27 by Martin 138q VcedipakNo ratings yet
- AWS Solutions Architect Certification Training Brochure Converted 1Document18 pagesAWS Solutions Architect Certification Training Brochure Converted 1PAnkaj DHullNo ratings yet