Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Revit Architecture Training Institute in Ameerpet
Revit Architecture Training Institute in Ameerpet
Uploaded by
futuregen technologies0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
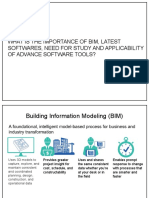
7 views6 pagesRevit Architecture is design for Architects, Civil Engineers, Draftsmen and Interior Designers to design and document a building by creating a parametric three dimensional model that includes both geometry and non-geometry design and construction information which is also known as building information modeling (BIM).
Original Title
Revit Architecture training institute in ameerpet
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentRevit Architecture is design for Architects, Civil Engineers, Draftsmen and Interior Designers to design and document a building by creating a parametric three dimensional model that includes both geometry and non-geometry design and construction information which is also known as building information modeling (BIM).
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views6 pagesRevit Architecture Training Institute in Ameerpet
Revit Architecture Training Institute in Ameerpet
Uploaded by
futuregen technologiesRevit Architecture is design for Architects, Civil Engineers, Draftsmen and Interior Designers to design and document a building by creating a parametric three dimensional model that includes both geometry and non-geometry design and construction information which is also known as building information modeling (BIM).
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
Mail Us:-info@futuregentechnologies.
com
Phone: +91 8328253848
Revit Architecture is design for Architects, Civil
Engineers, Draftsmen and Interior Designers to
design and document a building by creating a
parametric three dimensional model that includes
both geometry and non-geometry design and
construction information which is also known as
building information modeling (BIM).
The Fundamental benefits of BIM
Quick Changes to Design, No Repetitive Tasks:
During the design phase, the building structure and floor plans needed to be modified frequently. With
Revit BIM software, architecture designing and drafting becomes very fast and accurate. In Revit
architecture model, all building components such as plans, sections, and elevations are intelligently
connected to each another. Whenever a change is made to the model, the software automatically
updates every related component, affecting the whole building model.
High Quality Construction Documents:
3D modeling capacity of Revit architecture enables designers and drafters to easily identify the clashes
and areas of congestion, and resolve them early in the process. It results in error-free and high quality
construction documentations.
Accurate Estimation of Quantities and Cost:
One of the most important advantages of building information modeling software is the automatic
generation of bill of quantities (BOQ). BIM modeling software like Revit produces accurate material
quantity takeouts as a by-product, with less-efforts. This advantage helps the contractors and owners to
determine if the project adheres to budgets.
Improved Coordination :
BIM drafting software Revit unifies design, drafting, construction and facility management processes in
single environment, allowing all stakeholders to remain updated and aware of their responsibilities, and
thus improving overall coordination. A total understanding by everyone on the projects of whats
happening removes the design conflicts and risks.
High Level of Flexibility :
Unlike AutoCAD, Revit allows all projects data to be stored in single project file. It allows multiple users to
work on the same project file and merge their changes with every save. Besides, Revit exports and
imports DWG, DXF, DGN, PDF, JPEG files.
The list of BIM advantages continues. It is proved that BIM approach is significantly more efficient that
the traditional drafting- based approach. A significant numbers of architecture design and drafting
company are realizing the implementation of BIM software.
Introduction
Core Concepts
Introducing building information modelling (BIM)
Working in one model with many views
Understanding Revit element hierarchy
Getting Comfortable with the Revit Environment
Understanding the different versions of Revit
Exploring the application menu
Exploring the application menu
Understanding context ribbons
Using the Properties palette
Navigating views: Zooming, panning
The basics of selecting and modifying
Starting a Project
Creating a new project from a template
Accessing a multi-user project with work sharing
Configuring project settings
Adding levels
Adding levels
Refining a layout with temporary dimensions
Adding columns
Adding walls
Using snap
Modeling Basics
Exploring wall properties and types
Locating walls
Using the modify tools
Adding doors and windows
Using constraints
Adding plumbing fixtures and other components
Links, Imports, and Groups
Linking AutoCAD DWG files
Creating topography from a DWG link
Understanding CAD inserts
Creating a group
Creating Revit links
Rotating and aligning a Revit
Managing links
Adding walls
Using snaps
Sketch-Based Modeling Components
Working with floors
Working with footprint roofs
Working with extrusion roofs
Attaching walls to roofs
Attaching walls to roofs
Adding openings
Working with stairs
Adding railings to stairs
Adding railings to stairs
Visibility and Graphic Controls
Working with visibility and graphic overrides
Using view templates
Hiding and isolating objects in a model
Understanding view range
Schedules and Tags
Understanding tags
Adding schedule views
Modifying schedule views
Creating a key schedule
Annotation and Details
Adding text
Adding dimensions
Adding symbols
Adding legend views
Creating a detail callout
Using arrays to duplicate objects parametrically
Adding filled and masking regions
Basic Editing Tools
Basic Editing Tools
Using Filter
Use Of The TAB Key
Moving And Copying
Copy And Paste
Copy And Paste
Mirror
Linear Arrays
Radial Arrays
Extend And Trim
The Align tool
Offset
Re-Hosting Elements
Views
Controlling Visibility
Initial Plan Views
View Duplication
Elevations
Sections
Creating Callouts
Ceiling Plans
Section Box
Scope Box
Spaces And Zones
Spaces And Zones
Creating Spaces
Space Separation Boundaries
Modifying Spaces
Space Tags
Area And Volume Calculations
Creating Zones
The System Browser And Zones
Color Schemes
The Basics of Families
Understanding families
Creating a new family from a template
Using reference planes, parameters, and constraints
Adding solid geometry
Cutting holes using void geometry
Adding blends
Completing the family
Sheets, Plotting, and Publishing
Adding sheets
Outputting sheets to a DWF file
Exporting to AutoCAD
Plotting and creating a PDF
You might also like
- Log in or Sign UpDocument9 pagesLog in or Sign UpgirmshNo ratings yet
- PED 4074G Pedders GVM Folders GVM Matrix TableDocument1 pagePED 4074G Pedders GVM Folders GVM Matrix Tableubwdo22No ratings yet
- Revit Standards Manual V2Document91 pagesRevit Standards Manual V2Nhu Huynh100% (1)
- Application Note 98: VFP Support CodeDocument27 pagesApplication Note 98: VFP Support CodenfwuNo ratings yet
- Case Study Analysis CASBAADocument2 pagesCase Study Analysis CASBAAkrishna chaitanya0% (1)
- Project Acceptance CriteriaDocument26 pagesProject Acceptance CriteriaRobertPietras100% (1)
- MultiMedia Quiz 6Document3 pagesMultiMedia Quiz 6Mark Anthony DagonNo ratings yet
- Revit Architecture Training in HyderabadDocument7 pagesRevit Architecture Training in Hyderabadfuturegen technologiesNo ratings yet
- ARCADIS White Paper Building Information Modeling HalvorsonDocument16 pagesARCADIS White Paper Building Information Modeling HalvorsonCarlos Lopez FigueroaNo ratings yet
- Revit Architecture 2010 BrochureDocument6 pagesRevit Architecture 2010 BrochuregopalNo ratings yet
- Welcome : Revit ArchitectureDocument20 pagesWelcome : Revit ArchitectureRahul kumar ChandelNo ratings yet
- Revit Structure 2010 BrochureDocument6 pagesRevit Structure 2010 BrochureMohamed Omer HassanNo ratings yet
- Autodesk Revit What Is Autodesk Revit?Document3 pagesAutodesk Revit What Is Autodesk Revit?Vidya Muthukrishnan100% (1)
- Internship On Revit ArchitectureDocument26 pagesInternship On Revit ArchitectureSumit Sulibhavi 2BA18CV434100% (1)
- Revit Architecture Overview Brochure enDocument6 pagesRevit Architecture Overview Brochure enapi-81040815No ratings yet
- Software Application For Quantity Surveying ReportDocument29 pagesSoftware Application For Quantity Surveying ReportDarrenTofuNo ratings yet
- What Is Role of Revit in Construction Industry?Document3 pagesWhat Is Role of Revit in Construction Industry?Dhyan AcademyNo ratings yet
- BIMDocument15 pagesBIMAhmed AbdelMaksoud100% (1)
- Introduction To BIM: Prelim Learning ResourceDocument79 pagesIntroduction To BIM: Prelim Learning ResourceLUGA JONNAH LORRAINE100% (1)
- Revit MEP UsesDocument2 pagesRevit MEP UsesMahesh MohanNo ratings yet
- What Is RevitDocument1 pageWhat Is RevitFuture MaskNo ratings yet
- Get To Know About What Is Benifit of Autodesk Revit MEP?Document6 pagesGet To Know About What Is Benifit of Autodesk Revit MEP?AutuCadNo ratings yet
- Bachelor of Quantity Surveying (Honours) Construction Supply Chain Management (MGT 60803) Group Assignment March 2017Document23 pagesBachelor of Quantity Surveying (Honours) Construction Supply Chain Management (MGT 60803) Group Assignment March 2017Shinde vishalNo ratings yet
- Autodesk Revit: Objective of TrainingDocument3 pagesAutodesk Revit: Objective of TrainingNotes 56No ratings yet
- RVT PMDocument2 pagesRVT PMFELIXNo ratings yet
- Autodesk Revit Building For Autocad Users: True 3D DesignDocument5 pagesAutodesk Revit Building For Autocad Users: True 3D DesignSonam TobgyeNo ratings yet
- Autodesk Revit Master Course: ModeDocument4 pagesAutodesk Revit Master Course: ModeThai chheanghourtNo ratings yet
- Bim y CadDocument3 pagesBim y CadcatalinaNo ratings yet
- Revitarchitecture 171211161251Document48 pagesRevitarchitecture 171211161251ARUNIMA S RAJUNo ratings yet
- RevitDocument6 pagesRevitsuhail.akhoon100% (1)
- BIM Tools MatrixDocument5 pagesBIM Tools MatrixbdiitNo ratings yet
- Building Information Modeling Presentation by Kamal ShawkyDocument24 pagesBuilding Information Modeling Presentation by Kamal ShawkyKamal Shawky67% (3)
- BIM Mechanical, Electrical and Plumbing (MEP) CourseDocument14 pagesBIM Mechanical, Electrical and Plumbing (MEP) CourseMohammed Nadeem KhanNo ratings yet
- Bim, HWDocument4 pagesBim, HWSamahrNo ratings yet
- Autodesk Revit Architecture 2013Document4 pagesAutodesk Revit Architecture 2013pastor2009No ratings yet
- Architects Guide To 3D ModelingDocument25 pagesArchitects Guide To 3D ModelingOzgur OzkanNo ratings yet
- Online Revit Architecture Course-Bes PDFDocument5 pagesOnline Revit Architecture Course-Bes PDFirfan akramNo ratings yet
- 19H61A0152Document27 pages19H61A0152153-B RAKSHITHANo ratings yet
- Revit Software: Rafia Ameer BEE153113Document4 pagesRevit Software: Rafia Ameer BEE153113Nayab abbaxiNo ratings yet
- Archetecture ThesisDocument65 pagesArchetecture ThesisAin roseNo ratings yet
- Building Information Modeling NotesDocument12 pagesBuilding Information Modeling NotesAldrín Calma BaluyotNo ratings yet
- Building Information Modeling (BIM) Technology: Seamlessly Bridging Communication Throughout The Building ProcessDocument7 pagesBuilding Information Modeling (BIM) Technology: Seamlessly Bridging Communication Throughout The Building ProcessJulio Humberto Díaz RondánNo ratings yet
- Quiz1-Haneen HamdonaDocument3 pagesQuiz1-Haneen HamdonaHaneen HamdonaNo ratings yet
- Using The Coordination Monitoring Feature in Revit Structure PDFDocument14 pagesUsing The Coordination Monitoring Feature in Revit Structure PDFJeneish JustusNo ratings yet
- Irjet-4D ScheduleDocument8 pagesIrjet-4D ScheduleDivyesh ParmarNo ratings yet
- Autodesk® Revit® Getting Started GuideDocument73 pagesAutodesk® Revit® Getting Started GuideDSunte Wilson100% (2)
- 4 - Revit Course OutlineDocument2 pages4 - Revit Course OutlinedjgiumixNo ratings yet
- Impact of Information Technology On ArchitectureDocument12 pagesImpact of Information Technology On ArchitectureaparnaNo ratings yet
- Create Complex Façade Design With The Help of Revit - Parametric Freeform ElementsDocument7 pagesCreate Complex Façade Design With The Help of Revit - Parametric Freeform ElementsManpreet KaurNo ratings yet
- BIM and Latest Architectural SoftwareDocument39 pagesBIM and Latest Architectural SoftwareRuchy LakhaniNo ratings yet
- Tutorial REVIT para PrincipiantesDocument17 pagesTutorial REVIT para PrincipiantesBRENDA FERNANDEZNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1506 CR1506-L-P Construction Modeling in Revit PresentationDocument6 pagesPresentation 1506 CR1506-L-P Construction Modeling in Revit PresentationJuan Manuel Morales GómezNo ratings yet
- SDI Comprehensive Course On State-Of-The-Art BIM Practices With RevitDocument2 pagesSDI Comprehensive Course On State-Of-The-Art BIM Practices With RevitdjgiumixNo ratings yet
- Building Information Modelling (BIM) User Guide For Development and Construction Division of Hong Kong Housing Authority PDFDocument53 pagesBuilding Information Modelling (BIM) User Guide For Development and Construction Division of Hong Kong Housing Authority PDFracing.phreakNo ratings yet
- AB208 3 Autodesk Revit For Urban DesignDocument15 pagesAB208 3 Autodesk Revit For Urban DesignSergio Moruno SanchezNo ratings yet
- Revit SoftwareDocument2 pagesRevit Softwaremjrobust05No ratings yet
- Autodesk Architecture Brochure Letter En1Document4 pagesAutodesk Architecture Brochure Letter En1nguyenmythien_91No ratings yet
- The Ultimate Guide To Revit MEPDocument17 pagesThe Ultimate Guide To Revit MEPprakashsamthomasNo ratings yet
- BIM Cost Estimating enDocument8 pagesBIM Cost Estimating enIsmail MedoNo ratings yet
- AGACAD Booklet 2014Document12 pagesAGACAD Booklet 2014Dominik ŠvigirNo ratings yet
- Integrity of Revit With Structural Analysis SoftwaDocument8 pagesIntegrity of Revit With Structural Analysis SoftwaabdetaNo ratings yet
- Multi Disciplinary Project Collaboration Using BIMDocument31 pagesMulti Disciplinary Project Collaboration Using BIMFoo LoongNo ratings yet
- Exploring Autodesk Revit 2024 for Structure, 14th EditionFrom EverandExploring Autodesk Revit 2024 for Structure, 14th EditionNo ratings yet
- AIProject UG201110023Document4 pagesAIProject UG201110023pdffreedownloadNo ratings yet
- Visual FoxproDocument11 pagesVisual FoxprorvsnsatyamNo ratings yet
- 2012S1 Cosc 1301 5246Document10 pages2012S1 Cosc 1301 5246Christine LogueNo ratings yet
- Basic Machine Codes For CNC MillingDocument46 pagesBasic Machine Codes For CNC MillingMohd Zaieri100% (5)
- How To Run IOL ImagesDocument6 pagesHow To Run IOL Imagesafanbaloch1596No ratings yet
- ps1 PDFDocument5 pagesps1 PDFAnilNo ratings yet
- CloudonomicsDocument11 pagesCloudonomicsRojaNo ratings yet
- CM508Document1 pageCM508MarshdeLangeNo ratings yet
- 458 Socom Quickload 405 SPDocument2 pages458 Socom Quickload 405 SPDirk BucknerNo ratings yet
- E-Wallet ResearchDocument22 pagesE-Wallet ResearchMrudul BhattNo ratings yet
- RR, HTMLDocument4 pagesRR, HTMLAnonymous ONrIStAd3fNo ratings yet
- 2015-2-NSembilan-SMK ST Paul - MATHS QADocument8 pages2015-2-NSembilan-SMK ST Paul - MATHS QAVishalinie RamanNo ratings yet
- Backflush and Its Priority in Use - SAP BlogsDocument7 pagesBackflush and Its Priority in Use - SAP BlogsnabigcsNo ratings yet
- JJJJJJJDocument3 pagesJJJJJJJJoãoLucianiFerreiraNo ratings yet
- Midi Oberheim Mc3000 MC3000 GBDocument76 pagesMidi Oberheim Mc3000 MC3000 GBGiovanni FerrazziNo ratings yet
- Class5 Computer Worksheet Chapter 8Document3 pagesClass5 Computer Worksheet Chapter 8DevNo ratings yet
- Self Assessment ChecklistDocument3 pagesSelf Assessment ChecklistNausheen Ahmed NobaNo ratings yet
- Multi Thread ProgrammingDocument0 pagesMulti Thread ProgrammingVarun BhanNo ratings yet
- Sources of Mistakes in PFD Calculations For Safety-Related Loop TypicalsDocument4 pagesSources of Mistakes in PFD Calculations For Safety-Related Loop TypicalsAbdul HakimNo ratings yet
- Experiment No.2-Arithmetic Operation: Addition of Two 16-Bit Numbers-Signed & UnsignedDocument30 pagesExperiment No.2-Arithmetic Operation: Addition of Two 16-Bit Numbers-Signed & UnsignedHarinath ReddyNo ratings yet
- Remiv3.0 Manual PDFDocument79 pagesRemiv3.0 Manual PDFSpecific Earthquake ProjectNo ratings yet
- Cost, Revenue and ProfitDocument3 pagesCost, Revenue and ProfitmasyatiNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Pmbok VSN 3 and Prince2 Rel 4 Pmbok V3 Prince2 Rel 4 CommentsDocument14 pagesComparison of Pmbok VSN 3 and Prince2 Rel 4 Pmbok V3 Prince2 Rel 4 CommentsziasalahuddinNo ratings yet
- Program in CDocument10 pagesProgram in CNikhil MallviyaNo ratings yet