Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 1 - Basic Concept of Consumer Behavior
Uploaded by
Muhammad MunibCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 1 - Basic Concept of Consumer Behavior
Uploaded by
Muhammad MunibCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 1
Consumer Behavior:
Its Origins and
Strategic Applications
Consumer Behavior,
Ninth Edition
Schiffman & Kanuk
Copyright 2007 by Prentice Hall
Chapter Outline
• Overview of Consumer Behavior
• The Marketing Concept
• The Marketing Mix and Relationships
• Digital Technologies
• Societal Marketing Concept
• A Simplified Model of Consumer
Decision Making
Copyright 2007 by Prentice Hall 1-2
Consumer Behavior
The behavior that consumers display in
searching for, purchasing, using,
evaluating, and disposing of products
and services that they expect will satisfy
their needs.
Copyright 2007 by Prentice Hall 1-3
Customers Search for Products
weblink
Copyright 2007 by Prentice Hall 1-4
Personal Consumer
The individual who buys goods and
services for his or her own use, for
household use, for the use of a family
member, or for a friend.
Copyright 2007 by Prentice Hall 1-5
Organizational Consumer
A business, government agency, or other
institution (profit or nonprofit) that buys
the goods, services, and/or equipment
necessary for the organization to
function.
Copyright 2007 by Prentice Hall 1-6
Government Buying
weblink
Copyright 2007 by Prentice Hall 1-7
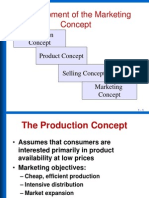
Development of the Marketing
Concept
Production
Concept
Product Concept
Selling Concept
Marketing
Concept
Copyright 2007 by Prentice Hall 1-8
The Production Concept
• Assumes that consumers are
interested primarily in product
availability at low prices
• Marketing objectives:
– Cheap, efficient production
– Intensive distribution
– Market expansion
Copyright 2007 by Prentice Hall 1-9
The Product Concept
• Assumes that consumers will buy the
product that offers them the highest
quality, the best performance, and the
most features
• Marketing objectives:
– Quality improvement
– Addition of features
• Tendency toward Marketing Myopia
Copyright 2007 by Prentice Hall 1 - 10
The Selling Concept
• Assumes that consumers are unlikely
to buy a product unless they are
aggressively persuaded to do so
• Marketing objectives:
– Sell, sell, sell
• Lack of concern for customer needs
and satisfaction
Copyright 2007 by Prentice Hall 1 - 11
The Marketing Concept
• Assumes that to be successful, a
company must determine the needs
and wants of specific target markets
and deliver the desired satisfactions
better than the competition
• Marketing objectives:
– Make what you can sell
– Focus on buyer’s needs
Copyright 2007 by Prentice Hall 1 - 12
Discussion Question
• What two companies do you believe
grasp and use the marketing concept?
• Why do you believe this?
Copyright 2007 by Prentice Hall 1 - 13
The Marketing Concept
Implementing the
Marketing Concept
• Consumer • The process and
Research tools used to study
• Segmentation consumer behavior
• Targeting • Two perspectives:
• Positioning – Positivist approach
– Interpretivist
approach
Copyright 2007 by Prentice Hall 1 - 14
weblink
Copyright 2007 by Prentice Hall 1 - 15
The Marketing Concept
Implementing the
Marketing Concept
• Consumer • Process of dividing
Research the market into
• Segmentation subsets of
• Targeting consumers with
common needs or
• Positioning characteristics
Copyright 2007 by Prentice Hall 1 - 16
Segmentation Used
by Sports Illustrated
Discussion Question
• What products that you regularly
purchase are highly segmented?
• What are the different segments?
• Why is segmentation useful to the
marketer for these products?
Copyright 2007 by Prentice Hall 1 - 18
The Marketing Concept
Implementing the
Marketing Concept
• Consumer The selection of one
Research or more of the
• Segmentation segments to pursue
• Targeting
• Positioning
Copyright 2007 by Prentice Hall 1 - 19
The Marketing Concept
Implementing the
Marketing Concept
• Consumer • Developing a distinct image
Research for the product in the mind
of the consumer
• Segmentation
• Successful positioning
• Targeting includes:
• Positioning – Communicating the
benefits of the product
– Communicating a unique
selling proposition
Copyright 2007 by Prentice Hall 1 - 20
This product is
positioned as
a solution to
facial redness.
The Marketing Mix
• Product
• Price
• Place
• Promotion
Copyright 2007 by Prentice Hall 1 - 22
Successful Relationships
Customer Customer
Value Retention
Customer
Satisfaction
Copyright 2007 by Prentice Hall 1 - 23
Successful Relationships
Value, Satisfaction,
and Retention
• Defined as the ratio between
• Customer the customer’s perceived
Value benefits and the resources
• Customer used to obtain those
Satisfaction benefits
• Perceived value is relative
• Customer
and subjective
Retention
• Developing a value
proposition is critical
Copyright 2007 by Prentice Hall 1 - 24
Discussion Question
• How does McDonald’s create value for
the consumer?
• How do they communicate this value?
Copyright 2007 by Prentice Hall 1 - 25
Successful Relationships
Value, Satisfaction,
and Retention
• Customer • The individual's perception of
the performance of the product
Value
or service in relation to his or
• Customer her expectations.
Satisfaction • Customers identified based on
• Customer loyalty include loyalists,
apostles, defectors, terrorists,
Retention
hostages, and mercenaries
Copyright 2007 by Prentice Hall 1 - 26
Successful Relationships
Value, Satisfaction,
and Retention
• The objective of providing value
• Customer is to retain highly satisfied
Value customers.
• Customer • Loyal customers are key
Satisfaction – They buy more products
• Customer – They are less price sensitive
Retention – They pay less attention to
competitors’ advertising
– Servicing them is cheaper
– They spread positive word of
mouth
Copyright 2007 by Prentice Hall 1 - 27
Customer Profitability-Focused
Marketing
• Tracks costs and revenues of
individual consumers
• Categorizes them into tiers based on
consumption behavior
• A customer pyramid groups customers
into four tiers
Copyright 2007 by Prentice Hall 1 - 28
Customer Profitability-Focused
Marketing
Tier 1: Platinum
Tier 2: Gold
Tier 3: Iron
Tier 4: Lead
Copyright 2007 by Prentice Hall 1 - 29
Traditional Marketing Concept Vs. Value
and Retention Focused Marketing
Table 1-2
Traditional Marketing Value and Retention
Concept Focused Marketing
Make only what you can sell instead Use technology that enables
of trying to sell what you make customers to customize what
you make
Do not focus on the product; focus on Focus on the product’s
the need that it satisfies perceived value, as well as the
need that it satisfies
Market products and services that Utilize an understanding of
match customers’ needs better than customer needs to develop
competitors’ offerings offerings that customers
perceive as more valuable than
competitors’ offerings
Copyright 2007 by Prentice Hall 1 - 30
Impact of Digital Technologies
• Consumers have more power and access to
information
• Marketers can gather more information about
consumers
• The exchange between marketer and
customers is interactive and instantaneous
and goes beyond the PC.
• Marketers must offer more products and
services
Copyright 2007 by Prentice Hall 1 - 31
Societal Marketing Concept
Marketers adhere to principles of social
responsibility in the marketing of their
goods and services; that is, they must
endeavor to satisfy the needs and
wants of their target markets in ways
that preserve and enhance the well-
being of consumers and society as a
whole.
Copyright 2007 by Prentice Hall 1 - 32
Consumer Behavior Is
Interdisciplinary
• Psychology
• Sociology
• Social psychology
• Anthropology
• Economics
Copyright 2007 by Prentice Hall 1 - 33
A Simplified Model of Consumer
Decision Making – Figure 1-1
Copyright 2007 by Prentice Hall 1 - 34
You might also like
- Psychometric AssessmentDocument9 pagesPsychometric Assessmentbalablooms100% (1)
- TalentDocument12 pagesTalentbalablooms100% (1)
- Factors That Shift The Supply-Demand Curve For Market of OrangeDocument14 pagesFactors That Shift The Supply-Demand Curve For Market of OrangeNurJalilah100% (2)
- Law of Supply and DemandDocument18 pagesLaw of Supply and DemandArnee Pantajo80% (5)
- 3-DAY Juice Fast: Satvic MovementDocument6 pages3-DAY Juice Fast: Satvic Movementbalablooms50% (2)
- 2 Unit Theories of Forwards & Future PricingDocument60 pages2 Unit Theories of Forwards & Future Pricingvijay kumarNo ratings yet
- Basic Microeconomics PDFDocument302 pagesBasic Microeconomics PDFSoniaNo ratings yet
- EthicsDocument31 pagesEthicsbalabloomsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5: The Five Generic Competitive Strategies: Which One To Employ?Document30 pagesChapter 5: The Five Generic Competitive Strategies: Which One To Employ?yrkprasadNo ratings yet
- Simply Better (Review and Analysis of Barwise and Meehan's Book)From EverandSimply Better (Review and Analysis of Barwise and Meehan's Book)No ratings yet
- Armstrong Mai13 Inppt 01Document52 pagesArmstrong Mai13 Inppt 01Đỗ ThúyNo ratings yet
- Topic 1Document22 pagesTopic 1CHUN CHENG CHOYNo ratings yet
- HTH 587 - Individual ProjectDocument10 pagesHTH 587 - Individual Projectwan aisya100% (3)
- Kotler MM 13e Basic 01Document23 pagesKotler MM 13e Basic 01MF RabbyNo ratings yet
- Ansoff's Matrix: Presented by:-P.Deepika Naidu Raj PatilDocument17 pagesAnsoff's Matrix: Presented by:-P.Deepika Naidu Raj PatilKritiYadavNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Entry and ExitDocument53 pagesChapter 6 - Entry and ExitMia Sentosa100% (2)
- Consumer Behavior: Its Origins and Strategic ApplicationsDocument27 pagesConsumer Behavior: Its Origins and Strategic ApplicationsjaafarNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behavior: Its Origins and Strategic ApplicationsDocument79 pagesConsumer Behavior: Its Origins and Strategic ApplicationsbabuluckyNo ratings yet
- CH - 01 Consumer BehaviourDocument29 pagesCH - 01 Consumer BehaviourPRIYA SRIVASTAVANo ratings yet
- CB Session1Document33 pagesCB Session1Chandra ShekarNo ratings yet
- ConceptsDocument32 pagesConceptsroshniNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behavior IntroductionDocument32 pagesConsumer Behavior IntroductionPreena SangdanNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behavior: Meeting Changes and ChallengesDocument22 pagesConsumer Behavior: Meeting Changes and ChallengesJagadeesh PutturuNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 Consumer, Marketers, and TechnologyDocument17 pagesTopic 1 Consumer, Marketers, and TechnologyKhang Nguyen DuyNo ratings yet
- Schiffman cb11 Ippt01Document34 pagesSchiffman cb11 Ippt01Shruti TayalNo ratings yet
- Schiffman CB10 PPT 01Document32 pagesSchiffman CB10 PPT 01via86100% (1)
- Cousumer Behaviour: - Dr. Satya Prasad VKDocument32 pagesCousumer Behaviour: - Dr. Satya Prasad VKVijju ChandraNo ratings yet
- Lec 1 CBDocument27 pagesLec 1 CBH. U. KonainNo ratings yet
- Principles of Marketing Eighth Edition Philip Kotler and Gary ArmstrongDocument15 pagesPrinciples of Marketing Eighth Edition Philip Kotler and Gary ArmstrongFahim KhanNo ratings yet
- 1 Determinants of Consumer Behavior Managing Customer ValueDocument39 pages1 Determinants of Consumer Behavior Managing Customer ValueSaurabh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Introduction: The Impact of The Digital Revolution On Consumer BehaviorDocument25 pagesIntroduction: The Impact of The Digital Revolution On Consumer Behaviormazhar_ibaNo ratings yet
- 2) 7. Market Identification and AnalysisDocument22 pages2) 7. Market Identification and AnalysisJhon Ace DuricoNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behavior: Meeting Changes and ChallengesDocument32 pagesConsumer Behavior: Meeting Changes and ChallengesHitesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behavior: Meeting Changes and ChallengesDocument22 pagesConsumer Behavior: Meeting Changes and Challengesmohamed ibrahimNo ratings yet
- Value Delivery Process Unit 2Document43 pagesValue Delivery Process Unit 2Amala SibyNo ratings yet
- Introduction: The Impact of The Digital Revolution On Consumer BehaviorDocument28 pagesIntroduction: The Impact of The Digital Revolution On Consumer BehaviorChristellaNo ratings yet
- Introduction: The Impact of The Digital Revolution On Consumer BehaviorDocument27 pagesIntroduction: The Impact of The Digital Revolution On Consumer BehaviorsekarangopiNo ratings yet
- Principles of Marketing REVIEWERDocument14 pagesPrinciples of Marketing REVIEWERAlthea SantillanNo ratings yet
- Module - I (Recap of FoM)Document19 pagesModule - I (Recap of FoM)Suvrata SarmaNo ratings yet
- Core Concepts-1Document12 pagesCore Concepts-1Sunidhi DasNo ratings yet
- Technology-Driven Consumer Behavior: Becamex Business SchoolDocument38 pagesTechnology-Driven Consumer Behavior: Becamex Business SchoolNhok NeoNo ratings yet
- Kotler MM 14e 01 IpptDocument20 pagesKotler MM 14e 01 IpptMahmuda ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Development of The Marketing Concept: Production Concept Product ConceptDocument21 pagesDevelopment of The Marketing Concept: Production Concept Product ConceptShaswat NigamNo ratings yet
- Armstrong Mai10e Stppt01Document20 pagesArmstrong Mai10e Stppt01ᘉNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behavior - Meeting Changes and ChallengesDocument39 pagesConsumer Behavior - Meeting Changes and ChallengesShah Ahmed RafizNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document29 pagesUnit 1Yaseen Nazir MallaNo ratings yet
- Kotler MM 13e Basic 01Document20 pagesKotler MM 13e Basic 01Pushpendra SinghNo ratings yet
- CH 1 Creating and Capturing Customer ValueDocument34 pagesCH 1 Creating and Capturing Customer ValueLuay MaaniNo ratings yet
- Intro To CBDocument48 pagesIntro To CBMikan SatoNo ratings yet
- Armstrong Mai13 Inppt 01Document47 pagesArmstrong Mai13 Inppt 01Hằng NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Chapter One: Creating and Capturing Customer ValueDocument32 pagesChapter One: Creating and Capturing Customer ValueTarek Monowar 1921659042No ratings yet
- Designing A Customer Value-Driven Marketing StrategyDocument12 pagesDesigning A Customer Value-Driven Marketing StrategyRenad AdnanNo ratings yet
- Revised - Fundamentals of Marketing - ClassDocument29 pagesRevised - Fundamentals of Marketing - ClassbonyNo ratings yet
- Session 2 Decision Areas in MarketingDocument31 pagesSession 2 Decision Areas in MarketingManan AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Perspective and Principle OfmarketingDocument24 pagesPerspective and Principle OfmarketingKrishna KumarNo ratings yet
- Chap 001 PDocument24 pagesChap 001 PyekoyesewNo ratings yet
- Meet Your Friendly LecturerDocument29 pagesMeet Your Friendly LecturerKevin SadeliNo ratings yet
- Marketing Q1-25 KanganaDocument15 pagesMarketing Q1-25 KanganaAnshuk PolasNo ratings yet
- S1 IntroductionDocument17 pagesS1 IntroductionNgoc Đặng Thị PhươngNo ratings yet
- Marketing and Marketing Management: Unit 1Document31 pagesMarketing and Marketing Management: Unit 1Suraj RouniyarNo ratings yet
- Marketing Chapter1Document36 pagesMarketing Chapter1KђaledܔܢܜܔNo ratings yet
- 01 Meeting Changes and ChallengesDocument28 pages01 Meeting Changes and ChallengesNawshin HuqNo ratings yet
- Chap001p MarketingDocument24 pagesChap001p MarketingMslkNo ratings yet
- Consumer Theory - Session OneDocument33 pagesConsumer Theory - Session OnePavitra KhandelwalNo ratings yet
- 01 Meeting Changes and ChallengesDocument28 pages01 Meeting Changes and ChallengesFariya PiashaNo ratings yet
- Advertising Chapt 01 KU DPADocument25 pagesAdvertising Chapt 01 KU DPATaha FayyazNo ratings yet
- 01 Meeting Changes and ChallengesDocument26 pages01 Meeting Changes and ChallengesRakibul Islam SrizonNo ratings yet
- Chapter7marketingmanagementv2 181123023210Document106 pagesChapter7marketingmanagementv2 181123023210budiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document34 pagesChapter 1muditha wijesundaraNo ratings yet
- Bienvenue Institute of Hotel and Catering ManagementDocument25 pagesBienvenue Institute of Hotel and Catering ManagementbalabloomsNo ratings yet
- Application Form - (Advt 1340 Dated 06-07-2018)Document2 pagesApplication Form - (Advt 1340 Dated 06-07-2018)balabloomsNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship and Start-Up Activities at Indian Higher Education InstitutionsDocument37 pagesEntrepreneurship and Start-Up Activities at Indian Higher Education InstitutionsbalabloomsNo ratings yet
- Proforma Form:Partnering Institution / Center: DateDocument4 pagesProforma Form:Partnering Institution / Center: DatebalabloomsNo ratings yet
- Invitation LetterDocument1 pageInvitation LetterbalabloomsNo ratings yet
- Resource Description and Access (RDA) and New Research PotentialsDocument5 pagesResource Description and Access (RDA) and New Research PotentialsbalabloomsNo ratings yet
- Teach EntrepreneurshipDocument12 pagesTeach EntrepreneurshipbalabloomsNo ratings yet
- 7 Key Components of An International Compensation ProgrammeDocument2 pages7 Key Components of An International Compensation ProgrammebalabloomsNo ratings yet
- Simsarc BrochureDocument2 pagesSimsarc BrochurebalabloomsNo ratings yet
- Snapdeal Aims: at Building The Most Impactful Digital Commerce Ecosystem in IndiaDocument2 pagesSnapdeal Aims: at Building The Most Impactful Digital Commerce Ecosystem in IndiabalabloomsNo ratings yet
- Score CardDocument19 pagesScore CardbalabloomsNo ratings yet
- Org StructureDocument27 pagesOrg StructurebalabloomsNo ratings yet
- Dr. Usha Natesan: Centre For Research Anna UniversityDocument1 pageDr. Usha Natesan: Centre For Research Anna UniversitybalabloomsNo ratings yet
- Mid MCDocument47 pagesMid MCPhuong PhamNo ratings yet
- Fin MarDocument3 pagesFin MarnhbNo ratings yet
- Unit 8. Firm Behaviour and Market Structure: Monopolistic Competition and Oligopoly Learning ObjectivesDocument9 pagesUnit 8. Firm Behaviour and Market Structure: Monopolistic Competition and Oligopoly Learning ObjectivesFahad FerozNo ratings yet
- Marketing Case StudyDocument2 pagesMarketing Case StudySandesh Kandel100% (2)
- Marketing Principles Revision NotesDocument12 pagesMarketing Principles Revision NotesCarol Helen90% (10)
- Solution To QUIZ 2Document1 pageSolution To QUIZ 2ALI HASSNAINNo ratings yet
- SCLMDocument6 pagesSCLMPraveen HansNo ratings yet
- C Commodity MarketDocument19 pagesC Commodity Marketshushalendra_6737803No ratings yet
- Economics, and Economic Terminology: BITS PilaniDocument408 pagesEconomics, and Economic Terminology: BITS PilaniModh MahatoNo ratings yet
- 11th Economics Full Study Material English Medium 2023-24Document75 pages11th Economics Full Study Material English Medium 2023-24TechnetNo ratings yet
- 2.2 and 2.5 Demand and Linear Demand RSDocument41 pages2.2 and 2.5 Demand and Linear Demand RSSyed HaroonNo ratings yet
- Microeconomics Assignment 2Document4 pagesMicroeconomics Assignment 2Stremio HubNo ratings yet
- Data-Driven Storytelling PresentationDocument5 pagesData-Driven Storytelling PresentationASMITA SONINo ratings yet
- Additional: Integration TopicsDocument23 pagesAdditional: Integration TopicshopebelleNo ratings yet
- Budget Constraint: Helia Rabie Spring 2021Document14 pagesBudget Constraint: Helia Rabie Spring 2021Helia RabieNo ratings yet
- Strategic Advertising Management: Chapter 5: The Strategic Planning ProcessDocument62 pagesStrategic Advertising Management: Chapter 5: The Strategic Planning ProcessYesfoo Al RiffaayNo ratings yet
- Kotler S SoftDocument238 pagesKotler S SoftMohit LakhotiaNo ratings yet
- Metabical Pricing Strategy - FarahqoonitaDocument10 pagesMetabical Pricing Strategy - FarahqoonitaFarah QoonitaNo ratings yet
- Microeconomics 5th Edition Besanko Test Bank 1Document25 pagesMicroeconomics 5th Edition Besanko Test Bank 1christina100% (52)
- Long: Bed Bath & Beyond (NASDAQ: BBBY) : Market ViewDocument1 pageLong: Bed Bath & Beyond (NASDAQ: BBBY) : Market ViewGeorge RaoNo ratings yet
- 1 1 Business Activity PDFDocument3 pages1 1 Business Activity PDFsuhaniNo ratings yet
- No 72, Keonics Electronic City, Phase-I Hosur Road, Bangalore Dipanita Deb Lala. Owner/ManagerDocument6 pagesNo 72, Keonics Electronic City, Phase-I Hosur Road, Bangalore Dipanita Deb Lala. Owner/ManagerDipanita Deb LalaNo ratings yet