Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Function of The Plecenta
The Function of The Plecenta
Uploaded by
redzuan19900 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views9 pagesThe placenta develops in the first two months of pregnancy and functions to connect the developing fetus to the uterine wall. It allows for nutrient, gas, and waste exchange between the mother and fetus by bringing the fetal and maternal blood supplies into close proximity while keeping them separate. The placenta transports oxygen, nutrients, antibodies, and some drugs and pathogens from the mother and transports carbon dioxide and waste products from the fetus. It also stores some nutrients and secretes important hormones to support the pregnancy.
Original Description:
Original Title
The Function of the Plecenta
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe placenta develops in the first two months of pregnancy and functions to connect the developing fetus to the uterine wall. It allows for nutrient, gas, and waste exchange between the mother and fetus by bringing the fetal and maternal blood supplies into close proximity while keeping them separate. The placenta transports oxygen, nutrients, antibodies, and some drugs and pathogens from the mother and transports carbon dioxide and waste products from the fetus. It also stores some nutrients and secretes important hormones to support the pregnancy.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views9 pagesThe Function of The Plecenta
The Function of The Plecenta
Uploaded by
redzuan1990The placenta develops in the first two months of pregnancy and functions to connect the developing fetus to the uterine wall. It allows for nutrient, gas, and waste exchange between the mother and fetus by bringing the fetal and maternal blood supplies into close proximity while keeping them separate. The placenta transports oxygen, nutrients, antibodies, and some drugs and pathogens from the mother and transports carbon dioxide and waste products from the fetus. It also stores some nutrients and secretes important hormones to support the pregnancy.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 9
THE FUNCTION OF THE
PLECENTA IN RELATION TO THE
DEVELOPMENT OF THE FOETUS
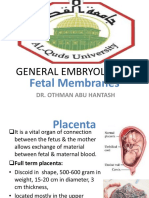
What is Placenta
• Placenta is the mechanical and
physiological connection between foetal
and maternal tissues for the nutrition,
respiration and excretion of the foetus
• This temporary organ develops in the
first two month and by the third month
its play full a functional to the foetus.
• The foetal part of the placenta consists of the
allantois and chorion.
• Chorion forms many large projections called
the chorionic villi that contain a dense
network of foetal capillaries.
• Foetal capillaries are connected to the
umbilical arteries and veins in the umbilical
cord.
• Umbilical arteries carries blood from the fetus
to the placenta while umbilical vein carries
blood in the opposite direction.
• The uterine tissue(endometrium) underlying
the chorionic villi contains maternal blood
vessels and pools of maternal blood (from the
breakdown maternal capillaries.
• Maternal blood in the endometrium is in close
proximity with foetal blood in the umbilical
capillaries but they do not mix together.
• This because between them are separate with
membrane.
The Function of Placenta
• Nutrition - Placenta helps to transport
nutrients from maternal blood into foetus.
• Respiration - It helps in getting oxygen from
the maternal blood into the foetus and CO2
from foetus blood into the maternal blood.
• Excretion - Nitrogenous waste products
produced in the embryo diffuse through the
placenta into the maternal blood stream.
• Immunity - Antibodies developed in the
mother against certain diseases like measles,
small pox, diphtheria pass from mother into
the foetal blood through the placenta.
• Transport of pathogens - Pathogenic
organisms like viruses diffuses through the
placenta. Viruses causing syphilis, measles,
rubella, small pox may infect the foetus, if the
mother gets the disease during pregnancy.
Some of these diseases may even cause
congenital deformities.
• Transport of drugs - Some of the drugs taken by
the mother during pregnancy cross the placental
barrier and may even cause developmental
deformities.
E.g., The drug thalidomide used to avoid nausea
and morning sickness during early pregnancy by
some women resulted in the child born to such
mothers to have deformities in the limb
development and heart. The children had flipper
like limbs, a condition called as phocomelia.
Children born to drug addicts, are born with
addiction and withdrawal symptoms
• Storage - Placenta stores some fats, glycogen
and iron.
• Secretion of hormones - Placenta secretes
many hormones like estrogen, progesterone,
gonadotropin and placental lactogen, thus
functioning as an endocrine gland.
You might also like
- Grade12 Year Notes by E.C Mabuza 1Document186 pagesGrade12 Year Notes by E.C Mabuza 1luyandakelebohile34100% (5)
- (Chapter 1) Organisation of Plant Tissue and GrowthDocument31 pages(Chapter 1) Organisation of Plant Tissue and Growthjolene ang min huiNo ratings yet
- PlacentaDocument11 pagesPlacentasubashikNo ratings yet
- Fetal CirculationDocument28 pagesFetal CirculationNelai GoNo ratings yet
- Holes Human Anatomy and Physiology 14th Edition Shier Test BankDocument43 pagesHoles Human Anatomy and Physiology 14th Edition Shier Test Bankpucelleheliozoa40wo100% (31)
- Case Study Presentation: Group 2Document12 pagesCase Study Presentation: Group 2Anna Marie Donaire0% (1)
- XN-Series Clinical Case ReportDocument82 pagesXN-Series Clinical Case ReportMirian soonNo ratings yet
- Anatomi Dan FisiologiDocument60 pagesAnatomi Dan FisiologiBimantoro SaputroNo ratings yet
- Case Study Bago Neonatal Sepsis PikeDocument30 pagesCase Study Bago Neonatal Sepsis PikeAlex VarelaNo ratings yet
- How To Have an Easy and Safe Pregnancy and Bring Forth a Healthy Baby: A Pregnancy Book for First Time Moms for a Successful and Healthy Journey through Pregnancy, Childbirth and NewbornFrom EverandHow To Have an Easy and Safe Pregnancy and Bring Forth a Healthy Baby: A Pregnancy Book for First Time Moms for a Successful and Healthy Journey through Pregnancy, Childbirth and NewbornNo ratings yet
- The Placenta BDocument48 pagesThe Placenta BLulano MbasuNo ratings yet
- Fetal PhysiologyDocument30 pagesFetal PhysiologyHassan DalmarNo ratings yet
- Embryology, Pathophysiology, and Ultrasound Characteristics of The Placenta ObjectivesDocument13 pagesEmbryology, Pathophysiology, and Ultrasound Characteristics of The Placenta ObjectivesAudrey100% (5)
- Lect12 - Amniotic Fluid ModifiedDocument22 pagesLect12 - Amniotic Fluid Modifiedyelisetti DakshayaniNo ratings yet
- Bio PresentationDocument17 pagesBio PresentationkamiiNo ratings yet
- Perkembangan Plasenta (Autosaved) .En - IdDocument18 pagesPerkembangan Plasenta (Autosaved) .En - IdFATIMAHNo ratings yet
- Placenta & Fetal CirculationDocument32 pagesPlacenta & Fetal CirculationFarxan Da Napolian BwoyNo ratings yet
- DR - Sumeya: Normal Fetal Development and GrowthDocument42 pagesDR - Sumeya: Normal Fetal Development and Growthhussain AltaherNo ratings yet
- How Do Organisms Reproduce Part-IIDocument16 pagesHow Do Organisms Reproduce Part-IIraghavrungtambwaNo ratings yet
- Developmental StagesDocument17 pagesDevelopmental StagesAhmer AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Premature Rupture of The MembranesDocument6 pagesPremature Rupture of The MembranesMaria Donabella OngueNo ratings yet
- 10 Kuliah PLACENTADocument33 pages10 Kuliah PLACENTAAya KamajayaNo ratings yet
- Embryo DevelopmentDocument2 pagesEmbryo DevelopmentAl BedwardNo ratings yet
- Functional Anatomy - Part II: Uterus, Fetal Circulation & Male Reproductive Organ Selected VariationsDocument69 pagesFunctional Anatomy - Part II: Uterus, Fetal Circulation & Male Reproductive Organ Selected Variationshfkxbbbty2No ratings yet
- Assessment of PlacentaDocument21 pagesAssessment of PlacentaAarti RajputNo ratings yet
- B13 Human Reproduction Study Notes 2.4.12Document7 pagesB13 Human Reproduction Study Notes 2.4.12ennes9141No ratings yet
- Pathologies of The Amniotic Fluid Volume: Prepared by DR N. Med. Radosław Blok - I Katedra Gin - Poł. AM WrocławDocument56 pagesPathologies of The Amniotic Fluid Volume: Prepared by DR N. Med. Radosław Blok - I Katedra Gin - Poł. AM WrocławSupreet Singh MalhiNo ratings yet
- OLDS Week2 QwizdomDocument142 pagesOLDS Week2 QwizdomJestoni Dulva ManiagoNo ratings yet
- ch.8 Embryo PDFDocument22 pagesch.8 Embryo PDFMohammad GhannamNo ratings yet
- 4.3 Development of ZygoteDocument18 pages4.3 Development of ZygoteKasmahwati MattailNo ratings yet
- L9 PDFDocument16 pagesL9 PDFSteve AgNo ratings yet
- Physiological Changes in Pregnancy + Placenta & Parturition, Lactation + Neonatal PhysiologyDocument31 pagesPhysiological Changes in Pregnancy + Placenta & Parturition, Lactation + Neonatal PhysiologySalman KhanNo ratings yet
- ABO Incompatibility PDFDocument57 pagesABO Incompatibility PDFPachieNo ratings yet
- Normal PregnancyDocument86 pagesNormal PregnancygayleesinfuegoNo ratings yet
- Reprodcution in Humans 3Document10 pagesReprodcution in Humans 3thraaaladyNo ratings yet
- 11th Lecture Amnion& Amniotic FluidDocument35 pages11th Lecture Amnion& Amniotic FluidHussein Al Saedi100% (1)
- Notes Topic 3.10 - (1)Document2 pagesNotes Topic 3.10 - (1)ahmedNo ratings yet
- Embryology - The PlacentaDocument14 pagesEmbryology - The PlacentaDr. SaG SaugatNo ratings yet
- Reproduction and HeredityDocument10 pagesReproduction and HeredityMonkey LoverNo ratings yet
- Placenta and Amniotic Fluid Structure FunctionDocument52 pagesPlacenta and Amniotic Fluid Structure FunctionDoli P Hutauruk100% (1)
- 4 3 Development of ZygoteDocument18 pages4 3 Development of ZygoteManas Ranjan JenaNo ratings yet
- Functions of The Placenta in Foetal DevelopmentDocument4 pagesFunctions of The Placenta in Foetal DevelopmentJoanne LauNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in Humans Part 3Document39 pagesSexual Reproduction in Humans Part 3Janae CampbellNo ratings yet
- Colorful Abstract Geometric Illustrated Education Science Lesson PresentationDocument14 pagesColorful Abstract Geometric Illustrated Education Science Lesson PresentationabibhaskaramulyaNo ratings yet
- Group 2 Science-ReportDocument16 pagesGroup 2 Science-ReportIgnacio FelicityNo ratings yet
- PlacentaDocument21 pagesPlacentaGrace MendozaNo ratings yet
- 10 Placenta DR - GosaiDocument29 pages10 Placenta DR - GosaiDr.B.B.GosaiNo ratings yet
- Human Reproductive SystemDocument16 pagesHuman Reproductive SystemHtet Htet NaingNo ratings yet
- The Antenatal Care-Maternal Changes During Pregnancy 7Document75 pagesThe Antenatal Care-Maternal Changes During Pregnancy 795kscbyqxmNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Child Health Nursing (NCM 101 Lect) Part 1Document4 pagesMaternal and Child Health Nursing (NCM 101 Lect) Part 1yunjung0518100% (7)
- Placenta and Amniotic Fluid Structure FunctionDocument66 pagesPlacenta and Amniotic Fluid Structure FunctionmadyNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive System PDFDocument111 pagesFemale Reproductive System PDFGayathri SNo ratings yet
- BreastfeedingDocument32 pagesBreastfeedingAhmed MadkourNo ratings yet
- Place Ntation 2Document38 pagesPlace Ntation 2Dr. Vinay VijayakumarNo ratings yet
- Place Ntation 1Document38 pagesPlace Ntation 1Dr. Vinay VijayakumarNo ratings yet
- Abhinav 3 Obg TeachingDocument22 pagesAbhinav 3 Obg TeachingEkta RajputNo ratings yet
- PlacentaDocument24 pagesPlacentaNibedita 2015No ratings yet
- Lecture 1physiology of PregnancyDocument58 pagesLecture 1physiology of PregnancyОлександра ЗагородняNo ratings yet
- Human ReproductionDocument5 pagesHuman ReproductionKrishna SharmaNo ratings yet
- The Growing FetusDocument62 pagesThe Growing Fetuscoosa liquorsNo ratings yet
- Day 2 Review Pregnancy Fetal Development and Labor and DeliveryDocument84 pagesDay 2 Review Pregnancy Fetal Development and Labor and DeliveryInah SaritaNo ratings yet
- Stages of Fetal Growth and DevelopmentDocument10 pagesStages of Fetal Growth and DevelopmentGrant KhangabNo ratings yet
- AKHIRDocument3 pagesAKHIRredzuan1990No ratings yet
- Kelas Mata Pelajaran Jenis Ujian: Senarai Markah PelajarDocument2 pagesKelas Mata Pelajaran Jenis Ujian: Senarai Markah Pelajarredzuan1990No ratings yet
- Markah Sains THN 4Document1 pageMarkah Sains THN 4redzuan1990No ratings yet
- Kelas Mata Pelajaran Jenis Ujian: Senarai Markah PelajarDocument2 pagesKelas Mata Pelajaran Jenis Ujian: Senarai Markah Pelajarredzuan1990No ratings yet
- THN 1 Bijak DSTDocument1 pageTHN 1 Bijak DSTredzuan1990No ratings yet
- Rule Changes ITODocument82 pagesRule Changes ITOredzuan1990No ratings yet
- Respiratory Disorders AssigmentDocument1 pageRespiratory Disorders Assigmentredzuan1990No ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument2 pagesIntroductionredzuan1990No ratings yet
- Rust Chemistry: Fe(s) - Fe (Aq) + 2eDocument2 pagesRust Chemistry: Fe(s) - Fe (Aq) + 2eredzuan1990No ratings yet
- Ionic EquilibriumDocument3 pagesIonic Equilibriumredzuan1990No ratings yet
- FuebdDocument6 pagesFuebddjaerNo ratings yet
- Microbiology: Lec 2 Dr. Asaad Taha Dr. Maryam AbdDocument17 pagesMicrobiology: Lec 2 Dr. Asaad Taha Dr. Maryam AbdAhmed MazinNo ratings yet
- The Cell (Smallest Unit) : A Region of DNADocument2 pagesThe Cell (Smallest Unit) : A Region of DNAIZZATY ATIRAH IBRAHIMNo ratings yet
- Minireview Aquaporin Water Channels: Molecular Mechanisms For Human Diseases1Document13 pagesMinireview Aquaporin Water Channels: Molecular Mechanisms For Human Diseases1GrenlyKerehNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Meditation in The Treatment of Androgenetic AlopeciaDocument14 pagesThe Impact of Meditation in The Treatment of Androgenetic Alopeciapedroptt85No ratings yet
- Plant Anatomi-Plant OrgansDocument70 pagesPlant Anatomi-Plant OrgansHambaukaiNo ratings yet
- Biology AML NMAT ReviewerDocument15 pagesBiology AML NMAT ReviewerJocelyn Mae CabreraNo ratings yet
- Summative Test # 2 Q2Document11 pagesSummative Test # 2 Q2kayerencaoleNo ratings yet
- Week 1-2 - Veterinary Embryology IntroductionDocument8 pagesWeek 1-2 - Veterinary Embryology IntroductionAleia GoNo ratings yet
- NSO (International Science Olympiad) Class 4 Paper 2018 Part 2 Download All The Papers For 2021 ExamDocument5 pagesNSO (International Science Olympiad) Class 4 Paper 2018 Part 2 Download All The Papers For 2021 ExamSwaroop ChakravortyNo ratings yet
- Lipidomics Vol 2 Leading Research From Wiley 2021001006 MRKDocument40 pagesLipidomics Vol 2 Leading Research From Wiley 2021001006 MRKknowledge is powerNo ratings yet
- AS Bio MS Answers PDFDocument34 pagesAS Bio MS Answers PDFGame ZoneNo ratings yet
- Wellness Massage 10: Lesson 2Document56 pagesWellness Massage 10: Lesson 2Vanessa DE GUZMANNo ratings yet
- Literature Review On Blood GroupDocument7 pagesLiterature Review On Blood Groupaebvqfzmi100% (1)
- Body Fluid: Dr. Dr. H. Busjra M. Nur, MS Dept. Physiology FKUI/ FKK UMJDocument50 pagesBody Fluid: Dr. Dr. H. Busjra M. Nur, MS Dept. Physiology FKUI/ FKK UMJGhaidaa SadeqNo ratings yet
- Saura, Jasmin E. - DVM - 2B Biochemistry (Activity 1)Document4 pagesSaura, Jasmin E. - DVM - 2B Biochemistry (Activity 1)Jasmin SauraNo ratings yet
- ANIMAL BEHAVIOR Lectures 1Document4 pagesANIMAL BEHAVIOR Lectures 1ifraNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument3 pagesRespiratory SystemUzumaki Naruto (NARUTADIKS)No ratings yet
- 1 - Ditta - BIO173 - Introduction - 20204Document23 pages1 - Ditta - BIO173 - Introduction - 20204John ChoiNo ratings yet
- Question BankDocument28 pagesQuestion Bankas3941asNo ratings yet
- Endokrin (1) - TerkunciDocument25 pagesEndokrin (1) - TerkuncihafizauliaNo ratings yet
- PhlebotomyDocument50 pagesPhlebotomyEuan LopezNo ratings yet
- 9 Human NutritionDocument56 pages9 Human NutritionSaamir SadmanNo ratings yet
- Messina Et Al-2022-Intensive Care Medicine ExperimentalDocument15 pagesMessina Et Al-2022-Intensive Care Medicine ExperimentalAna Belén Viteri luzuriagaNo ratings yet
- Bmi2603 2016 6 e 1Document2 pagesBmi2603 2016 6 e 1Pasipanodya MuzendaNo ratings yet
- Nihms 7136222Document43 pagesNihms 7136222Ivor Wiguna Hartanto WilopoNo ratings yet