Professional Documents
Culture Documents
SST Modul Ns
Uploaded by
Galang Kharisma Putra0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views21 pagesSst Modul Ns
Original Title
Sst Modul Ns
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentSst Modul Ns
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views21 pagesSST Modul Ns
Uploaded by
Galang Kharisma PutraSst Modul Ns
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 21
SEDATIVE-HYPNOTIC DRUGS
Sedative Hypnotic Drugs
• The sedative-hypnotic produce dose dependent
CNS depressant effect
• Sedation : Reduction of anxiety
Hypnosis : Induction of sleep
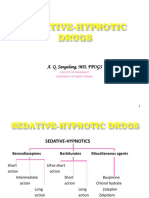
• Subgroup :
- Benzodiazepine (Chlordiazepoxide, diazepam,
temazepam)
- Barbiturat (Phenobarbital, pentobarbital,
thiopental)
- Others (buspirone, zolpidem, chloralhydrate,
zaleplon)
Sedative Hypnotic Drugs
• Benzodiazepine :
- short acting (triazolam)
- intermediate acting (estazolam,
temazepam)
- long acting (flurazepam, quazepam)
Sedative Hypnotic Drugs
• Barbiturates :
- Ultra short acting
- Short acting
- Long acting
Sedative Hypnotic Drugs
(Pharmacokkinetics)
• All sedative hypnotic are lipid soluble
and absorbed well from GI tract
• Good distribution to the brain in oral
administration
Sedative Hypnotic Drugs
(Metabolism and Excretion)
• Metabolized mainly by hepatic enzymes
• Many benzodiazepine are converted to
active metabolites
Accumulation of active metabolites can
lead to excessive sedation
• The barbiturates are extensively
metabolized,except phenobarbital
Sedative Hypnotic Drugs
(Mechanisms of Action)
BENZODIAZEPINES
• Receptors for benzodiazepines (BZ receptors)
are present in the thalamus,limbic
structures,and the cerbralcortex.
• Binding of Benzodiazepines facilitates the
inhibitory actions of GABA,which are exerted
through increased chloride ion conductance.
• GABA is the major inhibitoric neurotransmitter
in the CNS
Sedative Hypnotic Drugs
(Mechanisms of Action)
Barbiturates
• Barbiturates depress neuronalactivity in the
midbrain reticular formation, facilitating and
prolonging the inhibitory effects of GABA
Other drugs
• Mechanism of anxiolytic effect of buspirone is
unknown, but buspirone interact with the 5-
HT as partial agonist
• Zolpidem & zaleplon interact with BZ1 bind
selectively with GABAA receptor
Sedative Hypnotic Drugs
(Pharmacodynamics)
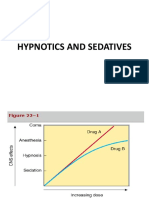
• The CNS effect depend on dose
• Effects : sedation & relief of anxiety, through
hypnosis (facilitation of sleep) to anesthesia
and coma
• When 2 or more drugs are given
togetherdepressant effect +++
• Sedation : sedative action with relief of
anxiety
• Hypnosis : promote sleep onset and
duration of the sleep state
Sedative Hypnotic Drugs
(Pharmacodynamics)
• Anesthesia : conscious with amnesia &
supressions of reflexes (at highdose). Can
produce by most barbiturates (eg,thiopental)
& certain benzodiazepines (eg,midazolam)
• Anticonvulsant actions : supression of seizure
activity (high dose),usually accompany by
sedation effect.
Selective anticonvulsant (supression of
convulsion at dose that do not cause severe
sedation is Phenobarbital, clonazepam
Sedative Hypnotic Drugs
(Pharmacodynamics)
• Muscle relaxation : relaxation of skeletal
muscle (at high dose)
Diazepam at sedative dose effective for
spasticity states
Selective muscle relaxant : Meprobomate
• Medullary depression :
High dose can cause depression of medullarry
neurons,leading to respiratory arrest,
hypotension & CV collapse death
Sedative Hypnotic Drugs
(Pharmacodynamics)
• Tolerance& dependence :
tolerance – a decrease in responsiveness, occurs
when used chronically or in high dose
physiologic dependence– an altered state that
leads to an abstinence syndrome (withdrawal
state) when the drug is discontinued
Sign : anxiety, tremors,hyperreflexia, seizure
Sedative Hypnotic Drugs
(Clinical Uses)
• Anxiety states (alprazolam, clonazepam,
buspirone)
The anxiolityc effect of buspirone occur
without sedation or cognitive impairment
• Sleep disorder (estazolam,flurazepam,
triazolam)
• Induction of anesthesia (thiopental,
diazepam, midazolam)
• Management of seizure disorders
(clonazepam,phenobarbital)
Sedative Hypnotic Drugs
(Clinical Uses)
• Management of withdrawal states in
persons physiologically dependent on
ethanol & sedative hypnotics
(chlordiazepoxide, diazepam)
Sedative Hypnotic Drugs
(Toxicity)
• Cognitive impairment
• Decreased psychomotor skills
• Unwanted daytime sedation
• Anterograde amnesia
• Additive CNS depression
when used with other drugs in the class
(antihistamines,antipsychotic drugs, opioid
analgesics, tricyclic antidepressants)
• Overdosage severe respiratory & CV depression
Flumazenil may reverse CNS depressant effect of
benzodiazepines, zolpidem & zaleplon
You might also like
- Pharmacology CNS DepressantDocument31 pagesPharmacology CNS DepressantQueenie PuzonNo ratings yet
- Principles of Pharmacology - The Pathophysiologic Basis of Drug TherapyDocument978 pagesPrinciples of Pharmacology - The Pathophysiologic Basis of Drug TherapyChemistix100% (4)
- Drugs Used in Mental IllnessDocument60 pagesDrugs Used in Mental IllnessDixa MeNo ratings yet
- Beating the Benzo Blues: Getting off BenzodiazapinesFrom EverandBeating the Benzo Blues: Getting off BenzodiazapinesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Sedative Hypnotic PoisoningDocument37 pagesSedative Hypnotic PoisoningDeepa WilliamNo ratings yet
- NURSING PRACTICE I - Foundation of PROFESSIONAL Nursing Practice SITUATIONALDocument102 pagesNURSING PRACTICE I - Foundation of PROFESSIONAL Nursing Practice SITUATIONALAlyssa BusalpaNo ratings yet
- Sedative-Hypnotics (SeH) and AnxiolyticsDocument101 pagesSedative-Hypnotics (SeH) and Anxiolyticsmatchees-gone rogueNo ratings yet
- Cosmetics LectureDocument11 pagesCosmetics LectureShanice Langaman100% (2)
- Drugs Acting On CNSDocument19 pagesDrugs Acting On CNSAditya sagarNo ratings yet
- 2016 Pharmacology of Sedative-HypnoticDocument46 pages2016 Pharmacology of Sedative-HypnoticFansisca SiallaganNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Neurotropic Drugs 2015Document44 pagesPharmacology Neurotropic Drugs 2015Migz BrosasNo ratings yet
- Lecture 28 - 3rd Asessment - Sedatives, HypnoticsDocument32 pagesLecture 28 - 3rd Asessment - Sedatives, Hypnoticsapi-3703352100% (1)
- Sedative & HypnoticsDocument60 pagesSedative & HypnoticsDr Nilesh Patel100% (1)
- Anxiolytic, Sedative-Hypnotic DrugsDocument39 pagesAnxiolytic, Sedative-Hypnotic DrugsNina100% (1)
- Sedative-Hypnotic Drugs: Anita Q. Sangalang, MD, FPOGSDocument43 pagesSedative-Hypnotic Drugs: Anita Q. Sangalang, MD, FPOGSdave_1128No ratings yet
- Antianxiety SedativeDocument44 pagesAntianxiety Sedativemohsen mirdamadiNo ratings yet
- Reflexology Manual VTCTDocument151 pagesReflexology Manual VTCTAhmad Mehdi100% (1)
- Advances in Psychiatry PDFDocument729 pagesAdvances in Psychiatry PDFSorinaNI100% (2)
- Blood Banking LawDocument50 pagesBlood Banking LawDayledaniel SorvetoNo ratings yet
- Depression & Anxiety: What You Need To Know About Treatment with Medications, Herbs & SupplementsFrom EverandDepression & Anxiety: What You Need To Know About Treatment with Medications, Herbs & SupplementsNo ratings yet
- MAS FrequencyTherapyDocument49 pagesMAS FrequencyTherapyjohn nagamine100% (2)
- Anxiolytic and Hypnotic DrugsDocument27 pagesAnxiolytic and Hypnotic DrugsEjaj SumitNo ratings yet
- 2 Attitude Knowledge and Practices of The Community of Santa Maria Bulacan Towards 10 Halamang Gamot.Document7 pages2 Attitude Knowledge and Practices of The Community of Santa Maria Bulacan Towards 10 Halamang Gamot.Jonille EchevarriaNo ratings yet
- Sedatives and Hypnotics LectureDocument55 pagesSedatives and Hypnotics LectureOSAKA THOMASNo ratings yet
- 23-Discharge Against Medical Advice (Dama)Document3 pages23-Discharge Against Medical Advice (Dama)akositabonNo ratings yet
- Sedative Hypnotic DrugsDocument21 pagesSedative Hypnotic DrugstamaNo ratings yet
- Hypnotics and SedativesDocument22 pagesHypnotics and Sedativeskavya nainitaNo ratings yet
- Sedative-Hypnotic Drugs: Dr. Hiwa K. Saaed, HD, Msc. PHDDocument51 pagesSedative-Hypnotic Drugs: Dr. Hiwa K. Saaed, HD, Msc. PHDHiwa Khidhir saaedNo ratings yet
- Sleep Medication For InsomniaDocument32 pagesSleep Medication For InsomniaMelanieNo ratings yet
- SEDATIVE - HYPNOTICS DRUGS - PharmaDocument66 pagesSEDATIVE - HYPNOTICS DRUGS - PharmaKenneth NuñezNo ratings yet
- CNS Depressants: - Sedatives and Hypnotics - General Anesthetics - Narcotic AnalgesicsDocument118 pagesCNS Depressants: - Sedatives and Hypnotics - General Anesthetics - Narcotic Analgesicsbiruk getahunNo ratings yet
- Anxiolytic and Hypnotic DrugsDocument22 pagesAnxiolytic and Hypnotic DrugsAbdullah BhattiNo ratings yet
- 02 Sedative Hypnotic and Anxiolytic DrugsDocument23 pages02 Sedative Hypnotic and Anxiolytic DrugsFilippo PhilippNo ratings yet
- 7 - Anxiolytics-Sedatives-HypnoticsDocument46 pages7 - Anxiolytics-Sedatives-HypnoticsHadeelNo ratings yet
- Sedative-Hypnotic-Anxiolytics: Benzodiazepines & OthersDocument37 pagesSedative-Hypnotic-Anxiolytics: Benzodiazepines & OthersManWol JangNo ratings yet
- Cns Depressants: BarbituratesDocument18 pagesCns Depressants: BarbituratesGenevieve Caecilia Linda KNo ratings yet
- Nm-Lec15 - (Anxiolytics, Sedatives & Hypnotics)Document39 pagesNm-Lec15 - (Anxiolytics, Sedatives & Hypnotics)geng gengNo ratings yet
- WEEK 6 7-CNS Medications StudentDocument83 pagesWEEK 6 7-CNS Medications Studentx8jdbj5gphNo ratings yet
- Anxiolytics and HypnoticsDocument43 pagesAnxiolytics and HypnoticshamzabhayatNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12Document6 pagesChapter 12Candice ChengNo ratings yet
- Hypnoti and SedativeDocument30 pagesHypnoti and SedativeC velmuruganNo ratings yet
- CNS DepressantsDocument69 pagesCNS DepressantsMicah Lou Calamba100% (1)
- Classification of Anxiolytic and Hypnotic DrugsDocument16 pagesClassification of Anxiolytic and Hypnotic DrugsSheemaNo ratings yet
- 02 Sedative Hypnotic and Anxiolytic DrugsDocument16 pages02 Sedative Hypnotic and Anxiolytic DrugsGilbert OsengoNo ratings yet
- Psych DrugsDocument46 pagesPsych DrugsDaniela OrtalNo ratings yet
- Sedative HypnoticsDocument22 pagesSedative Hypnoticsmadeha goharNo ratings yet
- Psychotro Pic Drugs: Sedative and Hypnotic DrugsDocument15 pagesPsychotro Pic Drugs: Sedative and Hypnotic DrugsBajoijoi Ordiz-sandro EncisaNo ratings yet
- Sedative & Hypnotics: Prof. Hanan Hagar Pharmacology Department Medical College King Saud UniversityDocument51 pagesSedative & Hypnotics: Prof. Hanan Hagar Pharmacology Department Medical College King Saud UniversityRose Ann Raquiza-PeranteNo ratings yet
- Anxiolytics Sedatives Hypnotics Pharm 3Document38 pagesAnxiolytics Sedatives Hypnotics Pharm 3Peter Harris100% (1)
- Anxiolytic Sedative-Hypnotic DrugsDocument31 pagesAnxiolytic Sedative-Hypnotic DrugsRoman MamunNo ratings yet
- 13 Psychiatric DRUGSDocument42 pages13 Psychiatric DRUGSPande Indra PremanaNo ratings yet
- 6) 5th Semester - Sedative Hypnotics and Antianxiety DrugsDocument34 pages6) 5th Semester - Sedative Hypnotics and Antianxiety DrugsFizza ImamNo ratings yet
- HypnoticsDocument27 pagesHypnoticsattu farrayalNo ratings yet
- Pharma AnxietyDocument19 pagesPharma AnxietySomaia mohammedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 22 Sedative HypnoticsDocument7 pagesChapter 22 Sedative HypnoticsChristine Annmarie TapawanNo ratings yet
- AnxiolyticsDocument17 pagesAnxiolyticsKhadija ArshadNo ratings yet
- Antiinsomnia and AxyoliticDocument21 pagesAntiinsomnia and AxyoliticGita Tanbao SuselinNo ratings yet
- Unit 2-CNS and ANS (Part 3) Modified 2021Document30 pagesUnit 2-CNS and ANS (Part 3) Modified 2021Donia ShormanNo ratings yet
- 5 Sedative-Hypnotic DrugsDocument26 pages5 Sedative-Hypnotic DrugsDylan Panashe KwendaNo ratings yet
- Sedatives, Hypnotics & AnxiolyticsDocument27 pagesSedatives, Hypnotics & AnxiolyticsSaima IftikharNo ratings yet
- Sedative-Hypnotic Drugs: College of Pharmacy Our Lady of Fatima UniversityDocument27 pagesSedative-Hypnotic Drugs: College of Pharmacy Our Lady of Fatima UniversityK WangNo ratings yet
- Sedative - HypnoticsDocument60 pagesSedative - HypnoticsNurul AinNo ratings yet
- Cns Depressants Sedative-Hypnotic Drugs: Dr. Hiwa K. Saaed, BSC, HD, Msc. PHDDocument42 pagesCns Depressants Sedative-Hypnotic Drugs: Dr. Hiwa K. Saaed, BSC, HD, Msc. PHDAnaliza Kitongan LantayanNo ratings yet
- F22 Sedative Hypnotic DrugsDocument37 pagesF22 Sedative Hypnotic DrugsJoyce SumagaysayNo ratings yet
- Sedative HypnoticsDocument33 pagesSedative HypnoticsIkram HamacheNo ratings yet
- Anxiolytics and Sedative-HypnoticsDocument27 pagesAnxiolytics and Sedative-HypnoticsLaime CaceresNo ratings yet
- Cns AgentsDocument10 pagesCns Agentsroldanmarygrace023No ratings yet
- Bruximo PDFDocument44 pagesBruximo PDFcemoaraNo ratings yet
- Marathon FuelingDocument4 pagesMarathon Fuelingshreyas todankarNo ratings yet
- Philippines - Bridging Care To The Barangay-1Document2 pagesPhilippines - Bridging Care To The Barangay-1Richard ErickNo ratings yet
- 06390G TocDocument5 pages06390G TocBhawani Singh RajawatNo ratings yet
- A Technique of Endoscopic Nipple-Sparing Mastectomy For Breast CancerDocument8 pagesA Technique of Endoscopic Nipple-Sparing Mastectomy For Breast CancerMuhamad Amar'sNo ratings yet
- CefepimeDocument3 pagesCefepimeMae Ann Bueno CastillonNo ratings yet
- Life Brought at A Tender Age: The Lived Experiences of Filipino Teenage Pregnant WomenDocument5 pagesLife Brought at A Tender Age: The Lived Experiences of Filipino Teenage Pregnant WomenAsia Pacific Journal of Multidisciplinary ResearchNo ratings yet
- Epidemiological Study of Bloody Diarrhoea Among Children in Baghdad, IraqDocument9 pagesEpidemiological Study of Bloody Diarrhoea Among Children in Baghdad, IraqInternational Medical PublisherNo ratings yet
- Methyl Salicylate MsdsDocument12 pagesMethyl Salicylate MsdsWilliam ChandraNo ratings yet
- Dialogue On Medical Surgical NursingDocument3 pagesDialogue On Medical Surgical NursingAnonymous XEV3a17n3YNo ratings yet
- Resume Lismari Reyes MunozDocument2 pagesResume Lismari Reyes Munozapi-253469228No ratings yet
- History TakingDocument55 pagesHistory TakingDeepika MahajanNo ratings yet
- Analgesic Efficacy of Erector Spinae Plane BlocksDocument7 pagesAnalgesic Efficacy of Erector Spinae Plane BlocksAlejandra SanchezNo ratings yet
- Destive System: What Is Digestion?Document2 pagesDestive System: What Is Digestion?Pepy PeachNo ratings yet
- Problems With Dressing in The Frail ElderlyDocument11 pagesProblems With Dressing in The Frail ElderlyBiswa Bikash SinghNo ratings yet
- 2022 Bartek Janacek Summative ProfileDocument4 pages2022 Bartek Janacek Summative Profilenavishana MalikNo ratings yet
- Basics of Critical Care.....Document34 pagesBasics of Critical Care.....XamanNo ratings yet
- EPAR FludarabineDocument8 pagesEPAR FludarabinerajugNo ratings yet
- CÁNCER DE OVARIO Diagnóstico y Tratamiento Dr. HERNÁNDEZ 2019Document122 pagesCÁNCER DE OVARIO Diagnóstico y Tratamiento Dr. HERNÁNDEZ 2019Pedro Hernandez Moron100% (1)
- Lions Club of Bangalore Sundarnagar e Scrap Book Upto December 18Document64 pagesLions Club of Bangalore Sundarnagar e Scrap Book Upto December 18Vinay BabanagarNo ratings yet
- Eichel (2020), Antimicrobial Effects of Mustard Oil-Containing Plants Against Oral Pathogens: An in Vitro StudyDocument7 pagesEichel (2020), Antimicrobial Effects of Mustard Oil-Containing Plants Against Oral Pathogens: An in Vitro StudyPhuong ThaoNo ratings yet