0% found this document useful (0 votes)
58 views11 pagesDifferences Between Plant and Animal Cells
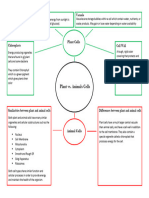
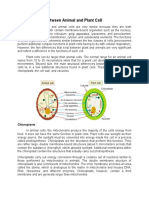
Plant and animal cells share some similarities as eukaryotic cells containing organelles like the nucleus and mitochondria. However, plant cells tend to be larger and contain additional structures like chloroplasts, a cell wall, and central vacuoles that can occupy 90% of the cell volume. While animal cell sizes vary from 10-30 micrometers, plant cells are more uniform in size. The organelles in animal cells produce energy and synthesize molecules to power cellular functions.
Uploaded by
Imman Ray Loriezo AguilarCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
58 views11 pagesDifferences Between Plant and Animal Cells
Plant and animal cells share some similarities as eukaryotic cells containing organelles like the nucleus and mitochondria. However, plant cells tend to be larger and contain additional structures like chloroplasts, a cell wall, and central vacuoles that can occupy 90% of the cell volume. While animal cell sizes vary from 10-30 micrometers, plant cells are more uniform in size. The organelles in animal cells produce energy and synthesize molecules to power cellular functions.
Uploaded by
Imman Ray Loriezo AguilarCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd