Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Notes On Biology 124
Uploaded by
AlexanderDennisSladeOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Notes On Biology 124
Uploaded by
AlexanderDennisSladeCopyright:
Available Formats
Notes on Bio 124
First, we find the covalent bond chatting up the hydrogen bond. What’s
up? Asks the hydrogen bond.
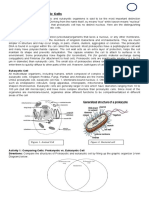
Structurally, plant and animal cells are very similar because they
are both eukaryotic cells. They both contain membrane-bound
organelles such as the nucleus, mitochondria, endoplasmic
reticulum, golgi apparatus, lysosomes, and peroxisomes. Both
also contain similar membranes, cytosol, and cytoskeletal
elements. The functions of these organelles are extremely similar
between the two classes of cells (peroxisomes perform additional
complex functions in plant cells having to do with cellular
respiration). However, the few differences that exist between plant
and animals are very significant and reflect a difference in the
functions of each cell.
Plant cells can be larger than animal cells. The normal range for
an animal cell varies from 10 to 30 micrometers while that for a
plant cell stretches from 10 to 100 micrometers. Beyond size, the
main structural differences between plant and animal cells lie in a
few additional structures found in plant cells. These structures
include: chloroplasts, the cell wall, and vacuoles.
You might also like
- Animal and Plant CellsDocument22 pagesAnimal and Plant CellsKrizza AguidanNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument1 pageUntitledJubaer UtshobNo ratings yet
- biology bacterium yeast animals atoms mycoplasmas μmDocument4 pagesbiology bacterium yeast animals atoms mycoplasmas μmLeenie A.A.ANo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal CellDocument7 pagesPlant and Animal CellHera Lopez100% (1)
- Cell Biology What Is A Cell? What Are The Essential Characteristics of Cells?Document11 pagesCell Biology What Is A Cell? What Are The Essential Characteristics of Cells?Renel Esteves RestauroNo ratings yet
- What Is A CellDocument9 pagesWhat Is A CellAristeo EbioNo ratings yet
- GeneticsDocument2 pagesGeneticsdellavajames192000No ratings yet
- The CellDocument5 pagesThe CellAfida Razuna AveNo ratings yet
- Plant Cell and Animal Cell StructureDocument4 pagesPlant Cell and Animal Cell StructureMarkhill Veran TiosanNo ratings yet
- TEXTBOOK BIOSEL and BIOMOLDocument89 pagesTEXTBOOK BIOSEL and BIOMOLTsamarah NafisNo ratings yet
- Textbook Cell BiologyDocument50 pagesTextbook Cell Biologyaeisyah hananiNo ratings yet
- WWW Biologyonline Com Dictionary Plant Cell - Text A 20plant 20cell 20has 20a Are 20key 20organelles 20in 20photosynthesisDocument4 pagesWWW Biologyonline Com Dictionary Plant Cell - Text A 20plant 20cell 20has 20a Are 20key 20organelles 20in 20photosynthesisᏗᏕᎥᎷ ᏗᏝᎥNo ratings yet
- Building Blocks of LifeDocument5 pagesBuilding Blocks of LifeJesse James Olac PigonNo ratings yet
- A. What Are The Similarities and Differences of Prokaryotic Cell and Eukaryotic Cell? SimilaritiesDocument3 pagesA. What Are The Similarities and Differences of Prokaryotic Cell and Eukaryotic Cell? SimilaritiesIa Hannah SamillanoNo ratings yet
- BIO111 NEW1 CompleteDocument25 pagesBIO111 NEW1 Completealiu sodiqNo ratings yet
- Cell Definition, Types, & Functions BritannicaDocument10 pagesCell Definition, Types, & Functions BritannicaKolade YousuffNo ratings yet
- The CellDocument20 pagesThe CellganeshchandraroutrayNo ratings yet
- Gen Biology Module Lesson 2&3Document13 pagesGen Biology Module Lesson 2&3Albert Jade Pontimayor LegariaNo ratings yet
- The Internal Organization of CellsDocument11 pagesThe Internal Organization of CellsmylightstarNo ratings yet
- 1.1cell ConceptDocument10 pages1.1cell ConceptMokariya SanjayNo ratings yet
- Arsenii Vasylcehnko BG - Unit 3 - Project - Cellular Structure and FunctionDocument3 pagesArsenii Vasylcehnko BG - Unit 3 - Project - Cellular Structure and FunctionАрсений ВасильченкоNo ratings yet
- Earth & Life ScienceDocument14 pagesEarth & Life ScienceYhazmeen Lily LibrodoNo ratings yet
- The Science of Cytology Cell Theory: The Principle Core of BiologyDocument6 pagesThe Science of Cytology Cell Theory: The Principle Core of Biologyhendrix obciana100% (1)
- ProkaryoticDocument8 pagesProkaryoticFraulin Leslie Sablas IrisariNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY INVESTIGATORY PROJECT (Cell The Unit of Life)Document27 pagesBIOLOGY INVESTIGATORY PROJECT (Cell The Unit of Life)Ashay Kumar0% (1)
- Difference Between Animal and Plant CellsDocument1 pageDifference Between Animal and Plant CellsNorsham Binti KhairNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio Module 2Document11 pagesGen Bio Module 2rodriguezelmind20No ratings yet
- 1.2 Ultrastructure of CellsDocument6 pages1.2 Ultrastructure of CellsEleonora RaimondoNo ratings yet
- CellDocument4 pagesCellzenfonemaxproma812No ratings yet
- Biology Bacterium Yeast: Cell, inDocument11 pagesBiology Bacterium Yeast: Cell, inAlelli Bianca Daniel AlipioNo ratings yet
- The CellDocument10 pagesThe CellAbeer Alnajjar عبير النجارNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Cell: The Unit of Life 8.1 What Is A Cell? 8.2 Cell TheoryDocument10 pagesChapter 8 Cell: The Unit of Life 8.1 What Is A Cell? 8.2 Cell TheoryCharin KadianNo ratings yet
- Essay 3Document3 pagesEssay 3Tri HardiyantiNo ratings yet
- Cell - The Building Blocks of LifeDocument4 pagesCell - The Building Blocks of LifeUzair SoomroNo ratings yet
- Cell The Unit of LifeDocument58 pagesCell The Unit of LifeRUSHIKESH SINDKHEDKARNo ratings yet
- Inte Sci Grade 9 - Week 2Document11 pagesInte Sci Grade 9 - Week 2Anasatcia Mcpherson 9c FNo ratings yet
- Bombay & Romero - AIL 2Document7 pagesBombay & Romero - AIL 2aira bombayNo ratings yet
- Sadava MSCDocument118 pagesSadava MSCNikkizGogasNo ratings yet
- Gen. Bio 1 Module 2Document6 pagesGen. Bio 1 Module 2Evelyn MagbarilNo ratings yet
- Cell - The Unit of LifeDocument26 pagesCell - The Unit of LifeKunal MahadikNo ratings yet
- Cells InfoDocument1 pageCells InfoWho ?No ratings yet
- Eukaryotes: The Basic Structure of A ProkaryoteDocument2 pagesEukaryotes: The Basic Structure of A ProkaryoteAnnie Jay BedeNo ratings yet
- Notes For Cell Biology BT-I YearDocument16 pagesNotes For Cell Biology BT-I YearKRATIKA TYAGINo ratings yet
- Gen Bio 1 18-19 Cells Reference PPT1Document68 pagesGen Bio 1 18-19 Cells Reference PPT1Ciena GaddiNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Plant and Animal Cells: February 2017Document11 pagesDifference Between Plant and Animal Cells: February 2017Agung PriyantoNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument9 pagesProkaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsKwo Chai Wing100% (1)
- ZH Core IV - Cell BiologyDocument95 pagesZH Core IV - Cell Biologysahib100% (1)
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument7 pagesProkaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsPrashant PatilNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology 1.1Document7 pagesCell Biology 1.1Mirunalini GobinathNo ratings yet
- Cell Structue and FunctionsDocument6 pagesCell Structue and FunctionsDrexel DalaygonNo ratings yet
- Teoría Celular 01Document5 pagesTeoría Celular 01Mildred Yaniret Guillermo ChávezNo ratings yet
- Bio SciDocument6 pagesBio ScilovemeluffyNo ratings yet
- The CellsDocument4 pagesThe CellsSlaheddineNo ratings yet
- Comparing Plant and Animal CellsDocument3 pagesComparing Plant and Animal CellsOrange HopeNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry (Powerpoint PresentationDocument39 pagesBiochemistry (Powerpoint PresentationAnonymous Person100% (1)
- HO1 - 8 - Biology April 23-24 PDFDocument10 pagesHO1 - 8 - Biology April 23-24 PDFSaghana SaravanakarthikNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument2 pagesProkaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsSerena Adeline RiveraNo ratings yet
- Cell PPT To PDF Class 9Document42 pagesCell PPT To PDF Class 9Aditya BajajNo ratings yet