Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Untitled
Untitled
Uploaded by
Jubaer Utshob0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views1 pageThere are two main types of cells - prokaryotic and eukaryotic. Prokaryotic cells are simpler, lacking a nucleus and other organelles, with genetic material in the cytoplasm. Eukaryotic cells are more complex, containing a membrane-bound nucleus and organelles like mitochondria. While both have a plasma membrane and ribosomes, eukaryotic cells are generally larger and their components more advanced.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
TXT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThere are two main types of cells - prokaryotic and eukaryotic. Prokaryotic cells are simpler, lacking a nucleus and other organelles, with genetic material in the cytoplasm. Eukaryotic cells are more complex, containing a membrane-bound nucleus and organelles like mitochondria. While both have a plasma membrane and ribosomes, eukaryotic cells are generally larger and their components more advanced.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as TXT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views1 pageUntitled
Untitled
Uploaded by
Jubaer UtshobThere are two main types of cells - prokaryotic and eukaryotic. Prokaryotic cells are simpler, lacking a nucleus and other organelles, with genetic material in the cytoplasm. Eukaryotic cells are more complex, containing a membrane-bound nucleus and organelles like mitochondria. While both have a plasma membrane and ribosomes, eukaryotic cells are generally larger and their components more advanced.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as TXT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
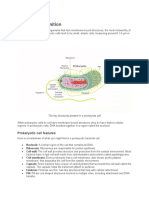
There are many different types of cells.
For example, there are blood cells, skin
cells, bone cells, and even bacteria in everyone.
Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells are two main types of cells that exist in living
organisms. Here are some differences between the two:
Prokaryotic Cells (Greek: pro-before;karyon-nucleus):
Prokaryotic cells are simple in structure compared to eukaryotic cells.
They lack of a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles (eg:
mitochondria,lysosomes).
The genetic material is present in a single, circular chromosome in the
cytoplasm.
cell division usually fission and no mitosis.
They are typically smaller in size than eukaryotic cells.Size generally 1-10
micron miter.
They are found in bacteria and archaea.
Eukaryotic Cells (Greek: eu-true;karyon-nucleus):
Eukaryotic cells are more complex in structure compared to prokaryotic cells.
They have a true nucleus, which is a membrane-bound organelle that contains the
genetic material.
They also have other membrane-bound organelles, such as mitochondria,
endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, and lysosomes.
cell division mitosis.
They are typically larger in size than prokaryotic cells.Size generally 10-100
micron miter.
They are found in animals, plants, fungi, and protists.
Both types of cells have a plasma membrane that encloses the cytoplasm and
regulates the flow of materials in and out of the cell. They also have ribosomes,
which are responsible for protein synthesis. However, eukaryotic ribosomes are
larger and more complex than prokaryotic ribosomes.
In summary, while both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells share some similarities,
they differ in many ways, including their structure, size, and complexity.
You might also like
- Training Manual For Medical RepresentativesDocument74 pagesTraining Manual For Medical RepresentativesAman Ghayas50% (4)
- The Cell: Eukaryotic Cells and Prokaryotic CellsDocument13 pagesThe Cell: Eukaryotic Cells and Prokaryotic CellsDiane CastroNo ratings yet
- Cell (Biology) : Cells in Different Phases of The Cell CycleDocument14 pagesCell (Biology) : Cells in Different Phases of The Cell CycleroavNo ratings yet
- The Cell/ All About CellsDocument35 pagesThe Cell/ All About CellsJandrew Gomez DimapasocNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument2 pagesProkaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsSerena Adeline RiveraNo ratings yet
- Group 3 Prokaryotic Vs Eukaryotic Cells HandoutsDocument4 pagesGroup 3 Prokaryotic Vs Eukaryotic Cells HandoutsClaire Angelie Ruaya100% (1)
- Gen. Bio 1 Module 2Document6 pagesGen. Bio 1 Module 2Evelyn MagbarilNo ratings yet
- Manual For Medical RepresentativesDocument74 pagesManual For Medical RepresentativesSyedMaqboolRaza100% (2)
- Cell PPT To PDF Class 9Document42 pagesCell PPT To PDF Class 9Aditya BajajNo ratings yet
- Cell OrganizationDocument6 pagesCell OrganizationKaarthigan RamaiahNo ratings yet
- Rozy KhanDocument18 pagesRozy KhanBANTU RANANo ratings yet
- CeluarDocument7 pagesCeluarJef PerezNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotic VS Prokaryotic CellsDocument1 pageEukaryotic VS Prokaryotic CellsShreya KadiyalaNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology - Unit - 1Document19 pagesCell Biology - Unit - 1shivangipurohitNo ratings yet
- Cell (Biology)Document18 pagesCell (Biology)Mihnea NaşcaNo ratings yet
- What Is A CellDocument9 pagesWhat Is A CellAristeo EbioNo ratings yet
- Prokaryote Definition: Prokaryotic Cell FeaturesDocument5 pagesProkaryote Definition: Prokaryotic Cell FeaturesAli ShanNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic VS Eukaryotic CellsDocument5 pagesProkaryotic VS Eukaryotic CellsAngelica FloraNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotic CellsDocument2 pagesEukaryotic CellsLolaNo ratings yet
- CellsDocument2 pagesCellsmalikaiman1015No ratings yet
- All About CellsDocument49 pagesAll About CellsJeanine CristobalNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Cell Parts and FunctionDocument60 pagesLecture 3 Cell Parts and FunctionEsther Suan-LancitaNo ratings yet
- The Basic Unit of Life: ObjectiveDocument4 pagesThe Basic Unit of Life: ObjectiveHershell ContaNo ratings yet
- 1.1cell ConceptDocument10 pages1.1cell ConceptMokariya SanjayNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY INVESTIGATORY PROJECT (Cell The Unit of Life)Document27 pagesBIOLOGY INVESTIGATORY PROJECT (Cell The Unit of Life)Ashay Kumar0% (1)
- Biology CH 8 BDocument25 pagesBiology CH 8 BPakhi GoelNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1-Introduction To The CellDocument18 pagesLecture 1-Introduction To The CellThuto SmithNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 4 EukaryotesDocument12 pagesLECTURE 4 EukaryotesNicole MandyNo ratings yet
- biology bacterium yeast animals atoms mycoplasmas μmDocument4 pagesbiology bacterium yeast animals atoms mycoplasmas μmLeenie A.A.ANo ratings yet
- Notes On Biology 124Document1 pageNotes On Biology 124AlexanderDennisSladeNo ratings yet
- Building Blocks of LifeDocument5 pagesBuilding Blocks of LifeJesse James Olac PigonNo ratings yet
- Human CellDocument12 pagesHuman CellCrystal GarciaNo ratings yet
- Cell StructuresDocument25 pagesCell StructuresAminul Islam Arafat 2132536642No ratings yet
- Notes For Cell Biology BT-I YearDocument16 pagesNotes For Cell Biology BT-I YearKRATIKA TYAGINo ratings yet
- Cell (Biology) : From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument15 pagesCell (Biology) : From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaShabbir Hussain MaloobhaiNo ratings yet
- BIO111 NEW1 CompleteDocument25 pagesBIO111 NEW1 Completealiu sodiqNo ratings yet
- Cell - The Building Blocks of LifeDocument4 pagesCell - The Building Blocks of LifeUzair SoomroNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic Cells: Main Article: ProkaryoteDocument6 pagesProkaryotic Cells: Main Article: ProkaryoteGian Carlo MagdalenoNo ratings yet
- L.3 - The CellDocument3 pagesL.3 - The CellJari JariNo ratings yet
- Microbes and Oral DiseasesDocument40 pagesMicrobes and Oral DiseasesRadwa MohamedNo ratings yet
- Cell - The Unit of LifeDocument26 pagesCell - The Unit of LifeKunal MahadikNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Cell: The Unit of Life 8.1 What Is A Cell? 8.2 Cell TheoryDocument10 pagesChapter 8 Cell: The Unit of Life 8.1 What Is A Cell? 8.2 Cell TheoryCharin KadianNo ratings yet
- Cell - The Unit of LifeDocument8 pagesCell - The Unit of Lifelpc4944No ratings yet
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument4 pagesProkaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsgnwosisiNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Cells, Development, Biodiversity and ConservationDocument47 pagesUnit 2 Cells, Development, Biodiversity and ConservationEllane leeNo ratings yet
- Cell (Biology) : Navigation SearchDocument5 pagesCell (Biology) : Navigation SearchChan WaiyinNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Cells Development Biodiversity and ConservationDocument47 pagesUnit 2 Cells Development Biodiversity and ConservationKevir Man100% (1)
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument7 pagesProkaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsPrashant PatilNo ratings yet
- Biotech Session 1Document18 pagesBiotech Session 1j_ngetich_k7375No ratings yet
- Bio 101 General BiologyDocument7 pagesBio 101 General BiologyMohammed kashimNo ratings yet
- Biology Fiitjee Chennai CentreDocument27 pagesBiology Fiitjee Chennai CentreT SunderamalolanNo ratings yet
- Cell The Unit of LifeDocument58 pagesCell The Unit of LifeRUSHIKESH SINDKHEDKARNo ratings yet
- The Cell: Supervised byDocument5 pagesThe Cell: Supervised byAhmed AliNo ratings yet
- EukaryotesDocument4 pagesEukaryotesWareesha BatoolNo ratings yet
- GeneticsDocument2 pagesGeneticsdellavajames192000No ratings yet
- Unit Cell. Organization of The Human Body: Organ SystemDocument12 pagesUnit Cell. Organization of The Human Body: Organ SystemD IngaNo ratings yet
- تخدير المحاضرة الاولىDocument7 pagesتخدير المحاضرة الاولىXcv FfgNo ratings yet
- 8 & 9: Cell Structure and Function: CellsDocument13 pages8 & 9: Cell Structure and Function: CellsEnmuskNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic Eukaryotic CellsDocument11 pagesProkaryotic Eukaryotic CellsKriezhel Kim TadleNo ratings yet