Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Eukaryotic VS Prokaryotic Cells
Eukaryotic VS Prokaryotic Cells
Uploaded by
Shreya KadiyalaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Eukaryotic VS Prokaryotic Cells
Eukaryotic VS Prokaryotic Cells
Uploaded by
Shreya KadiyalaCopyright:
Available Formats
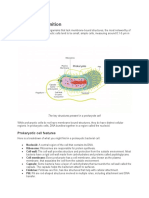
EUKARYOTIC VS PROKARYOTIC CELLS
Eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells are the two main types of cells found in the living world.
Eukaryotic cells are cells that have a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles, such as
mitochondria, ribosomes, and the endoplasmic reticulum. These cells are complex and are
typically larger in size than prokaryotic cells. Eukaryotic cells are found in organisms such as
plants, animals, fungi, and protists.
Prokaryotic cells, on the other hand, are simple cells that do not have a nucleus or other
membrane-bound organelles. They are typically smaller in size and are found in organisms
such as bacteria.
Similarities between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells include the presence of a cell
membrane, ribosomes, and DNA as their genetic material.
Differences between the two include:
Size: Eukaryotic cells are typically much larger than prokaryotic cells.
Nucleus: Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus, while prokaryotic cells do not.
Organelles: Eukaryotic cells have membrane-bound organelles, while prokaryotic
cells do not.
Cell division: Eukaryotic cells divide using mitosis, while prokaryotic cells divide
using binary fission.
In conclusion, eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells are different in their structure, complexity,
and the way they divide, but they share some basic similarities such as the presence of a cell
membrane and ribosomes.
You might also like
- The CellDocument5 pagesThe CellAfida Razuna AveNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument1 pageUntitledJubaer UtshobNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellDocument10 pagesChapter 2 Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellKylie VillafloresNo ratings yet
- Cell - The Building Blocks of LifeDocument4 pagesCell - The Building Blocks of LifeUzair SoomroNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells: Endoplasmic ReticulumDocument10 pagesProkaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells: Endoplasmic ReticulumChristopher PhilipNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 - Prokaryotic Vs Eukaryotic CellsDocument28 pagesLesson 3 - Prokaryotic Vs Eukaryotic Cellsloki67% (3)
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells: Two Types of CellsDocument2 pagesProkaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells: Two Types of CellsJanelle ArañaNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument6 pagesBiologyBlue TechNo ratings yet
- All About CellsDocument49 pagesAll About CellsJeanine CristobalNo ratings yet
- Biology-Chapter 2 CellsDocument2 pagesBiology-Chapter 2 CellsWen Jun LohNo ratings yet
- LESSON 3 - Prokaryotid Vs Eukaryotic CellsDocument41 pagesLESSON 3 - Prokaryotid Vs Eukaryotic CellsHyacinth RaeNo ratings yet
- Prokaryote Definition: Prokaryotic Cell FeaturesDocument5 pagesProkaryote Definition: Prokaryotic Cell FeaturesAli ShanNo ratings yet
- Environmental Microbiology UNIT 1Document43 pagesEnvironmental Microbiology UNIT 1Esai Kanaga YadavNo ratings yet
- Module 3-P. E. CellsDocument4 pagesModule 3-P. E. CellsRylle SimonNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic VS Eukaryotic CellsDocument5 pagesProkaryotic VS Eukaryotic CellsAngelica FloraNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic Eukaryotic CellsDocument11 pagesProkaryotic Eukaryotic CellsKriezhel Kim TadleNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument2 pagesProkaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsSerena Adeline RiveraNo ratings yet
- GB1 Module 1.2Document4 pagesGB1 Module 1.2beatriz OndilloNo ratings yet
- MBC AssignmentDocument6 pagesMBC AssignmentTemp TempNo ratings yet
- Cell OrganizationDocument6 pagesCell OrganizationKaarthigan RamaiahNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic vs. EukaryoticDocument2 pagesProkaryotic vs. EukaryoticJaniya KellyNo ratings yet
- Types of CellsDocument1 pageTypes of CellsWareesha BatoolNo ratings yet
- CellDocument32 pagesCelltunagunhan321No ratings yet
- ZH Core IV - Cell BiologyDocument95 pagesZH Core IV - Cell Biologysahib100% (1)
- Cell PPT To PDF Class 9Document42 pagesCell PPT To PDF Class 9Aditya BajajNo ratings yet
- Prokaryoticandeukaryotic Cells Close ReadingDocument4 pagesProkaryoticandeukaryotic Cells Close Readingapi-165869000No ratings yet
- Eukaryotic Cell Vs Prokaryotic Cell: EukaryoteDocument1 pageEukaryotic Cell Vs Prokaryotic Cell: EukaryoteFakhar AbbasNo ratings yet
- CellsDocument2 pagesCellsmalikaiman1015No ratings yet
- Difference Between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells: February 2017Document12 pagesDifference Between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells: February 2017ufaysa gensaNo ratings yet
- Cell Types: Prokaryotes and EukaryotesDocument4 pagesCell Types: Prokaryotes and Eukaryotesمصطفى رسول هاديNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells: February 2017Document12 pagesDifference Between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells: February 2017Farman MunawarNo ratings yet
- 2.3: Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells: Two Types of CellsDocument3 pages2.3: Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells: Two Types of CellsJubaer UtshobNo ratings yet
- Prokaryote Vs EukaryoteDocument19 pagesProkaryote Vs EukaryotehamnaNo ratings yet
- Technological Institute of The Philippines Quiapo, ManilaDocument4 pagesTechnological Institute of The Philippines Quiapo, ManilaKrystel LahomNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic & Eukaryotic CellsDocument20 pagesProkaryotic & Eukaryotic CellsZay SalazarNo ratings yet
- Cell and Organelle: Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Stores DNA DifferentlyDocument2 pagesCell and Organelle: Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Stores DNA DifferentlyyonisNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Prokaryotes and EukaryotesDocument2 pagesIntroduction To Prokaryotes and EukaryotesRahul PalsNo ratings yet
- Eukaryots and ProkaryotsDocument8 pagesEukaryots and ProkaryotsNida AhmadNo ratings yet
- The CellsDocument4 pagesThe CellsSlaheddineNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology 1.1Document7 pagesCell Biology 1.1Mirunalini GobinathNo ratings yet
- تخدير المحاضرة الاولىDocument7 pagesتخدير المحاضرة الاولىXcv FfgNo ratings yet
- Lecturer 3Document22 pagesLecturer 3Rao ChandNo ratings yet
- Bio 101 General BiologyDocument7 pagesBio 101 General BiologyMohammed kashimNo ratings yet
- JOHN-AHL MATIAS - W3-Reading Material On Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells and Plant vs. Animal TissuesDocument9 pagesJOHN-AHL MATIAS - W3-Reading Material On Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells and Plant vs. Animal TissuesJOHN-AHL MATIASNo ratings yet
- The Cell: Supervised byDocument5 pagesThe Cell: Supervised byAhmed AliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Reviewer in BiosciDocument10 pagesChapter 4 Reviewer in BiosciAngelica PaulinoNo ratings yet
- Biology ReportDocument3 pagesBiology ReportKathlene Anne MENDOZANo ratings yet
- Quilapio - bsph2 B.biochem - Lab 1Document10 pagesQuilapio - bsph2 B.biochem - Lab 1Julius QuilapioNo ratings yet
- PRPLLLDocument19 pagesPRPLLLPraveen KolaganiNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument9 pagesProkaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsKwo Chai Wing100% (1)
- Cells and StructureDocument17 pagesCells and StructurekayleenerikaNo ratings yet
- Cell Types, Prokaryotic and EukaryoticDocument33 pagesCell Types, Prokaryotic and EukaryoticJefrey PaglinawanNo ratings yet
- How To Compare Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic CellsDocument2 pagesHow To Compare Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic CellsMuhamad AzrinNo ratings yet
- The Cell/ All About CellsDocument35 pagesThe Cell/ All About CellsJandrew Gomez DimapasocNo ratings yet
- Microbes and Oral DiseasesDocument40 pagesMicrobes and Oral DiseasesRadwa MohamedNo ratings yet
- Biology 2Document3 pagesBiology 2Karriel AguilarNo ratings yet
- Biology: Classification of CellsDocument28 pagesBiology: Classification of CellskerbieNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure ComponentsDocument3 pagesCell Structure ComponentsequlleniiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 - Cell TypesDocument16 pagesLesson 3 - Cell TypesArvin Jay LamberteNo ratings yet
- Important Science PointsDocument1 pageImportant Science PointsShreya KadiyalaNo ratings yet
- Impossible To PossibleDocument1 pageImpossible To PossibleShreya KadiyalaNo ratings yet
- Sample EssayDocument1 pageSample EssayShreya KadiyalaNo ratings yet
- Latest Circles Questions (2019-2021)Document8 pagesLatest Circles Questions (2019-2021)Shreya KadiyalaNo ratings yet